6, SHORT TERM MEMORY- COG-PSY
Memory: The process by which information is retained for later use
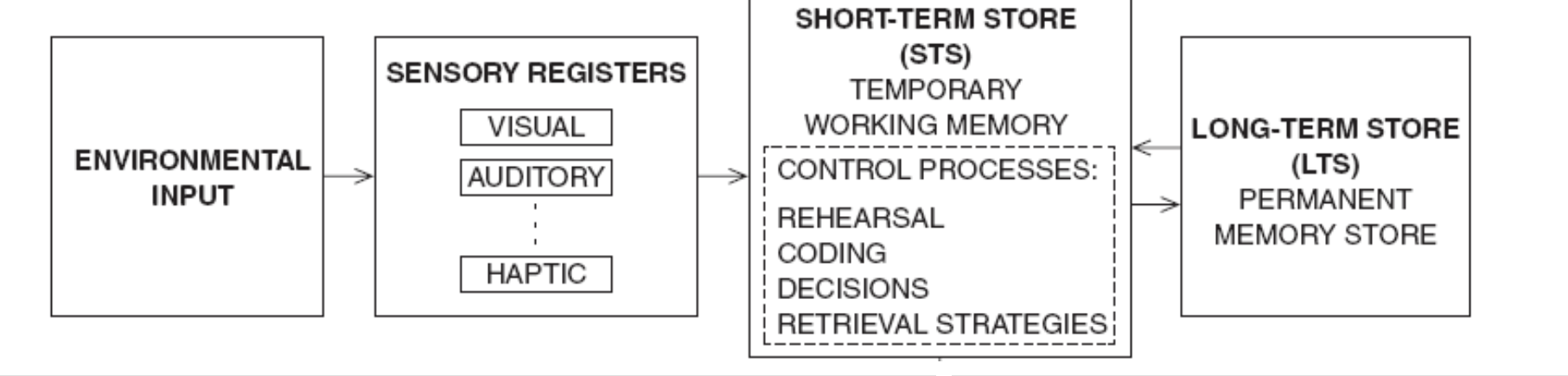
Sensory memory: holds information very briefly (~0.5-2s) and is
modality specific (iconic, echoic stores—transient visual and
auditory input that is mainly unprocessed).
Sensory memory example: don’t remember every tiktok scroll past
Short-term stores: extremely limited capacity (Miller (1956): 7+2 bits)
and quite fragile as any distraction usually causes forgetting almost
immediately (Peterson & Peterson, 1959).
Long term stores: could be permanent and unlimited!
George Miller: suggested people can keep only about seven items active in short-term storage, and that this limitation influences performance on a wide range of mental tasks
memory span: is the longest list of items that a person can repeat back in correct order immediately after
presentation.
Performance on the memory span task is also closely linked to language learning abilities; improving verbal memory capacities may therefore aid mastery of a new language.
Chunking: Miller, single items can be grouped into higher level units of organization where there are 4 bits of information instead of 12, and now we can remember them
Chunking example: cnnibmmtvusa = cnn ibm mtv usa
short term memory is only reliable for 3-5 seconds without rehearsal/chunking!
IQ ≠ how much you can remember
80% of ppl w alzheimer have signifiicant short term memory impairments 2 years before symptoms so can put them on Aricept