INFO TECH
THE COMPUTER
A computer is defined as an electronic device, which accepts, processes and store data for later use or sends out data as information.
TYPES
embedded
mobile computer
Personal computer
mainframe Computer
Supercomputer
ADVANTAGES OF USING A COMPUTER
Consistency and accuracy of the results provided
Enhanced storage
DISADVANTAGES OF USING A COMPUTER
the initial set up cost is high
easier for security and integrity of data to be compromised
HARDWARE
Hardware is any part of the computer that has physical structure, including the computer’s internal parts.
All computer systems need hardware to carry out the following four main processes:
Accepting Input
Processing that Input
Producing output information
Storing data and/or information for later retrieval and use
NOTE
Input- The act of accepting data form the outside world
Input device - a device responsible for getting data into a computer
Processing- The act of transforming data into information that will be useful to the user
Output- The act of presenting information to the user
Output device- get processed data out of the computer
Storage- The act of holding data, program instructions & information for later use.
Memory enables a computer to temporarily store instructions and data
THE CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT (CPU)
This is the brain of the computer it manages and orchestrates how the computer functions it consists of the CU & ALU
CU - executes software instructions and guides data flow
ALU- responsible for all calculations and logical operations
!!Peripheral devices- located outside the CPU but controlled by it.!!
WHAT IS PRIMARY STORAGE?
This is the component of the computer that holds data, programs and instructions that are currently being used.
WHAT IS SECONDARY STORAGE?
Secondary storage includes non-volatile devices for storing data outside of a computer's main memory (RAM).
MAIN MEMORY
RAM (random access memory)
a type of computer memory that serves as the short-term working memory of a computer
Dynamic RAM
Static RAM
CHARACTERISTICS
Volatile (data is lost when power is lost)
Larger in Capacity
Temporary
Faster and expensive
ROM (Read Only Memory)
PROM-Can only be modified ONCE by the user
EPROM-Data can be erased using ultraviolet rays and can be reprogrammed
EEPROM- Data can be erased and reprogrammed repeatedly by applying an electrical voltage that is higher than normal. (over 10k times)
CHARACTERISTICS
Non-volatile (data is lost when power is lost)
Small Capacity
Slower but cheaper
WHAT IS STORAGE UNIT?
A unit of measure used to show how much info can be saved and kept on a computer.
8 bits = 1 byte
1024 bytes= 1 kilobyte
Nibble = ½ a byte
CLOUD STORAGE
The process of storing data in an online space that spans multiple servers and locations, and it is usually maintained by a hosting company.
People pay these companies to keep their data on servers and give them access to it anytime once they have internet connection.
Examples: Google drive and Icloud
LOCAL STORAGE
the process of storing digital data on physical storage devices (hard disk drives and external storage devices)
SOFTWARE
Software is a program that is executed by the hardware of the computer
TYPES - System software Application programs
SYSTEM SOFTWARE- used to operate and maintain a computer system includes the
operating system
utility programs
language translators
OPEERATING SYSTEMS
A set of programs that governs the operation of the computer.
6 primary functions (usfrmp)
User Interface- This is the point at which human user interact with a computer.
Types of user interface
Graphic user interface
Hardware interface
Software interface
Command driven
Menu-driven interface
Security Management- maintains a secure computing environment.
File Management - manages files and folders.
Resource Management- manages storage devices, input & output devices.
Memory Management- manages memory.
Process Management- manage processor resources.
Examples are MacOS, IOS, Windows
SYSTEM UTILITY
a specialized program that assists in maintaining and improving the efficiency of a computer system.
Back up
Defragmenter - reorganize
Disc error checker
Disc cleanup
Antivirus
APPLICATION SOFTWARE NEEDS TOUCH UP
Programs that help the user perform specific ask
GENERAL PURPOSE: These are software that are not specific to anyone organization or business and can be used by anybody. For e.g.: Word, database, PowerPoint, Canva
Customized software: general purpose software that has been modified to perform specific task for user.
Custom Written: Also known as TaylorMade is written for use in specific organization.
