PAT Review
Biological Diversity
- Natural vs. Artificial selection
→ Natural - Occurs when the environment “selects” which individuals will survive long enough to reproduce
→ Artificial - When humans choose which traits are most desirable to use for changing genetic structure
- Variation within species (What is it?)
→ Each member of a species is born differently, they can have different weight, height or wingspan
- Symbiosis and symbiotic relationships
→ Association between members of different species (sym = together, bio = life) Three types of symbiosis:
→ Commensalism - One of the participating organisms benefits, but the other does not; however there is no harm done to the second organism
→ Mutualism - Benefits both organisms
→ Parasitism - one organism benefits and the other is harmed but not killed
- Niches vs. habitat
→ Generalist niche species - fills many roles, usually lives in a broad territory (broad niche)
→ Specialist niche species - has only a few roles, usually lives in a small amount of territory (narrow niche) \n → Organisms will live in places that fill their role in their niche
- Heritable vs. non-heritable traits
→ Heritable - Passed from generation to generation (ex. Eye colour, hair type, skin colour) \n → Non-Heritable - Not passed from generation to generation (ex. Playing the piano is acquired)
- Discrete vs continuous traits
→ Discrete Variation - Variation in a heritable characteristic that has an either/or form (being albino or not) \n → Continuous Variation - Variation in a heritable characteristic that fall within a range (height, hand span)
- Dominant and recessive traits/incomplete dominance
→ Dominant - two opposite acting alleles are inherited
→ Recessive - two same acting, non-dominant alleles are inherited
(Ex. Brown eyes=Dominant, Blue eyes=Recessive)
→ Incomplete Dominance - When 2 different alleles are present at the same gene, but neither is dominant
- Purebred vs hybrid
→ Purebred - a plant or animal that has ancestors with all the same form of a trait
→ Hybrid - An organism produced by crossing two purebred individuals for different forms of a trait
- Parts of the flower and function
→ Male Parts - Stamen: Male part of the flower, Anther: produces pollen and stores it, Pollen: Fine yellow powder on the anthers of flowers, consisting of grains that contain male gametes
→ Female Parts - Pistil: entire female reproductive organ of the flower, Stigma: receives pollen, Style: Structure that supports the stigma and connects it with the ovary of a plant, Ovary: Female reproductive organ in which egg cells are produced, Ovulues: Sac containing the female gametes of a plant
- Sexual vs. asexual reproduction: Types of each, advantages and disadvantages
→ Asexual Reproduction - Reproduction without the fusion of sex cells resulting in identical offspring and parent
Binary Fission: a parent cell divides into 2 identical cells (amoebas and other organisms)
Budding: a new organism develops from an outgrowth or bud on the parent
Spores: cell produced by asexual reproduction in certain organisms (fungi, non flowering plants)
Vegetative Reproduction: Type of asexual reproduction in plants that does not involve the formation of a seed (cuttings, tubers, shoots, sap suckers)
→ Sexual Reproduction - Reproduction involving the exchange of genetic material between two individuals resulting in offspring that are genetically different from the parents
- Chromosomes, DNA, genes: Where are they, what are they?
→ Chromosomes - packages whose contents are neatly put together into structures that easily fit into the cell
→ DNA - Deoxyribonucleic Acid
→ Genes - An uninterrupted segment of DNA
- Number of chromosomes in gametes/zygote etc for a human.
→ 23 for each gamete, together in one cell = 46
- Mitosis vs. Meiosis: What kind of cells and how many chromosomes result?
→ Mitosis - Type of cell division that produces two identical daughter cells from one parent cell, Responsible for growth and cellular repair of a multicellular organism, This process produces 2 new cells with the same number of chromosomes.
→ Meiosis - Type of cell division that produces cells with only ½ the DNA of a normal cell, Meiosis involves two cell divisions (not one but two!)
