Social Psychology - Part III
<<III. Social Influence<<
Social Influence = how others’ behaviors affect an individual
EQ: How do individuals respond to others’ expectations?
EQ: What impact does the presence of others have on an individual’s behavior?
EQ: What processes contribute to differential treatment of group members?
}}A. Conformity, Compliance, and Obedience}}
→ 3 ways to influence a person’s behavior
%%1. Conformity%%
Conformity = adapting your behavior to match others’
- indirect pressure / peer pressure
Helpful:
- useful when moving to new environment for adopting social norms of new group
- ex. different colleges or businesses have different ideas about appropriate clothing
Harmful:
- peer pressure for risky behaviors
- ex. drinking / hazing
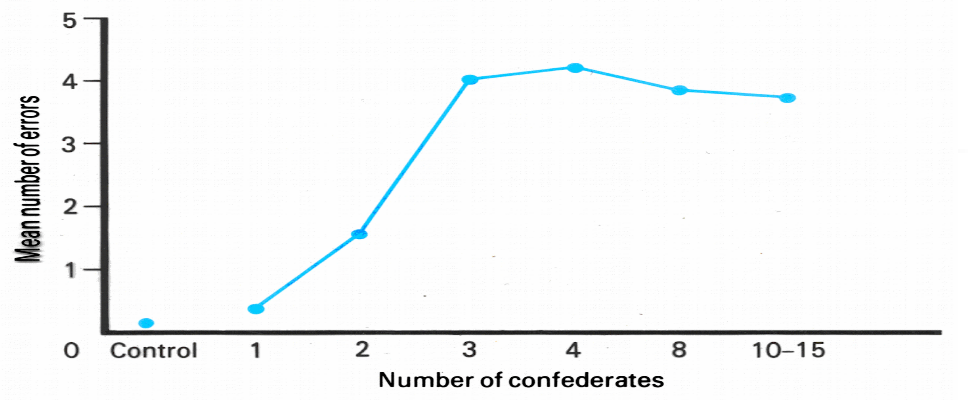
a. Asch’s Conformity Experiment
a group of students all looked at 1 vertical bar and then asked to compare it to 3 other bars of different lengths
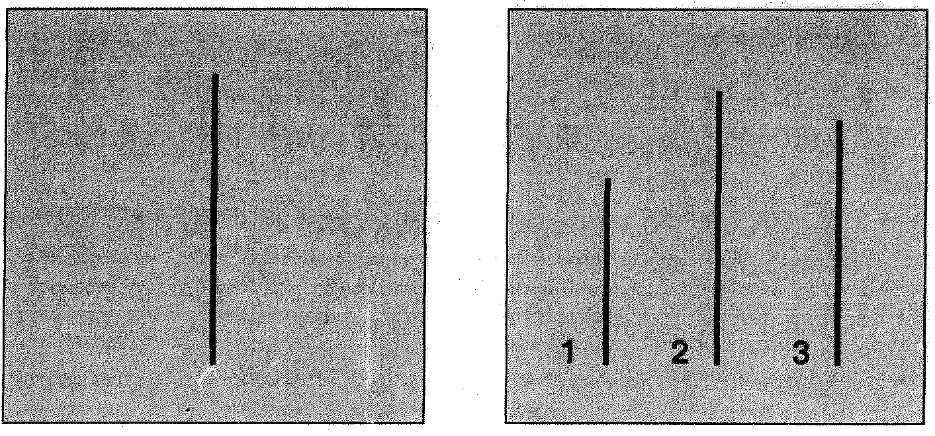

They were asked which of the 3 were the same as the left one
HOWEVER, only 1 student was the subject, everyone else was a confederate who were told to occasionally choose the wrong bar
Results:
at least some of the time, the subject changed his answer despite believing others were incorrect in their judgment
after 3+ people making the wrong choice, the subject felt more pressure to conform to the group’s answer
b. Factors that Contribute to Conformity
Group Desirability = How much the individual wants to belong to the group
Group Cohesiveness = How “tight” the group is
ex. 10 close friends are more likely to conform to the same idea than 10 classmates
Group Size = Small groups of 3-5 increase conformity (because no one wants to be the one who disagrees) / Large groups increase conformity (because of “mob mentality” and the belief that any 1 person’s actions are unidentifiable in a crowd
Visible Behavior = Increases conformity
ex. this is why democracies have secret ballots
Ambiguous Expectations = Low knowledge about a situation increase conformity (because people are unsure of what they are supposed to do and believe others know better)