SPECIALIZED SOFTWARE: This is software that is designed for specific need or task. For e.g.: A camera on your device
DATA
Raw unprocessed facts
Raw facts
no context
Plain numbers, text, etc.
INFORMATION
meaningful knowledge derived from raw data.
Data that has been processed/organized in a useful way
Processed data
data with context
2 types of sources
Thing that has been measured eg temperature | 28
Person or organization that provided the data from observation.
Source documents are documents that contains data for input into an information processing system.
Human-Readable Document
This is a document that can be read naturally by humans. It is not in a form that the computer can readily accept.
Machine-Readable Document
This is one that can be readily process be the computer. E.g. items within barcode
Turn-Around Document
This is a computer-generated form that is fill out, sent out and returned to the computer.
VERIFICATION
This is double checking for error with data that has already been entered.
Good verification significantly reduces the number of
Typographical errors (missing or extra letters)
Transposition errors (switching the position of 2 adjacent characters in a text)
Type of verification
Proofreading- a data entry clerk visually checks the source document against data that has already been input by another entry clerk.
Double data entry- when data is entered twice for comparison.
Validation
A checking process in a program which is aimed at finding out if the data entered is genuine
Type of validation
Data type check
Presences checks
Check digit.
Range check
Consistency check
Length check
Reasonableness check
Format check
NEW SHIT
COMPUTER SECURITY
What is Computer Security?
Computer Security is all the activities related to the identifying, assessing and managing vulnerabilities, threats and attacks on a computer system.
Elements of Computer Security
Computer security has FOUR (4) main elements:
Vulnerability
Exposure to the possibility of being harmed or attacked
Threat
A statement of intention to harm
Attack
Actual action that causes damage or harm
Countermeasure
An action taken to counteract a threat
What is Computer Misuse?
This is any activity during which a computer system or network’s data is accessed, modified or deleted without proper authorization.
Computer misuse includes acts which are likely to cause unauthorized modification, removal or copying of the contents of any computer system, Directly or indirectly obtaining computer service without proper authorization, Accessing programs or data on a computer with the intent to commit a crime or just unauthorized access to a computer system.
Computer Misuse Affecting Individuals
Cyberbullying:
Cyberbullying is a form of harassment or bullying in an online space. It can occur through SMS or online gaming platforms. Cyberbullying includes insulting , false, harmful or mean comments or the sharing of embarrassing content.
Identity Theft:
Identity theft is the deliberate use of someone else's identity, usually to gain a financial advantage
Your identity can be stolen to do a number of crimes
including:
False applications for loans and credit cards
Fraudulent withdrawals from bank accounts
Fraudulent use of online accounts
Fraudulently obtaining other goods or services
Phishing Attacks:
Phishing involves attempting to steal sensitive information (like usernames, passwords, or credit card details) through fake emails pretending to be from trusted organizations. Users are usually asked to click on a link and promised a reward.
Violation of Privacy:
Privacy refers to the right of individuals to decide freely under what conditions and to what extent they will disclose personal information about themselves. Governments and organizations that handle personal data, such as names, addresses, birth dates, bank details, and contact numbers, are responsible for maintaining its confidentiality. Violations of privacy occur when any of these rights are breached, including storing inaccurate personal data, sharing information without the individual's consent, or using data for purposes other than those originally intended.
Privacy policies outline how the data that websites collect will be used and what rights the user is giving up when they accept the website’s terms of service
Computer Misuse Affecting Organisations
Copyright Infringement & Software Piracy
Copyright infringement occurs when someone other than the rights holder reproduces, distributes, or benefits from the work without permission or paying required fees.
Software piracy is the unauthorized reproduction, distribution or use of software products. Software piracy negatively impacts the legal owners that produce the software because it reduces their revenues. It also harms national and regional economies. A lower number of legitimate software sales results in lost tax revenue.
Data Theft
Data theft is the unauthorized copying or removal of data from the legitimate owner’s computer System.
The Dark Net is the term given to the parts of the Internet that are kept hidden from the general public and cannot be accessed by standard search engines such as Google and Bing.
Denial of Service Attacks (DOS)
A denial of service attacks (DOS attack) is a cyber-attack where the intent is to prevent a service being delivered by the target system.