- Linnaean system of naming (genus, species)
→ Kings - Play - Chess - On - Fine - Green - Silk
→ Species, Genus, Family, Order, Class, Phylum, Kingdom
- Genetic Engineering
→ The intentional altering of DNA of an organism or population of organisms
→ Clones - A genetically identical copy of an entire organism or its cells or genes
→ Artificial Insemination - Artificial collection and injection of sperm from a male into a female
→ In Vitro Fertilization - Fertilization that happens outside the body, usually in a Petri dish;
- Extinction vs. extirpation
→ Extinction - Disappearance of every individual of a species from the entire planet
→ Extirpation - A local extinction or disappearance of a species from a particular area
- Exotic/ Non-Native/ Invasive Species
→ Exotic - organisms who belong to a way different place with a really different environment
→ Non-Native - organisms who belong to another place with a similar environment
→ Invasive Species - organisms that come to a place with intentions to take over a plant/animal species
- Population, community, species unity, species
→ Ecosystem - All living & non-living elements in an area that create a cycle
→ Community - The Biotic (living) component of an ecosystem
→ Population - Group of the same kind of species
Matter & Chemical Change (Chemistry)
- Particle model/States of matter
→ Matter is made of tiny particles, There is empty space between the particles, The particles are in constant motion, There are forces that act between the particles.

- Physical/Chemical Properties
→ Physical: The physical properties of a material (Ex. color, shine (luster), melting temp, freezing temp, boiling \n temp, density, hardness, solubility, conductivity (ability to transfer electricity), malleability, ductility (ability to be hammered into thin sheets or made into wire without breaking) \n → Chemical Determines the way a material behaves in a chemical reaction (Ex. reaction to oxygen, acids, heat, water, ability to burn)
- Physical vs. Chemical changes/reactions/evidence of these changes
→ Physical: A change in state or physical properties (state may be altered, but its chemical \n composition stays the same)
→ Chemical: When 2 or more substances react and form 1 or more new substances
WHMIS symbols

Endothermic vs. exothermic reactions
→ Exothermic: reaction that releases heat energy (hot packs)
→ Endothermic: reaction that absorbs heat energy (cold packs)
- Oxidation reactions
→ Combustion: when oxygen reacts with a substance to form a new substance and give off energy (fire)
→ Corrosion: slow chemical change that occurs when oxygen in the air reacts to a metal (Rusting)
→ Cellular Respiration: A chemical reaction that takes place in the cells in your body (energy)
- Compounds vs. pure substances
→ Compounds: A substance formed by 2 or more different elements (chemically fixed)
→ Pure Substances: made of only 1 kind of matter
- Factors affecting reaction rate (surface area, temp. etc.)
→ The presence of a catalyst (help reactions go faster, enzymes) \n → Concentration of the reactants (greater concentration = faster reaction) \n → Temperature of the reactants (The more heat added = the faster the reaction) \n → Surface area of the reactants (The greater the surface area = more area is available for reaction)
- The Law of Conservation of mass/matter (products = reactants)
→ The total mass of the reactants will have the same total mass of the products. (everything equal)
- Chemical reactions (products and reactants)
→ Reactants (starting materials) produce Products (End materials that are formed)
- Models of the atom (Thompson, Bohr etc.)
