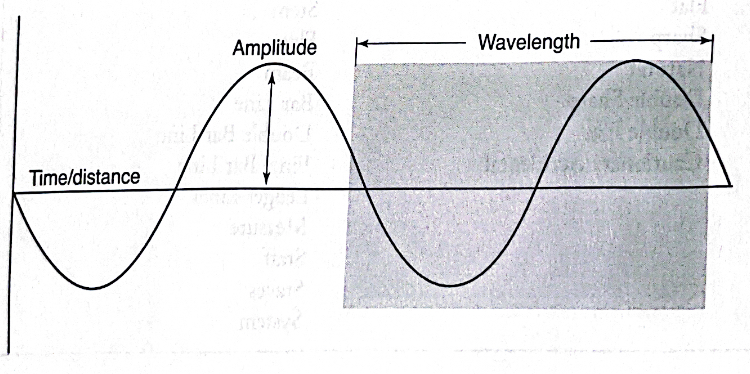
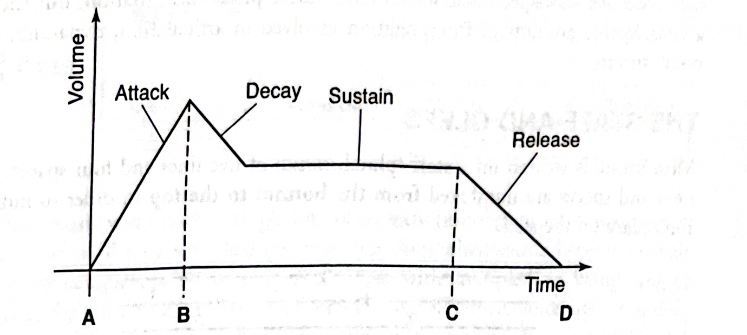
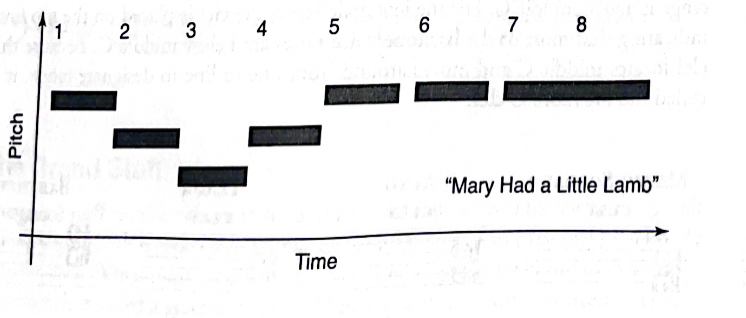
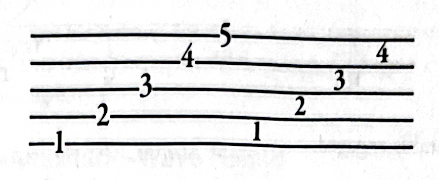
5.0(1)
Other AP Music Theory unit study guides
AP Music Theory Ultimate Guide
Unit 1: Music Fundamentals I: Pitch, Major Scales and Key Signatures, Rhythm, Meter, and Expressive Elements
Unit 2: Music Fundamentals II: Minor Scales and Key Signatures, Melody, Timbre, and Texture
Unit 3: Music Fundamentals III: Triads and Seventh Chords
Unit 4: Harmony and Voice Leading I: Chord Function, Cadence, and Phrase
Unit 5: Harmony and Voice Leading II: Chord Progressions and Predominant Function
Unit 6: Harmony and Voice Leading III: Embellishments, Motives, and Melodic Devices
Unit 7: Harmony and Voice Leading IV: Secondary Function
Unit 8: Modes and Form
Studying for another AP Exam?
Check out our other AP study guides
Tags
 Knowt
Knowt