The attack could be by an individual hacker exploiting a vulnerability in the target system to gain unauthorized access and so crash the system from within.
NB. When the attack is directed from the outside in, it may be a distributed denial of service attack.
Malware
Malware (malicious software) is software designed to disrupt, damage or gain unauthorized access to a computer system.
Malicious programs can be delivered:
Physically
Via the Internet
Via phishing attacks

Computer Misuse Affecting Governments
Electronic Eavesdropping
Electronic eavesdropping is the act of electronically intercepting communications without the knowledge or consent of at least one of the participants.It is used by both law enforcement and criminals.
Propaganda
Propaganda is communication of information that is of a biased or misleading nature and that is aimed at influencing the recipient. The content is usually repeated and dispersed over a wide variety of media
What is Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity is the body of technologies, processes and practices designed to protect networks, computers, programs, and data from attack, damage or unauthorized access
Cyberspace: A Cyberspace is any data or resources that are accessed through a network or internet operated space.
Cybercrime: Cybercrime is any crime perpetrated using computers and networks
Countermeasures To Mitigate Threats
Physical Measures, Software Measures and Personal Security Practices can be used to mitigate threats
Physical Measures
A physical security measure is any mechanism that reduces the risks of unauthorized access to a computer system’s hardware
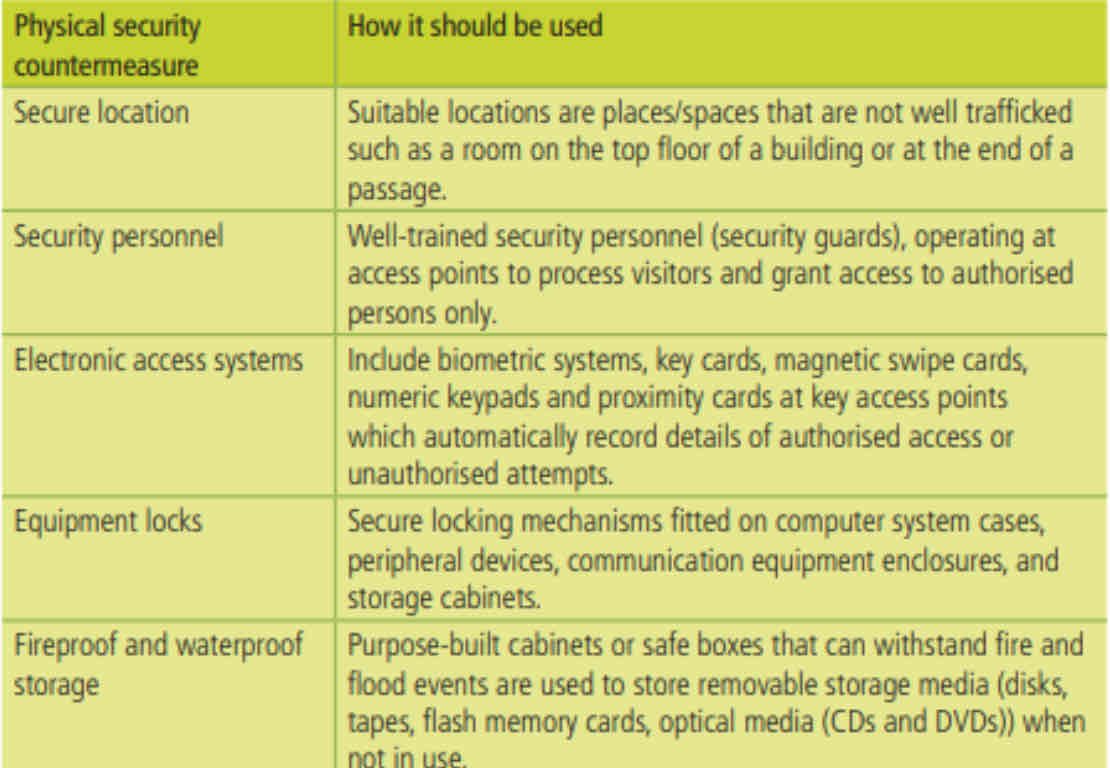
Software Measures
Software countermeasures are a combination of specialized system software and application software used to protect computer systems.
