Flight and Aerodynamics Vocab
Aerodynamics
Definition: the study of the behavior of air as it interacts with solid objects, like an airplane
Sentence: engineers design airplanes based on aerodynamics to reduce air resistance and improve efficiency
Real-World Connection: plays a crucial role in designing airplanes, cars, and even sports equipment to improve performance and efficiency
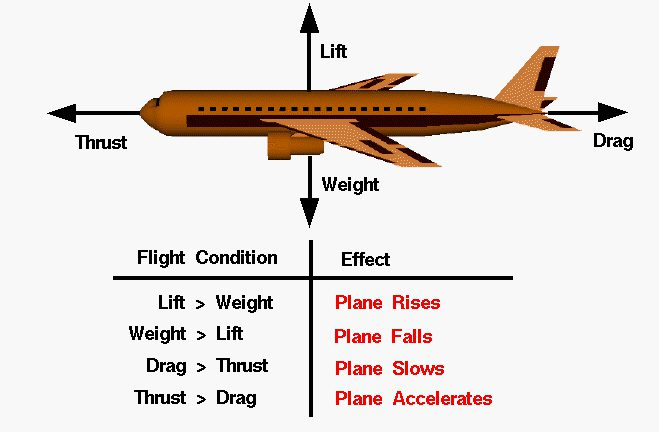
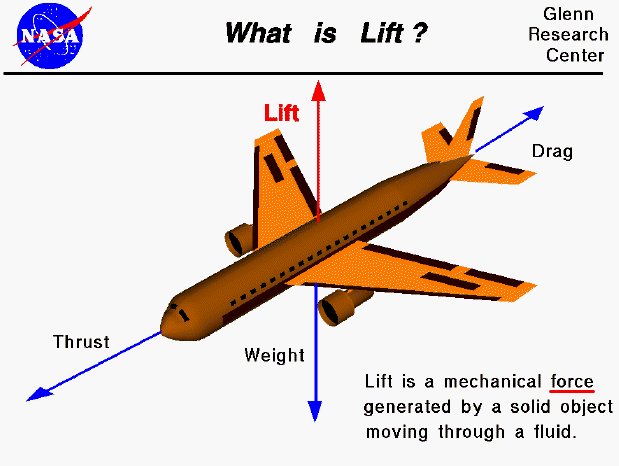
Lift
Definition: the upward force that opposes the weight of an airplane and is created by the movement of air over and under the wings
Sentence: an airplane’s wing helps it generate lift, allowing it to rise into the air
