Chapter 1: Why Intercultural Communication
Intro
Things that increase in shared connected spaces
Transportation Systems
Global Workforce
Travel (Foreign and Domestic)
Immigration and Migration
Domestic Diversity
Global Economy
Siloed spaces - segregated spaces, separations due to culture
To understand cultural differences you need to have…
Mindset to see from different angles
Competence to manage differences
Culture Blind - Socio-Psychological concept of referring to a lack of awareness and recognition of cultural differences within groups
Time and space have now been erased, global Village - McLuhan, 1962
Competent - Knowledge in action
Flexible Intercultural Communication - Managing cultural differences creatively and adaptively across a wide range of situations
Practical Reasons
Impact of Technology - Connect/work with others globally
Global and Domestic Diversity Workforce:
Global employee
Lower probability of groupthink
Groupthink - group of individuals reaches a consensus without critical reasoning or evaluation of the consequences or alternatives
New Norm
Non Traditional Relationships
Homogeneous Space Model - Inter-Relational landscape evolved (Friends/Partners), Structure, intersections of our identities with those of others
Global Healthcare Concerns and Opportunities
Culture drives healthcare!
Birthrate; Healthcare workers understanding of worldviews: Death/Burial/Caregiving and Treatments
Inclusivity
Expanding self awareness and other sensitivity
Expanding culture/Ethnic knowledge allow cultural strangers to feel acknowledged
Reactive → Proactive
Ethnocentric → Experience and Learn
Challenge the source of our assumptions
Personal Empowerment, Social Advocacy, Social justice
What is Culture
Culture - A learned meaning system
consists of…
traditions
beliefs
values
rituals
customs
rite of passage
norms
laws
symbols
arts
practices
history
artifacts
worldview
meanings
social hierarchy
Passed from generation → generation via interaction members of the community
Ideal Member - Fulfill expected behaviors
Members are nurtured by core values; promotes shared identity and solidarity
we/us - in group
they/them - out group
Iceberg
Deeper layers hidden: Only see the uppermost layers
Surface Level Culture
Pop Culture - Mass appeal
Inform others how to think of your cultural group
Feed perceptions
Intermediate
Symbols - Behavior standing for something meaningful: Verbal and non verbal
Artifacts
Words
Gestures
Meanings - Cue Objective and Subjective Reactions
Norms - Expectations of proper and improper behavior
Setting - Govern Compartment
Relationship Status - Degree of formality
Deep Level Culture
Levels
Normative Culture - Patterned way of living
Subjective Culture - Different degrees of important to aspects of culture
Shared
Traditions - Ceremonies, rituals, myths passed down
in group solidarity, communal memory, cultural stability
Birth, Weddings, Healing, Funerals
Beliefs - Fundamental assumptions that people hold without questions
The why
Values - Priorities Guiding good and bad behavior/ fair and unfair behavior
security and conformity
Seafloor Level
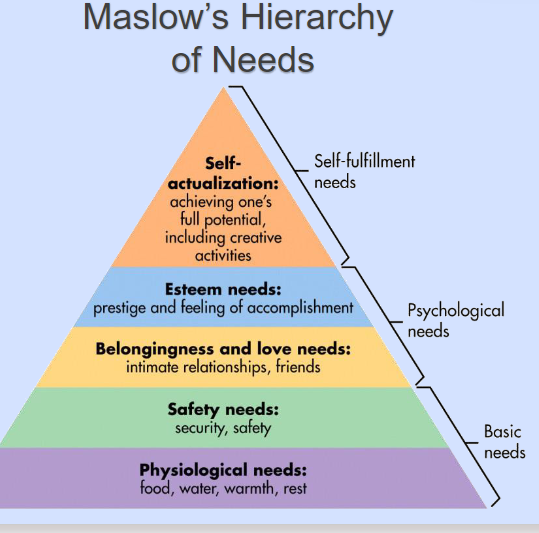
Human Needs
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Physiological → Safety → Love → Esteem → Self Actualization