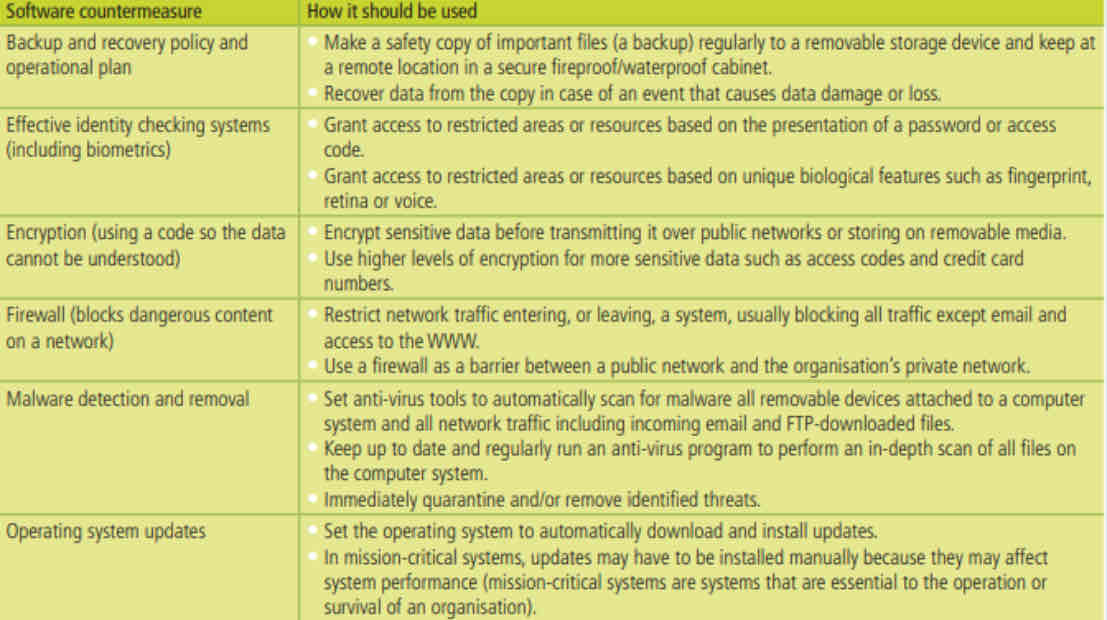
Personal Security Practices
Personal security practices are countermeasures used by individuals to implement computer security and cybersecurity.
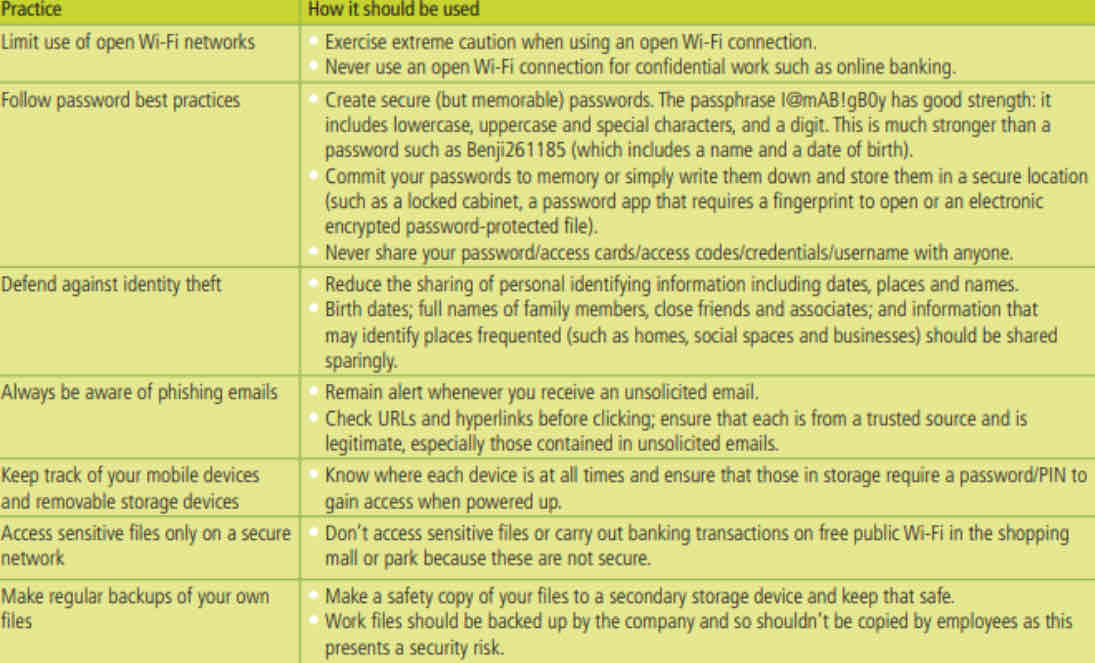
Problem Solving
What is a Problem?