Real-World Connection: lift is what allows airplanes to take off and stay in the air. This force is generated due to differences in air pressure above and below the wings.
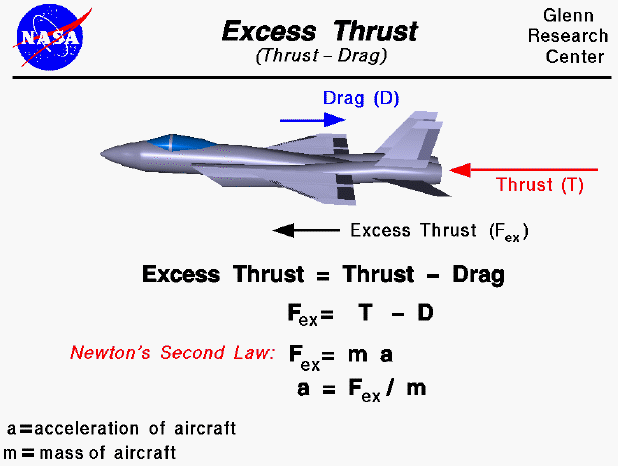
Thrust
Definition: the force that propels an aircraft forward, generated by engines or propellers
Sentence: a jet engine provides thrust by expelling hot gases at high speeds
Real-World Connection: thrust propels aircraft forward; jet engines generate thrust to push the plane
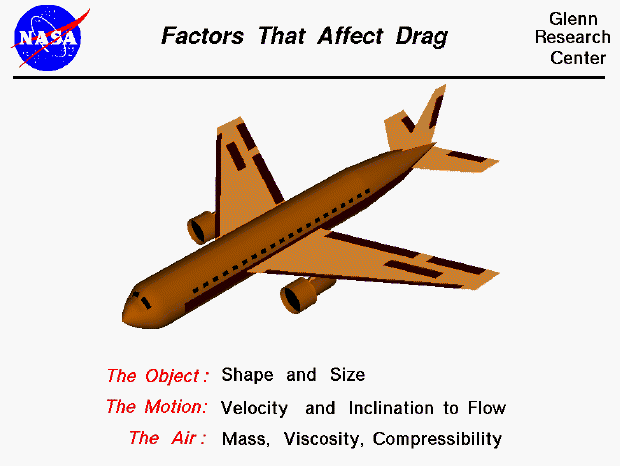
Drag
Definition: he resistance force that opposes an aircraft's motion through the air, caused by friction and differences in air pressure
Sentence: the tubular shape of an airplane reduces drag, allowing it to move more efficiently through the air
