Triglycerides
Adipose tissue is composed of adipose cells (adipocytes) that store insoluble fat in the form of triglycerides for long-term energy storage
Can form a thick layer under the skin, acting as a shock absorber and thermal insulator
When energy is needed, the stored triglycerides can go through hydrolysis reaction
--> releasing glycerol and fatty acids
They can be used in cell respiration to produce twice as much energy than sugar.
Function of Triglycerides in Adipose Tissue
Endotherms (birds and mammals) need to maintain a steady internal temperature regardless of their environmental temperature
They have thick adipose tissue called blubber
Blubber is found between the skin and muscle
Triglycerides are poor conductors of heat
Blubber helps trap the heat generated by the inner metabolic activities
| Triglycerides | Carbohydrates |
Type and location of tissue when energy stores are found | Adipose tissue beneath the skin and around organs in endotherms or seeds. Plants and cold-blooded animals store unsaturated fats, endotherms store saturated fats. | In skeletal muscle tissue and in the liver as glycogen, or as simple sugars (glucose/fructose) dissolved in blood. Plants in the form of starch. |
Energy contained per gram of storage form | Twice as much energy per gram, account for less mass than the equivalent energy in carbohydrates. This is because they can be oxidised. | Half as much energy contained per gram. Glycogen storages therefore account for a higher body mass. |
Short or long-term energy storage? | Long Term | Short term |
How soluble and easy to transport are the storage forms? | Insoluble in water. Can't be mobilised quickly. Do not cause osmotic consequences. | Glucose is soluble and can easily be transported around, glycogen and starch are much less soluble and therefore used as storage form. No osmotic effect. 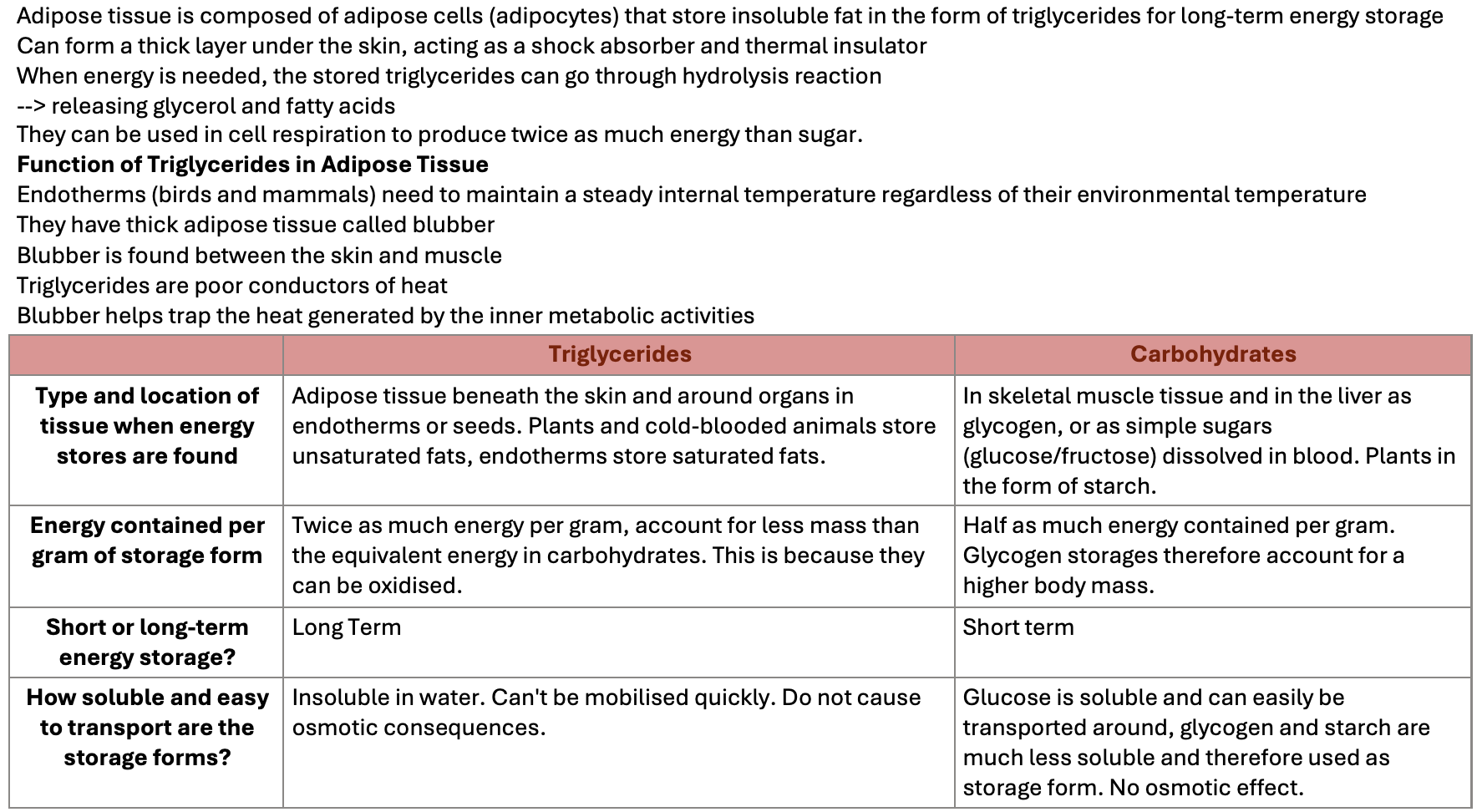 |