]]KEY: If even 1 person disagrees in a group, others a likely to break conformity]]
]](this is why freedom of the press is so important)]]
%%2. Compliance%%
Compliance = Submitting to direct social pressure (ex. a request from another person)
a. Factors that Increase Compliance
(both have funny names since they originated from the old days of the travelling salesmen)
- Foot-in-the-door Technique
Foot-in-the-door Technique = a compliance technique where a small request is made first and is then followed up with a larger one
ex. if someone is asked to sign a petition first, then they are more likely to comply when asked to make a small donation
- Door-in-the-face Technique
Door-in-the-face Technique = a compliance technique, making a large request that the person will likely turn down hoping they will agree to a second and more reasonable request
%%3. Obedience%%
Obedience = following the demand of an authority figure
- there is generally a threat of punishment (perceived or not) if the command is not followed
- alternatively, following demand might hold the promise of a reward (perceived or not)
a. Milgram’s experiment
- subject asked to shock the person if they made mistake, another authority figure encouraged subject to continue (shock level given increased each time)
- 2/3 continued to lethal levels while 1/3 disagreed and stopped shocking
}}B. Group Behaviors}}
Group Behavior = How people act in a group / how being a member affects behavior
%%1. Social Dilemma%%
Social Dilemma = Decision-Making question for individuals when they work in a group: do you opt for the immediate, individual reward, or do you work to get the long-term benefits for the entire group?
Social Trap = unproductive actions of individuals that hurt the group, because they fear “If I don’t do it, someone else will and so they will get the benefit and I will lose”
- when people choose the immediate, individual benefit, they may fall into the social trap of hurting themselves and the rest of the group in the future
Tragedy of the Commons = social trap that develops when a group shares a limited resource
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KZDjPnzoge0
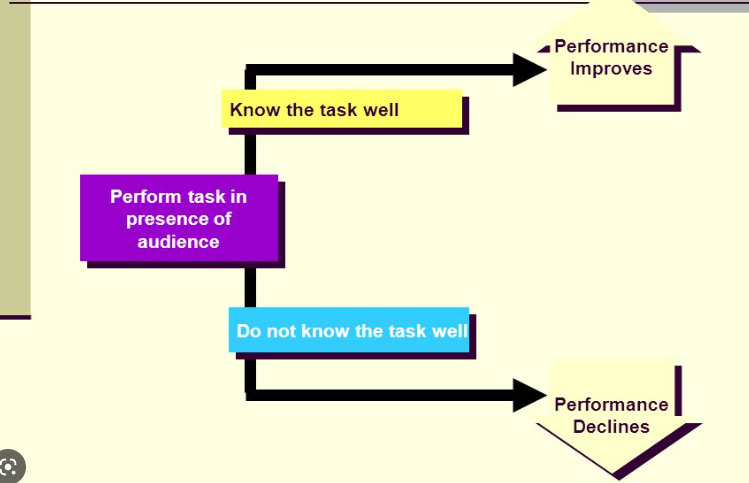
