Kinematics, Dynamics and Thermodynamics
Identify whether scientific quantities are scalar or vector quantities Recall SI units of measurements for distance/displacement Explain the differences between distance and displacement Convert between km, m and cm Calculate distance and displacement from graph and diagram
|
Explain the difference between speed and velocity Calculate speed and velocity using the equation Convert between m/s and km/h Compare instantaneous and average velocity of an object Explain the relationship between a displacement-time graph and a velocity-time graph Determine the speed or velocity of an object from a graph
|
Describe acceleration as both a change in speed and/or direction Recall the correct units for acceleration of m/s2 Calculate the acceleration of an object that is speeding up or slowing down using the equation Explain the relationship between a velocity-time graph and an acceleration-time graph Determine the acceleration of an object from a velocity-time graph
|
Recall the meanings and units for the variables v, u, s, a and t Apply the equations , , to solve for v, u, s and t for linear motion scenarios
|
Define inertia as the resistance of objects to changes in their motion. Identify the forces acting on a motor vehicle in straight line motion on a horizontal surfaces Calculate the resultant/net force in balanced and unbalanced force diagrams Define Force and provide examples of both contact and non-contact forces Explain how Newton's First law applies to objects in motion
|
Define Newton's second law of motion Apply the formula to calculate unknown variables in a variety of situations Recall the unit Newtons (N) used for Force
|
|
Define Gravitational Potential Energy (EP) Recall the value for acceleration due to gravity (9.8 ms-2) Apply the equation to determine the gravitational potential energy of an object Define Kinetic Energy (EK) Apply the formula to solve for kinetic energy Define work (W) as the change in energy of an object Solve problems involving work done by a force using
|
Define the Law of the Conservation of Energy Describe a simple model of energy transformation and transfer within a system Calculate the efficiency of a simple energy transformation 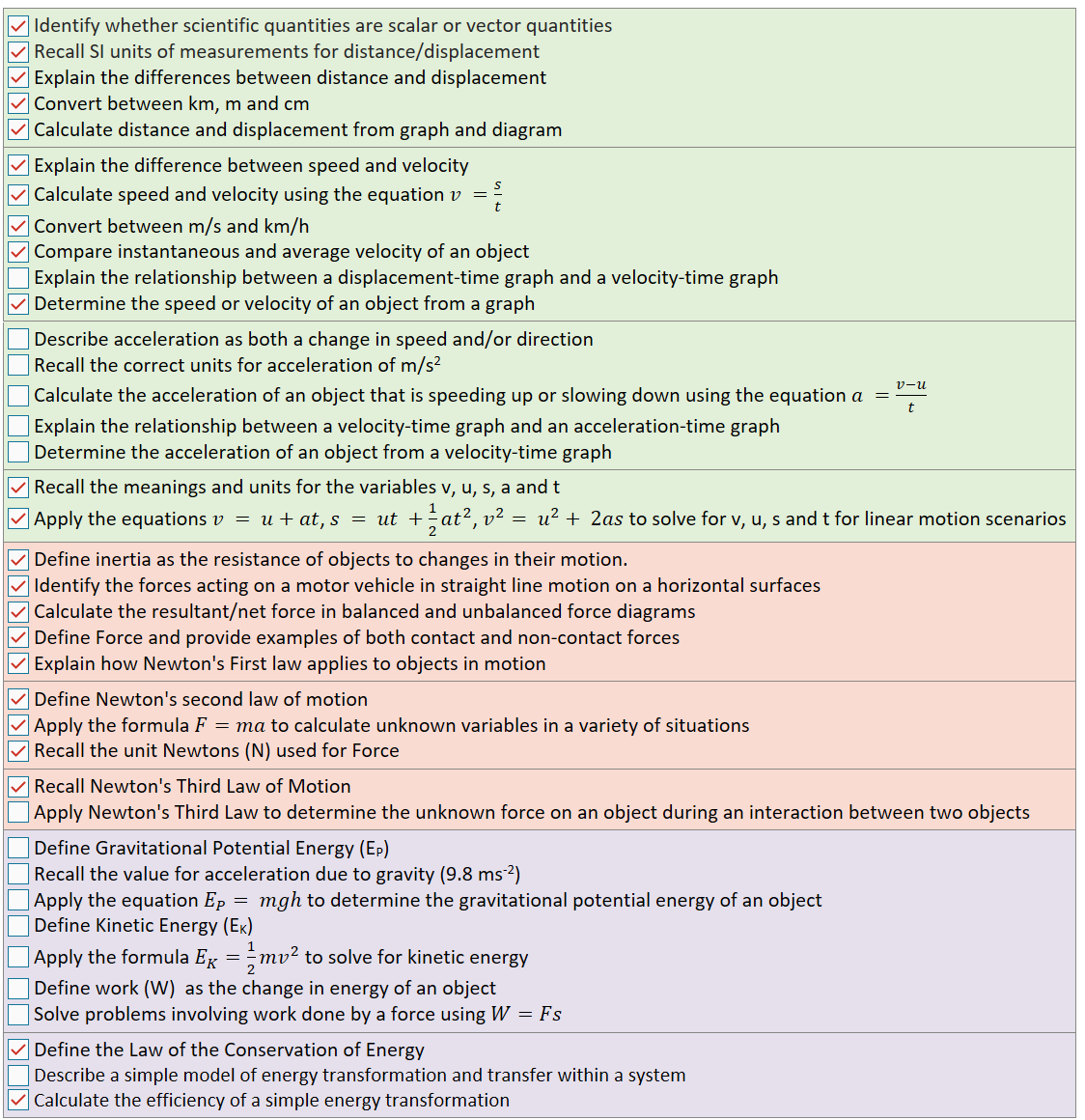
|