Real-World Connection: reducing drag improves fuel efficiency in airplanes and cars; athletes wear special clothing to reduce drag too
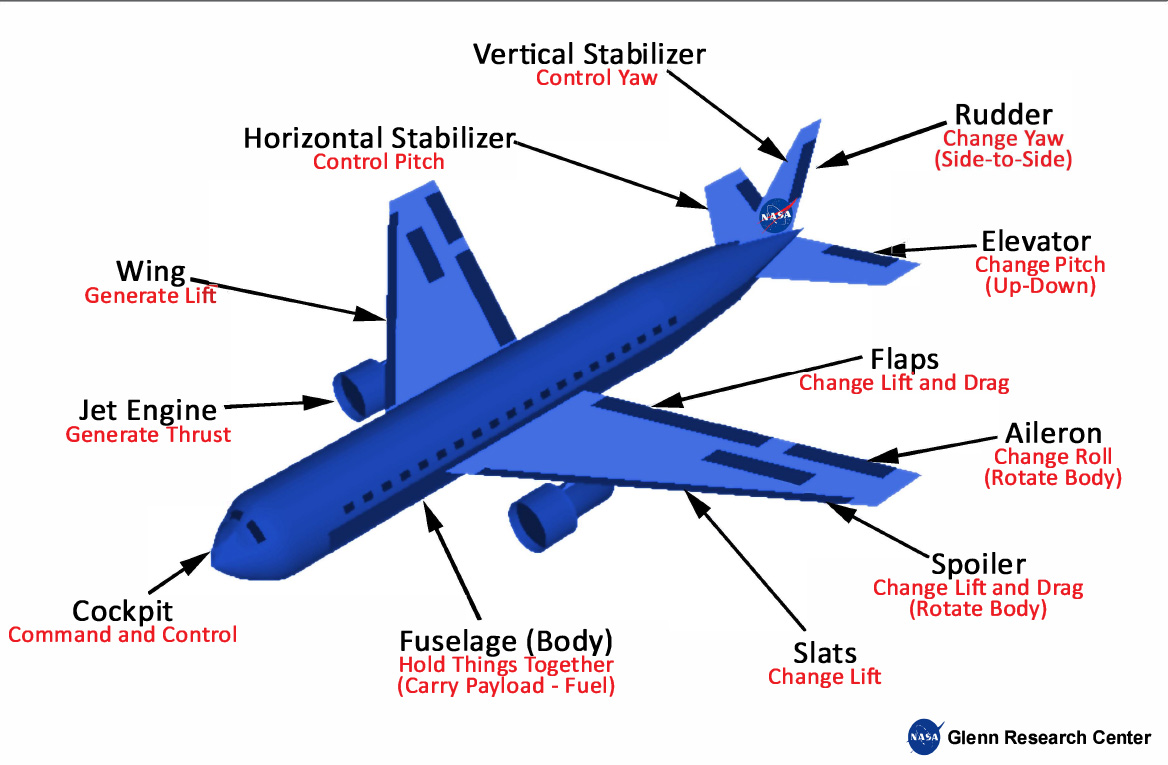
Wing
Definition: the part of an airplane that generates lift; its shape and angle are crucial for flight
Sentence: the wings of an airplane generate lift
Real-World Connection: wings are essential for flight; different wing designs affect speed and maneuverability
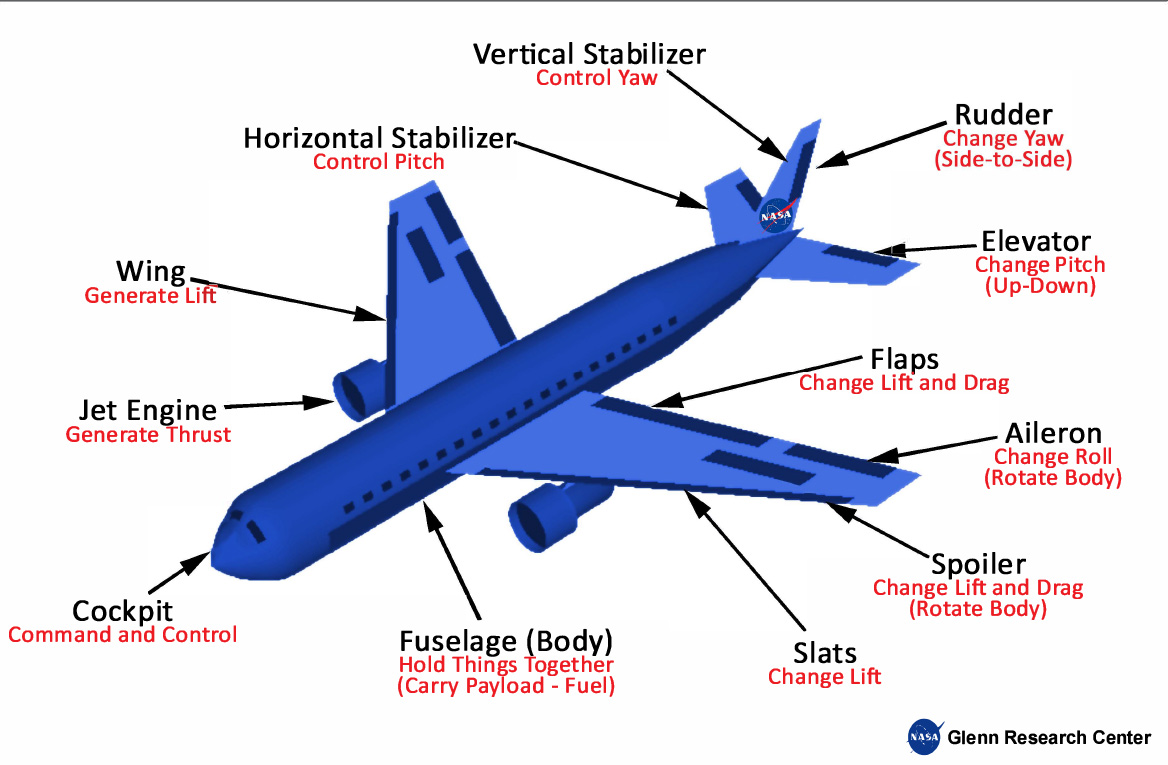
Fuselage
Definition: the main body of an aircraft, designed to hold passengers, cargo, and crew
Sentence: the fuselage of an airplane houses the cockpit, passengers, and cargo
Real-World Connection: it’s the main body of an aircraft, designed to balance weight and aerodynamics
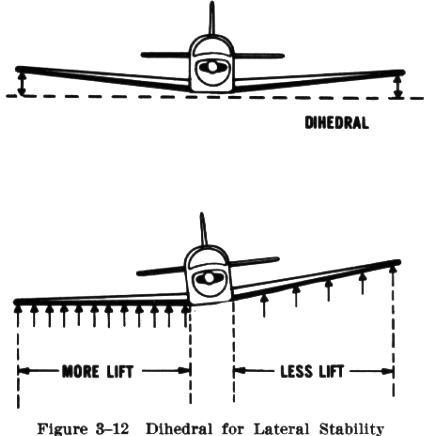
