W2 L4: The Thyroid Gland
Anatomy/Function of the Thyroid Gland:
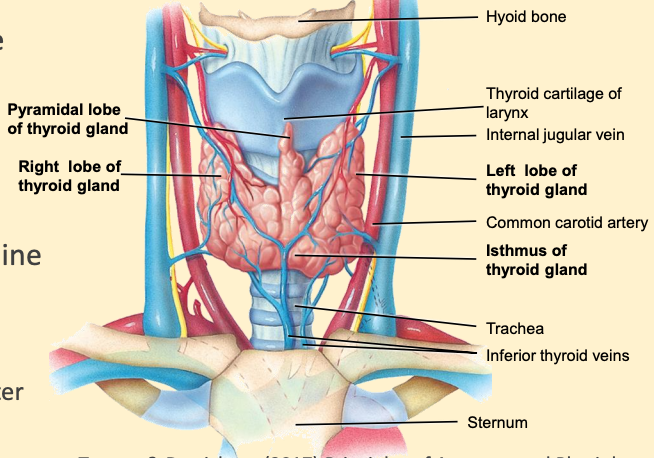
Adheres to the trachea, just below the larynx
- Tissue mass: 10-20g
- 2 flat lobes connected by an isthmus
right lobe > left
well supported by blood vessels so hormones can be easily transported around the body, iodine is supplied by the blood stream
Secretes thyroxine (T4), tri-iodothyronine (T3) and calcitonin
- T3, T4→ iodine containing hormones acting throughout the body
- Calcitonin→ regulates plasma calcium
Morphology of the Thyroid Gland
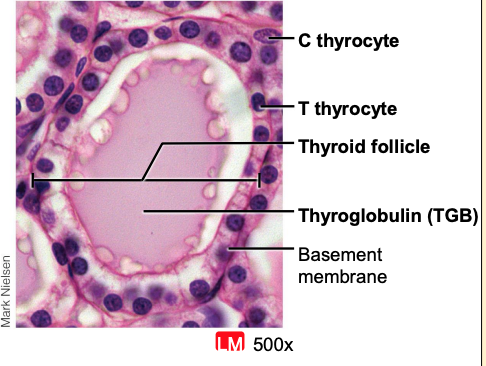
Functional unit → follicle
Basement membrane anchors follicle to connective tissue
Epithelial outer layer (“follicular cells”)→ secrete T3 and T4
- generating lots of T3 & T4 - colloid starts to shrink
- generating plentiful iodine - colloid swells
Central colloid-filled cavity
Changes morphology between active and inactive states (↑ activity → ↓ colloid storage)
Colloid: mainly consists of glycoprotein (thyroglobulin)
C-cells present in basement membrane and between follicles – Secrete calcitonin
Secretion regulated by ANS
Rich blood supply
- Approx twice kidney blood flow
- Regulated by ANS
Thyroid Feedback Pathways
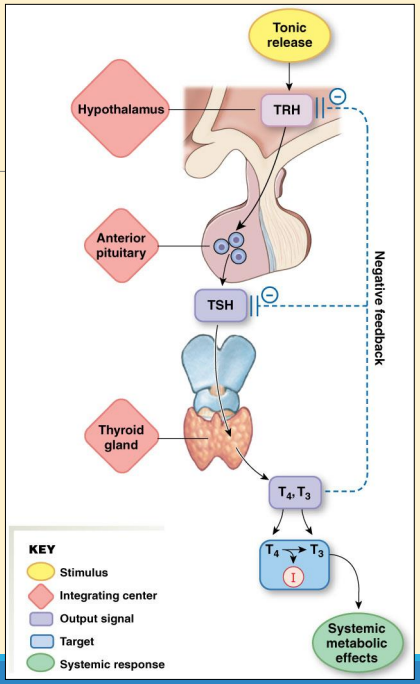
Thyrotrophin-releasing hormone (TRH) stimulates Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) release from anterior pituitary - TRH released from hypothalamus
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) controls the thyroid gland
Thyroid hormones promote oxidative metabolism, influence metabolism, necessary for full expression of growth hormone in children
T3 used to stimulate growth, metabolism and temp
Loads of T3 → turn on -ve feedback → bind to receptors in anterior pituitary and reduce TSH release
T4 slightly less active than T3- T4 more bioactive
Synthesis of Thyroid Hormones (T3 /T4 ): Thyroglobulin & Iodination
- 2 components are necessary: thyroglobulin and iodine
- Thyroglobulin = 670kDa glycoprotein
- Comprises 2 peptides of 330kDa and carbohydrate moieties
- Synthesised in follicular cell rough endoplasmic reticulum
- Packaged into vesicles and released into lumen by exocytosis
- Stored as colloid (known as organification) up to 3 months
- Iodination
- T3 and T4 require dietary iodine (≈ 75mg/day; 140µg/day recommended in UK)
- “Iodide trapping”: trapping iodine in the cell - ↑ conc
- Inorganic iodide enters follicular cells via Na/I symporter (NIS)
- Iodine transported → incorporated into tyrosine molecules to form follicle lumen
- Iodination of free tyrosine residues of thyroglobulin
- Hydrolysis of iodinated thyroglobulin → T3 /T4
- Some T3 synthesised, but approximately 20-fold more T4
- Thyroid stores several weeks supply of T3 /T4
Secretion of Thyroid Hormones
- Colloid droplets taken up by follicle cells by endocytosis
- endosomes fuse with lysosome
- Lysosomes fuse with colloid droplets
- Thyroglobulin degrades
- Degradation products recycled
- Released T3 and T4 hormones keep in vesicles until they diffuse into fenestrated capillaries surrounding the follicles