→ John Dalton: Billiard Ball Model
→ J.J. Thompson: Raisin Bun Model (electrons)
→ Hantaro Nagaoka: Mini Solar System
→ Ernest Rutherford: Nucleus in atom
→ Niels Bohr: Bohr Model (electron shells)
→ James Chadwick: Protons in atom
- Aristotle’s view of matter
→ Aristotle believed that everything was made of elements such as earth, air, fire, and water. (Incorrect)
- Characteristics of Ionic and Molecular compounds
→ Ionic: forms as a result of an attraction between particles of opposite charges (metals & non-metals)
→ Molecular: atoms combine they form a molecular compound (ALL are non-metals)
- How to write molecular compounds
→ Find chemical numbers, then find subscripts (ions), indicating physical state (state of matter)
- Common formulas (water, carbon dioxide, salt, baking soda, vinegar)
→ Water (H2O)
→ Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
→ Salt (NaCl) Sodium Chloride
→ Baking Soda (NaHCO₃) Sodium Bicarbonate
→ Vinegar (CH₃COOH) Acetic acid
Environmental Chemistry
- Biodegradable substances/Organic vs inorganic
→ Organic: Substances that contain carbon
→ Inorganic: Substances that don’t contain carbon
- pH and pH scale
→ A number that indicates how acidic or basic something is 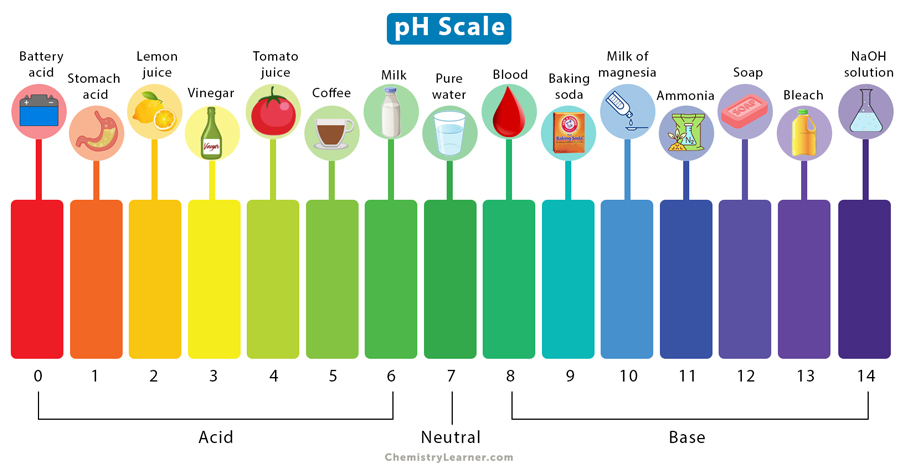
- Acids vs. bases (characteristics)
→ Bases: PH higher than 7 (Cleaning products)
→ Acids: PH lower than 7 (Vinegar)
→ Neutral: PH is exactly 7 (distilled water)
- Litmus paper tests
→ Tests to see how acidic or basic something is based on its color resulting from the reaction
- Neutralization: acids + base = salt + water
→ Combining an acid a base of similar potency to neutralize them and turn them into different substances
- Causes/components of acid rain
→ The combination of various greenhouse gasses
- Suspended solids/turbidity/turbulence and oxygen levels
→ Ways to determine water quality to see how fitting it is for living things
- Dispersion, Dilution & Deposition
→ Dispersion - scattering of a substance away from its source
→ Dilution - the dissolving of certain substances
→ Deposition - change of state from a gas to a solid
- Combustion reactions – harmful products of (heat/carbon dioxide)
→ Sulfur Dioxide - forms when sulfur combines with oxygen in the air. It's a major air pollutant that forms smog and acid rain. It mainly comes from industrial processes
→ Nitrogen Oxide - forms when nitrogen combines with oxygen as a result of fuel combustion. It gives smog its brown color and mainly comes from motor vehicles
→ Carbon Monoxide - a colorless & odorless gas. Its produced by incomplete combustion of chemicals containing carbon (e.g. hydrocarbons) It mainly comes from motor vehicles
→ Carbon Dioxide - a greenhouse gas because its releases in large amounts into the atmosphere (human activities)
- LD50
→ (Lethal Dose 50) amount of a substance that causes 50% of a group of test subjects to die if they are given a specified dose of the substance all at once
- Greenhouse/Enhanced Greenhouse effect
→ Greenhouse Effect: certain gasses trap heat from the sun & it regulates the earth’s temperature
→ Enhanced Greenhouse Effect: Greenhouse effect made greater by human activities that add greenhouse gasses to the atmosphere (this can create global warming)
- Biological indicators (What lives at what oxygen level)
→ Microbiological Indicators and Aquatic Invertebrates: Both are sensitive to PH levels,
- Biomagnification & Bioaccumulation
→ Biomagnetic - the increase in concentration of a chemical or element as it moves up the food chain
→ Bioaccumulation - the increasing concentration of the material in an organism over time
Electricity
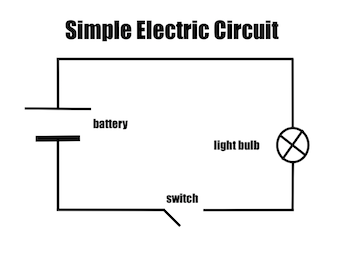