Stability
Definition: the ability of an aircraft to maintain or return to its original flying position after being disturbed
Sentence: proper weight distribution in an airplane ensures stability
Real-World Connection: prevents unwanted movements; pilots adjust controls to maintain stability
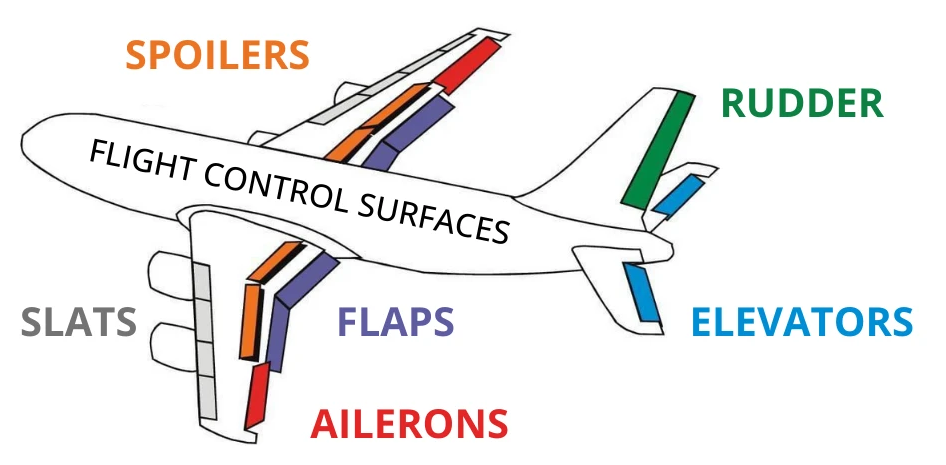
Control Surfaces
Definition: movable parts of an aircraft, such as ailerons and rudders, that help control its direction and attitude
Sentence: the pilot uses control surfaces to maneuver the plane
Real-World Connection: allow pilots to steer and stabilize the aircraft; ex: elevators control pitch, affecting altitude changes
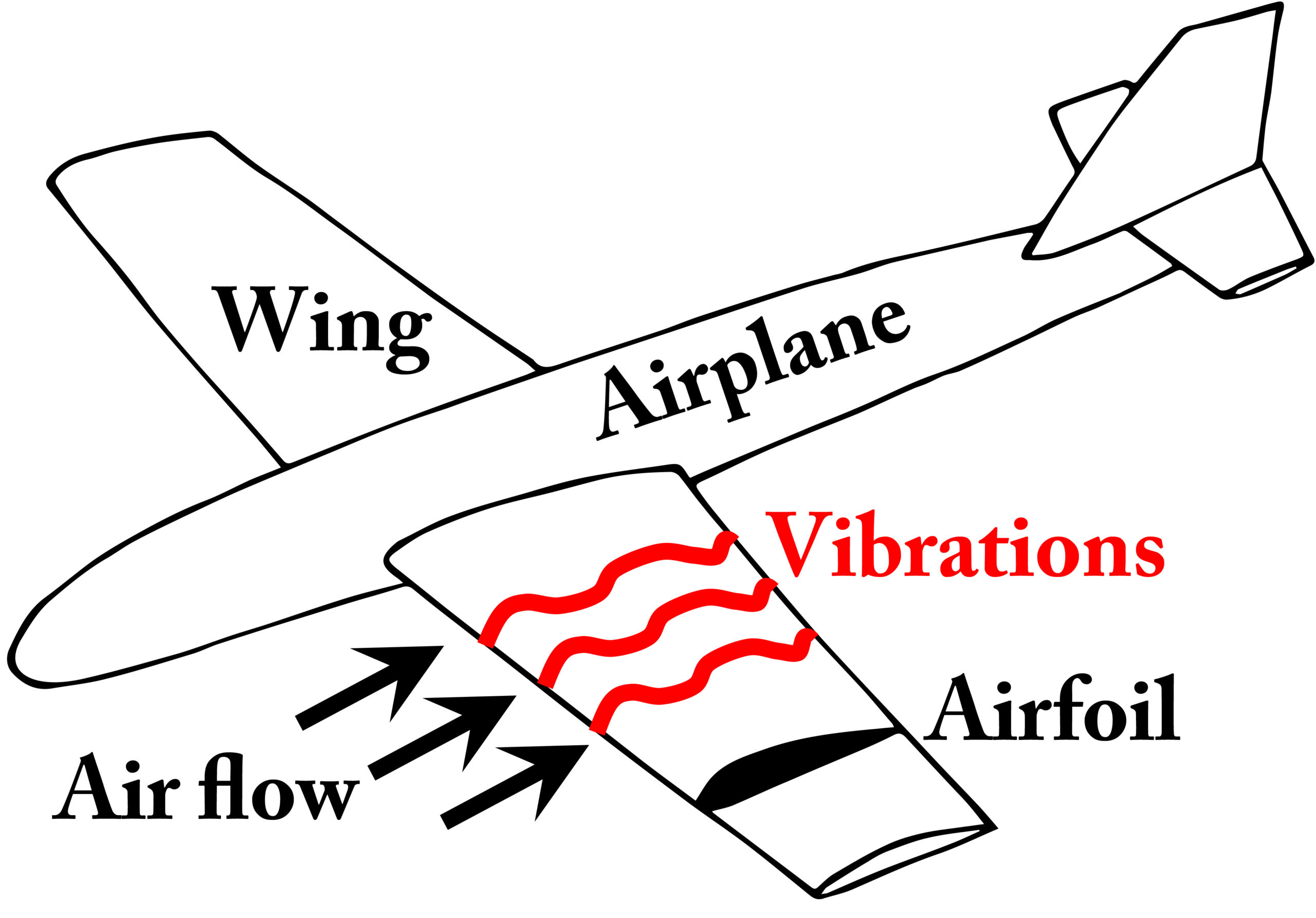
Airfoil