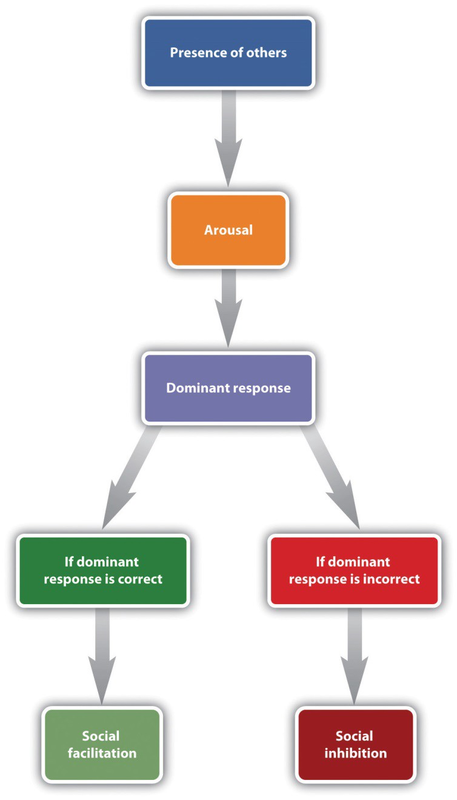
%%2. Social Facilitation and Social Inhibition%%
Social Facilitation and Social Inhibition = How an audience affects your performance
if Dominant Response is correct or easy → %%Social Facilitation%%
if Dominant Response is incorrect or difficult → ==Social Inhibition==
%%3. Group Decision-Making%%
- Making a decision while in a group is different than by yourself because others’ opinions often affect what the entire group does
- Just the presence of another person can change an individual’s behavior:
- teen driver driving alone = normal
- with other teens = reckless
- with adult = careful
a. Group Polarization
Group Polarization = the actions/beliefs of a group are more exaggerated than the individual members’ typical behaviors or thoughts
Effects:
Groups made up of risk-takers choose more dangerous group activities
ex. college student who likes scary activities thinks that bungee jumping would be a good spring break. When he gets together with like-minded friends, they choose naked bungee jumping into a pit of venomous snakes
Groups composed of risk-averse people choose even less riskier group activities
b. Groupthink
Groupthink = when all members of the group think similarly or are scared to voice an opposing opinion, the group often makes poor decisions
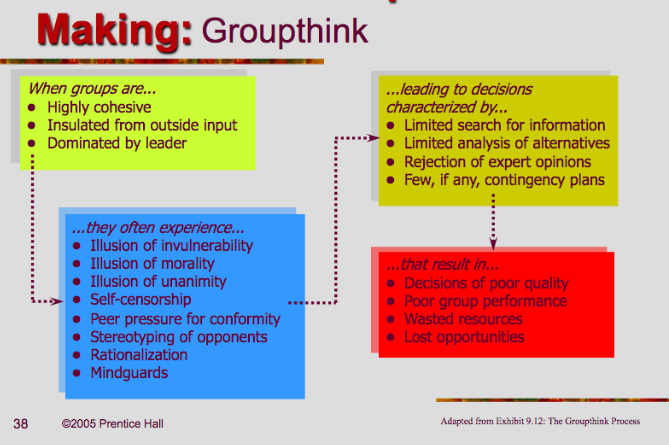 How to overcome groupthink?
How to overcome groupthink?
- some companies specifically have an employee whose job is to provide counter-arguments to managers’ ideas/policies
- the more diverse a leadership (in race, gender, education, experience, etc.), the higher profits (but also the leaders are less comfortable)
%%4. Social Loafing%%
 Social Loafing = when people tend to exert less effort to achieve a goal when they work in a group than when working alone (usually when each individual’s contribution is not obvious)
Social Loafing = when people tend to exert less effort to achieve a goal when they work in a group than when working alone (usually when each individual’s contribution is not obvious)
ex. in the tug of war example, loafing was exacerbated when everyone was blindfolded
How to reduce Social Loafing?
