Components of a Quantum Address
DIGIT #1: Principal Quantum Number (n)
Represented by the letter n (lowercase).
Indicates the PERIOD/ row number of the electron
Values can be whole numbers starting from 1 up to 7 (max row #)
DIGIT #2: Angular Momentum Quantum Number (l)
Denoted by lowercase l (in cursive).
Represents the shape of the electron’s orbital.
Possible values correspond to different shapes:
s = 0 (spherical shape)
p = 1 (figure 8s shape)
d = 2 (5-figure 8s shape)
f = 3 (complex shapes)
DIGIT #3: Magnetic Quantum Number (m_l)
Represented as m with a subscript l.
WHAT POD DOES IT LIVE IN/ COUNT?
Possible values include -2, -1, 0, +1, +2.
DIGIT #4: Spin Quantum Number (m_s)
Denoted by m with a subscript s.
Represents the spin of the electron.
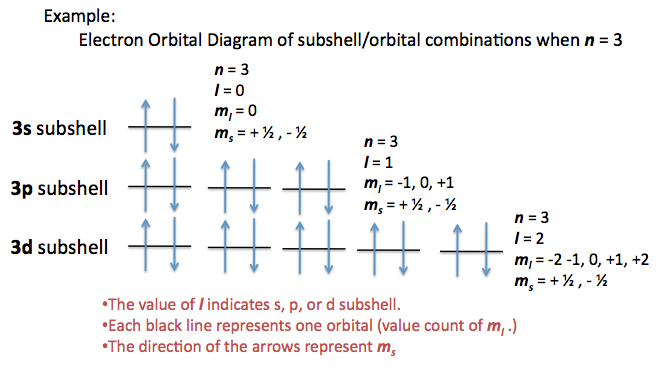
Possible values are:
+1/2 (ARROW UP) (clockwise spin)
-1/2 (ARROW DOWN) (counterclockwise spin)
Pod System (Digit #3)

Quantum Address
A quantum address consists of the four quantum numbers written in the format: (n, l, m_l, m_s).
Separated by commas and in the order of n, l, m_l, and m_s.
The fourth number (m_s) will always indicate the direction of spin, being either positive or negative.
Example: A quantum address could be formatted as (3, 1, 0, +1/2).
Maximum Principal Quantum Number
The maximum principal quantum number an atom can have is 7.
Corresponds to the seven rows (or energy levels) in the periodic table.