- In blood, hormones bind to plasma proteins
- Mostly thyronine-binding protein (TBP) (specific to T3 & T4)
- can bind to prealbumin (TBPA) & albumin
- T4 binds with ↑ affinity → ↑ half life (t½)
Summary of Synthesis and Secretion
- Primary function is to produce the hormones calcitonin, thyroxine (T4) and tri-iodothyronine (T3)
- Main steps in the synthesis, storage & secretion of thyroid hormone are:
- Iodide trapping → Iodine only moves in when the NIS is present
- Organification
- Secretion of T3 and T4
Roles of TSH in Thyroid Function
- TSH receptors on follicular cell surface
- G- protein coupled receptors (GPCR) coupled to adenylate cyclase (adenylate cyclase makes cAMP)
- Stimulation of hormone synthesis
- Iodide trapping via Na/I co-transporter
- ↑ Thyroglobulin synthesis
- ↑ Iodination of thyroglobulin
- Stimulation of hormone secretion
- ↑ Uptake of colloid by follicular cells
- Necessary for thyroid gland maintenance
- Gland rapidly atrophies in absence of TSH
Action of Thyroid Hormones
T3 has far greater activity than T4
- Intracellular conversion of T4 to T3 by deiodinase 2
- Deiodinase 2 provides a mechanism by which cells control sensitivity to thyroid hormones -
Act as “growth factors” in multiple tissues
Regulate gene transcription
- Cytoplasmic (intracellular) receptors → nucleus to turn on specific genes (when bond to T3)
- Effects take hours/days
Induce specific tissue effects; also ↑ O2 consumption and heat production of whole body
- Able to manipulate body temp
- Altered protein metabolism
- ↑ Basal Metabolic Rate (>100 enzyme systems sensitive to T3)
- ↑ activity of Na+ /K+ -ATPase
- ↑ glucose uptake & lipolysis by regulating glucose transporters
Abnormal Thyroid Function
Diagnoses confirmed by assay of plasma T3 and T4
- Hyperthyroidism (thyrotoxicosis)
- e.g. Grave’s disease (autoimmune – antibodies block TSH receptor- ↑ thyroid cells to try to ↑ NIS)
- Symptoms include goitre (enlarged thyroid), exophthalmos (protrusion of eyeballs). ↑ Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) & heart rate, weight loss (due to ↑ BMR)
- Treatment→ surgical removal or 131I ingestion
- Hypothyroidism
- Causes:
- Iodine deficiency → ↓ T3 feedback → ↑ TSH → goitre (haven’t got enough NIS, so generates more cells to produce more NIS)
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (autoimmune) → thyroid destruction
- Myxedema→ adults
- Symptoms include facial swelling, ↓ mental function, lethargy, ↓ BMR (↑ weight) & heart rate
- Cretinism→ congenital, children
- Symptoms inc. mental retardation (cretinism), ↓ body growth
- Treatment→ regular medication of hormone replacement (T4) or iodine supplements (in deficiency states)
Quiz
- • What would be the likely effect of 5 days without dietary iodine on,
- TRH
- TSH
- T3
- T4
- • What would be the likely effect of 5 weeks without dietary iodine on,
- TRH
- TSH
- T3
- T4
- How might a loss of deiodinase 2 activity affect physiology?
- What would be the effect of iodine supplementation in
Hashimoto’s disease?