- create individual tasks with individual rewards and punishments that contribute to the group project
- use positive peer pressure (the group leader sets expectations that if one person doesn’t do their task well, ten the entire group will suffer)
%%5. Helping/Ignoring Others who Need Help%%
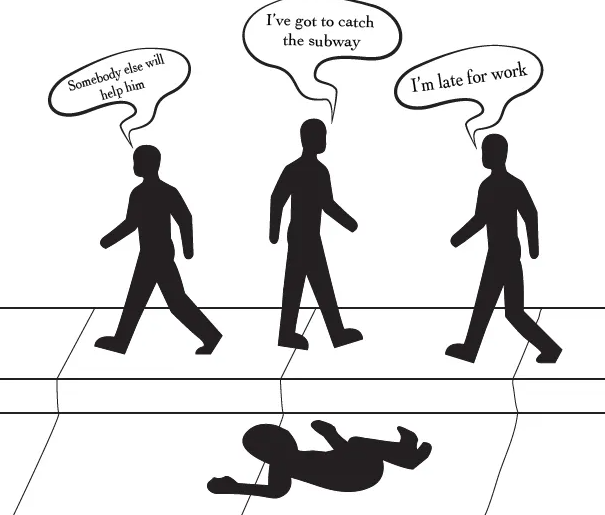
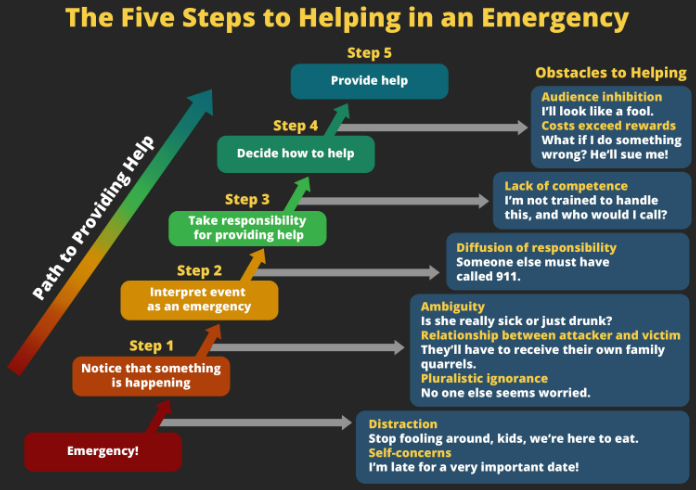
a. Bystander Effect
Bystander Effect = the phenomenon where the more people who witness an event, the less likely it is that anyone will respond
- due to Diffusion of Responsibility and Pluralistic Ignorance
b. Diffusion of Responsibility
Diffusion of Responsibility = when an individual sense of responsibility decreases in the presence of others
alone = 100% responsible
in a group of 5 = each think they are 20% responsible
The more people involved, the more likely it is that each person will do nothing, believing someone else from the group will probably respond
c. Pluralistic Ignorance
Pluralistic Ignorance = assuming nothing is wrong because nobody else looks concerned
d. Deindividuation
Deindividuation = stop thinking about people as individuals
We reduce others to less-than-human
- tactic often used intentionally by genocide leaders
We stop thinking about ourselves as an individual with responsibilities (and choice) and just accept the role we’ve been given
We assume we are unidentifiable in a crowd (and then behave in ways we would if we knew we could be identified)
- social media anonymity → trolls/cyberbllying
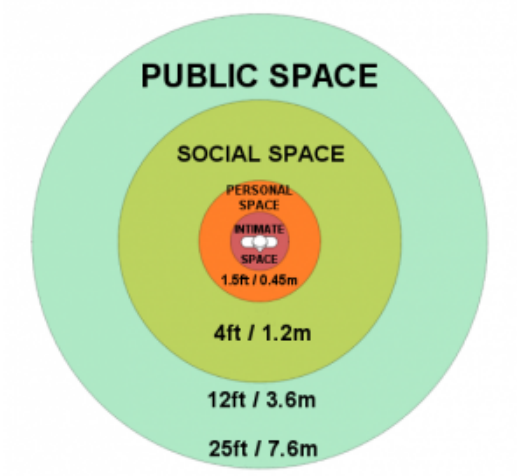
%%6. Personal Space%%
Personal Space = the distance we are from other people
comfortable amount of personal space depends on the relationship between the individuals and the culture of the individuals