Circuit diagrams and symbols
Resistors/insulators/conductors
→ Conductors: materials that allow heat or electricity to pass through them
→ Insulators: do not allow heat or electricity to pass through them
→ Resistance: measure of how difficult it is for electrons to move (measured in Ohm’s)
- Purpose of fuses and circuit breakers and the difference
→ Fuses: breakable cell that explode inside when they fail
→ Circuit Breakers: a device that shuts off all power when malfunctioning but can be reset
- Amperage
→ Current or how may electrons are moving in a circuit
- Wet cells/electrodes/electrolytes/electrodes serve as terminals like in flashlight batteries
→ Wet Cells: Electrolyte inside is a liquid
→ Dry Cells: Electrolyte inside is a paste
- Effects of varying electrodes and electrolytes
→ Used to transfer electricity and manipulate energy in a cell
- Energy conversions ie) in a toaster⋯electrical to thermal to light⋯
→ Photosynthesis: Solar Energy to Chemical Energy
→ Lamp: Electric Energy to Heat Energy and Light Energy
→ Burning Wood: Chemical energy to Heat and Light Energy
- Types of energy (Thermal, mechanical etc.)
→ Energy: the ability to do work
→ Chemical: gasoline, batteries, food, Electrical: batteries, power stations, generators, Mechanical: any object that has movement, Thermal: fire or any type of heat
- The electromagnet (Parts, how to make it stronger)
→ magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current
- The electric (St. Louis) motor: Parts and function
→ Uses permanent magnets, electromagnets and a controlled flow of electricity to produce mechanical movement
- Energy Formula
→ The amount of energy consumed and outputted
→ [E = (P) x (V)] Joules = Watts x seconds
- Power Formula
→ The rate at which a device converts energy (measured in Watts)
→ [P = (I) x (V)] watts= current x volts
- Efficiency formula
→ Joules of output divided by Joules of input x (100)
- Static vs. current electricity
→ Static: Electricity that does not move
→ Current: Moving electrons go from Negative to Positive
- Relationship between voltage/current/resistance (as resistance increases⋯)
→ current flowing through a circuit is directly proportional to the voltage and inversely proportional to the resistance
Space
- Planets: Characteristics of Jovian vs. terrestrial/rotation vs. revolution/order from the sun
→ Terrestrial: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars (Earth like, Smaller, Rocky, No rings)
→ Jovian: Jupiter, Saturn Uranus, Neptune (Jupiter-like, Gas giants, Have rings)
→ Rotation: an object spinning on it’s own axis
→ Revolution → An object travelling around another object
- Parallax and triangulation
→ Parallax: Apparent shift of an object when it is viewed from two different places (Longer base line = more accurate result)
→ Triangulation: Used to indirectly measure distance (Based on the geometry of a triangle)
- Telescope parts/types of telescopes/radio telescopes
- Orbiting telescopes
- The electromagnetic spectrum
- History of astronomy/devices
- Heliocentric vs. geocentric
- What is altitude and azimuth?
- Kepler’s discovery about orbits
- The spectrum of stars’ position and movement
- Using a star’s spectrum to determine composition
- Interferometry
- Rockets: parts and propulsion
- Solar winds⋯what protects us?
- AU and light years
- Satellites vs. Probes vs. Shuttles
- Ion drives
- Hertzsprung-Russel diagram
- Stars and life cycles
- Other solar bodies (meteors etc.)
- Galaxies (types)
- Constellations vs. asterisms
- Dangers of space travel
- Canadian contributions
Other
- Experimental variables: manipulated (independent), responding (dependant), controls