In Information Technology, a problem is a discrepancy (or difference) between the data we have and the information required.
Problem Solving Terms
Solution: A solution is a set of instructions that, if followed in order, will produce the required information.
Problem Solving:The process of creating a set of instructions that, when executed, is solving a problem that was indicated previously.
Pseudocode: Pseudo code is a formal way of writing an algorithm using structured English text, numbers and special characters.
Flowchart: A flowchart is a pictorial way of representing an algorithm using a set of standard symbols (shapes)
Steps in Problem Solving
Define the problem
Propose and evaluate solution
Determine the best solution
Develop the algorithm
Represent the algorithm as pseudocode or a flowchart
Test and validate the solution
IPO Charts
An input-Process-Output (IPO) chart is a helpful diagrammatic way to start breaking down a problem.
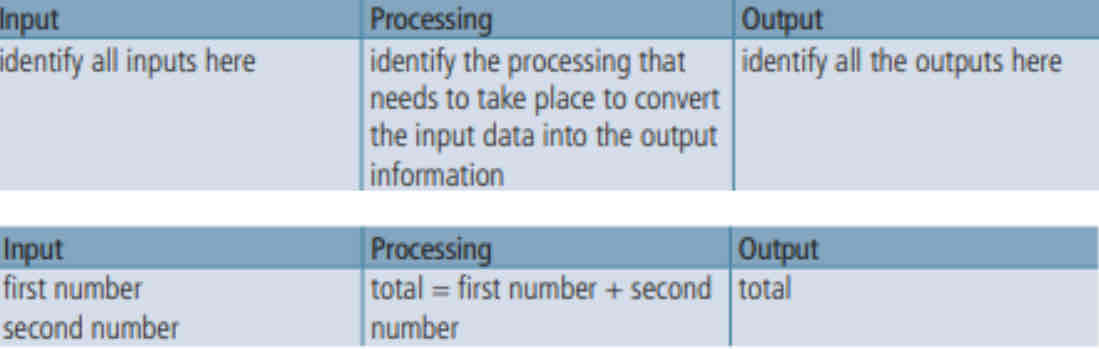
Variables & Constants
The IPO chart stores values: VARIABLES & CONSTANTS
In programming, a variable is a container that stores values capable of changing during processing .
A constant is also a container with a value, but that value cannot be changed during processing.
N.B All variables and constants have an identifier and a data type
Identifiers E.g 5 → (num1) September → (birth month)
Data Types
Integers: Whole numbers such as 1, 5, -7, etc
Float: Numbers which are not whole (decimals, fractions)
Character: letters, numerical values and special symbols such as @, b, 7 (single)
String: a SEQUENCE of characters (whole words, tele #) eg, boy, (8766)
Boolean: a true or false value (YES/NO)
Before use in a program they must be declared. This allows the computer to allocate the correct amount of memory to hold the values.
Algorithms
An algorithm is a sequence of instructions which rigorously defines a solution to a problem.
All algorithms are:
Unambiguous -not open to more than one interpretation.
FInite -must eventually finish.