Definition: a shape designed to create lift when air flows over it, commonly used in wings and propellers
Sentence: the curved shape of an airfoil helps generate lift by altering airflow
Real-World Connection: found in airplane wings, helicopter blades, and even wind turbine blades; optimize airflow and performance
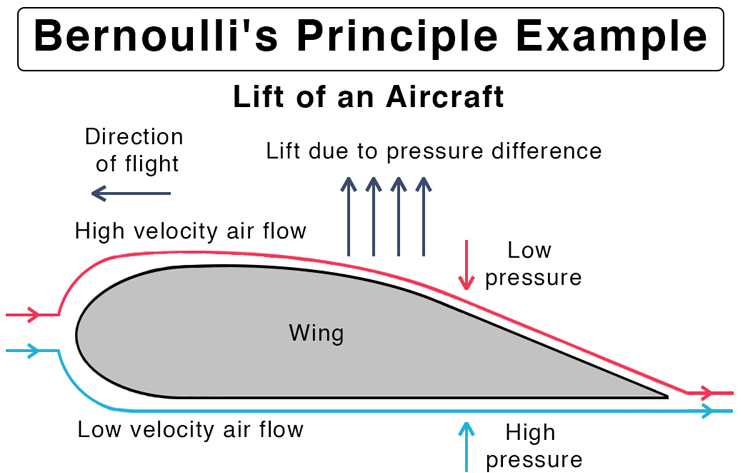
Bernoulli’s Principle
Definition: a principle that explains how the pressure of a fluid decreases as its velocity increases, crucial for understanding how lift is generated
Sentence: Bernoulli’s Principle explains why air moving faster over a curved surface creates lower pressure, creating lift
Real-World Connection: key to how airplane wings generate lift and how sports balls curve in the air due to pressure differences