Chapter 5: Syntax
- Syntax- the component of grammar that deals with how words and phrases are combined into larger phrases
Basic Ideas of Syntax
- Linguistic expression- a piece of language with certain form, meaning, and syntactic properties
- Syntax is broadly related to how expressions combine with one another to form larger expressions
- Grammatical- when a string of words form a meaningful sentence
- Ungrammatical- when a string of words do not form a sentence
- Grammaticality judgement- a reflection of speakers’ mental grammar
- Not necessarily concerned with prescriptive rules
- Principle of compositionality- the meaning of a sentence depends on the meanings of the expressions it contains and on the way they are syntactically combined
- Difference between syntax and semantics:
- Sentences can @@contain strange meaning@@, and non-sentences can @@convey ordinary meaning@@
- Syntactic properties of expressions @@cannot be predicted or explained@@ on the basis of an expression’s meaning
Syntactic Properties
- Syntactic properties- the restrictions on certain combinations of expressions
- Word order- how expressions are allowed to be ordered with respect to one another
- Co-occurrence- if some expression occurs in a sentence, what other expressions can or must co-occur with it in that sentence?
- Argument- when the occurrence of one expression necessitates the occurrence of another expression
- Complements- non-subject arguments
- Well-formed sentences need to have all and only the arguments they need
- Adjuncts- optional expressions that can be added without creating a non-sentence
- Agreement- distinct expressions that agree with respect to some grammatical feature with the same value
Syntactic Constituency
- Syntactic constituent- syntactic units that can make up larger phrases in certain groups of expressions
- You can tell if a string of words forms a syntactic constituent if the words can answer a question
- Ex) Where is the cat sleeping? On the desk
- “On the desk” is a constituent
- Cleft- a sentence in which some constituent is displaced to the left
- If the cleft is grammatical, the displaced expression is a constituent
- Ex) The cat was sleeping on the desk → It was the cat that was sleeping on the desk
- “The cat” is a constituent
- Substitution- replacing a string of words with a single word.
- If substitution results in a grammatical sentence, the string of words is a constituent
- Ex) The cat was sleeping on the desk → She was sleeping on the desk
- “The cat” is a constituent
Syntactic Categories
- Syntactic category- a set of expressions that have approximately the same word order and co-occurrence requirements
- Syntactic distribution- if two expressions are interchangeable in all syntactic environments
- Ex) Sally likes the cat → Sally likes Fluffy
- The cat and Fluffy have the same distribution
| Syntactic Category | Relevant Properties | Example |
|---|---|---|
| S (sentence) | can occur in Sally thinks that _ | Fluffy is cute |
| NP (noun phrase) | has the same distribution as a personal pronoun or a proper name | she, Sally, the cat, this cute dog, that cat under the bed |
| N (noun) | needs a determiner to its left to form a NP | cat, cute dog, cat under the bed |
| Det (determiner) | occurs to the left of the noun to form a NP | the, every, this |
| Adj (adjective) | occurs in between a determiner and a noun; can be a noun adjunct, that is, combines with a noun to its right which results in an expression that is also of category N | cute, fluffy, gray |
| VP (verb phrase) | consists minimally of a verb and all its complements; combines with an NP to its left which results in a sentence; has the same distribution as slept or did so | slept, write the letter quickly, liked Bob, walked, believed she liked that man |
| TV (transitive verb) | needs an NP complement to form a VP | liked, devoured |
| DTV (ditransitive verb) | needs two NP complement to form a VP | gave, sent |
| SV (sentential complement verb) | needs a sentential complement to form a VP | believed, said |
| Adv (adverb) | can be a VP adjunct, that is, combines with a VP to its left which results in an expression that is also of category VP | fast, quickly, tomorrow |
| P (preposition) | combines with an NP to form a PP | at, for, with |
| PP (prepositional phrase) | can be a VP or an N adjunct; consists of a preposition and its NP complement | at the table, for Sally, under the bed |
Constructing a Grammar
Phrase structure rules- captures patterns of syntactic combination
- Ex) In English, S → NP VP
Phrase structure tree- a visual display of the way a sentence is built up from lexical expressions using the phrase structure rules
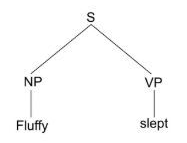
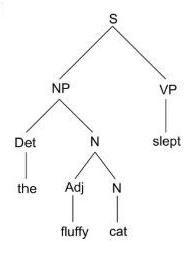
Ambiguous- linguistic forms can correspond to more than one expression
- Ex) They went for a walk vs They walk quickly
- Can be individual words or entire structures