Precise - They have instructions that pass the flow of control from one process/action to another.Instructions in an algorithm must be followed in a sequence, control passes from one process to the next until the algorithm terminates
EXAMPLE OF A SIMPLE ALGORITHM
START
DECLARE NUM1, NUM2, sum as INTEGER
PRINT “Please enter the first number”
READ NUM1
PRINT “Please enter the second number”
READ NUM2
sum = NUM1 + NUM2
PRINT “The sum is”, sum
STOP
Relational Operators
Relational operators test the relationship between two values in a condition and always result in true or false.
A condition is an expression that includes a relational operator and the two operands on which it
operates.
An operand is a data value, held in a variable that is part of a condition.
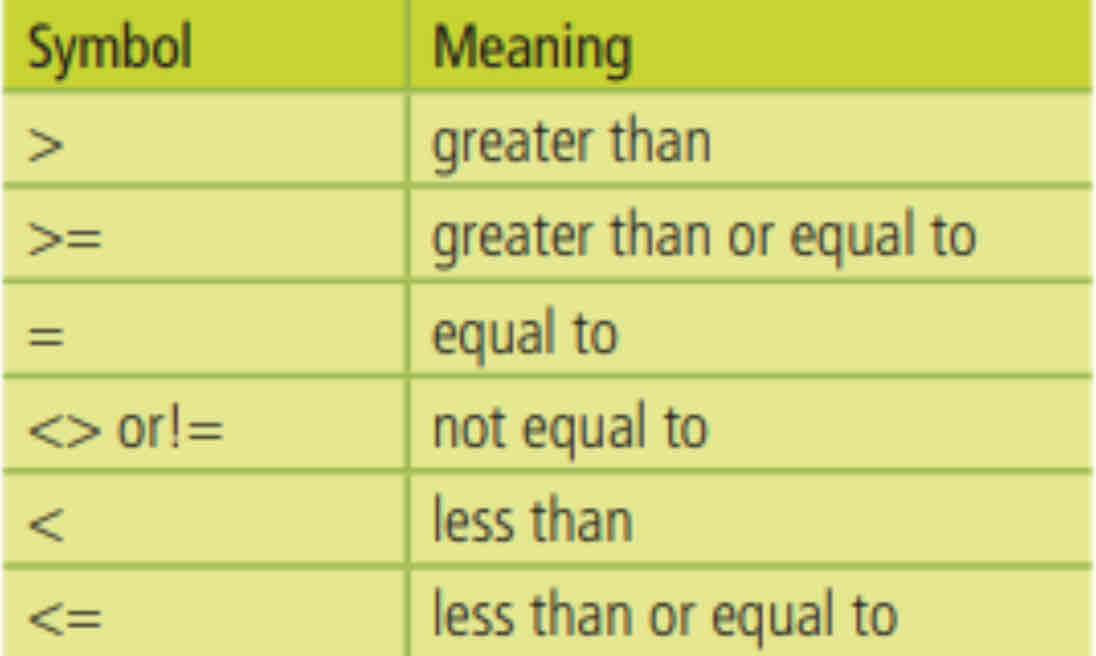
Arithmetic Operators
These are symbols that represent mathematical computations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication and division.
+ (Addition)
- (Subtraction)
? ( Multiplication)
/ (Division)
SPECIAL ARITHMETIC OPERATORS:
DIV: DIV is the integer division operator which discards the fractional part (remainder) of
the results.
For example 5 DIV 2 since the remainder, which is 1, is discarded.
MOD: The integer remainder operator which gives the fractional part (remainder) of the result.
For example 5 MOD 2 produces 1 since this is the remainder.

Conditional Branching
The performing of actions based on specific situations or conditions
Conditional Branching Statements
IF-THEN
The instruction(s) within the IF statement will be executed once the condition is
TRUE. If the condition is not met or it is FALSE, the instruction(s) within the IF statement will be ignored.
IF-THEN -ELSE
The first condition is checked. If the first condition is met, the instruction(s) within the statement will be executed. The second condition will be ignored, seeing that the first condition is already
TRUE.
If the first condition is false, the second condition is checked. If the second condition is TRUE:
The instruction(s) within the statement will be executed.
NESTED CONDITIONS
Conditional statements within or grouped with other conditional statements. The aim of is to check if multiple events or data is TRUE before executing the instruction(s).
 Knowt
Knowt
