What is Research?
Research
Process of collecting and analyzing data for the advancement knowledge
“Critical Method”
open minded, analyzes, and critiques
Scientific Method
Methodical
Structure
Systematic Inquiry
Describes a phenomenon, predicts an outcome
questions for further studies
(Ex: Pandemic —> Online Classes —> Loneliness))
Addresses issues and concerns
Looking into an unexplored phenomenon
Gathering data to address and answer problems
Reporting results to an audience
2 main purposes (2 G’s): Gather Evidence and Gain Knowledge
Qualities of Research
Deductive - When conducting deductive research, you always start with a theory. This is usually the result of inductive research
Start: Specification of hypotheses based on existing theories
End: Verification through evidence or data
Inductive - When there is little to no existing literature on a topic, it is common to perform inductive research, because there is no theory to test.
Start: Analysis of a phenomenon (Analysis)
End: Development of theory
Recursive - non-linear progression, rewriting of research
Empirical - verifiable, sense, evidence
Logical - process, reasons, structure
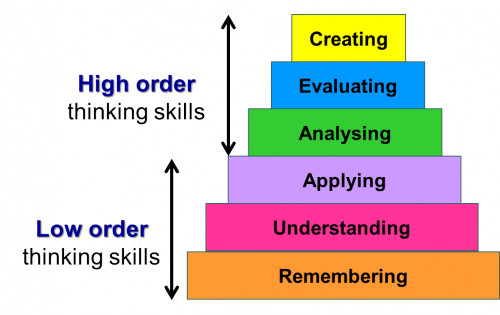
Requires High-Order Thinking Skills rather than Low order thinking skills
HOTS (High-Order Thinking Skills)
Applying, Analyzing, Evaluating, and Creating
LOTS (Low-Order Thinking Skills)
Remembering and Understanding
Replicable - can be copied
Solution-Oriented - future solutions to real-world problems
Objective - goal oriented, unbiased, in contrast to subjective approaches
Requires sufficient sources of data - SOURCE
Importance of Research
Importance to the individual
critical thinking
organization - focused, cohesive, coherent manner
self-discipline and perseverance
teamwork
Importance to society
government policies
decision-making
sociocultural interactions
medicinal and health research
environmental awareness and protection
inventions
Research is a systematic inquiry, an academic study that involves:
Defining a problem
investigating a question
formulating a hypothesis or argument
referring to different sources and ideas
collecting, analyzing, and organizing data
making deductions that lead to questions
Research Process (Order)
Select and narrow down the topic
Conduct preliminary research
Formulate thesis and research questions
Develop a preliminary outline
Gather additional references
Write the introduction and literature review
Plan the research methodology
Develop, adopt, and modify research instruments
Gather and analyze data
Revisit and revise the introduction and literature review
Write the results and discussion
Write the summary, conclusion, and recommendations
Consolidate the full paper and add a reference list
Edit the full paper
Disseminate research findings (presentation or publication)
Research Ethics
Set of Moral Principles and Code of Conduct that define what good and acceptable research is
General Research Practices
Be objective
Disclose any potential conflict of interest
Data Management and Plagiarism
Avoid fabricating or making up data or results
Avoid falsifying data just to prove your point
Always cite your sources
Avoid self-plagiarism
Avoid ghostwriting
Ensure confidentiality of collected data
Authorship
Author must be involved in:
Conceptualizing the study
Conducting the methodology
Analyzing and interpreting the data
Writing the paper
Use of human and animals
Inform and ask permission from the people who will be the subject of your research
Refrain from inflicting harm on human participants
Animals can only be harmed if there are legitimate scientific benefits from doing so
When it comes to personal information, collect only those that are relevant to the study
Refrain from forcing anyone to participate in your research
Avoid choosing participants based on convenience alone
Informed Consent Form (ICF)
Purpose, process, duration of research
Their right to withdraw and how
Foreseeable consequences, risks, and benefits
Protection or limitations of confidentiality and anonymity
Contact information for questions
Other ethical considerations: compensation, deception, debriefing
Types of Research According to Paper
Basic Research
Develops or tests theories and propositions
Expands knowledge and satisfies curiosity
No immediate application to the real world
Descriptive
Ex: Student Engagement/Participation in Facebook Activities
Applied Research
Tests theory in an actual problem situation
Addressing practical concerns
Ex: Using Facebook to Enhance the Academic Collaboration Among College Students in the Philippines
Action Research
Focuses on solving problems within an organization or community
Locally intended. Not universally applicable
Ex: Using Facebook-based e-portfolios to an
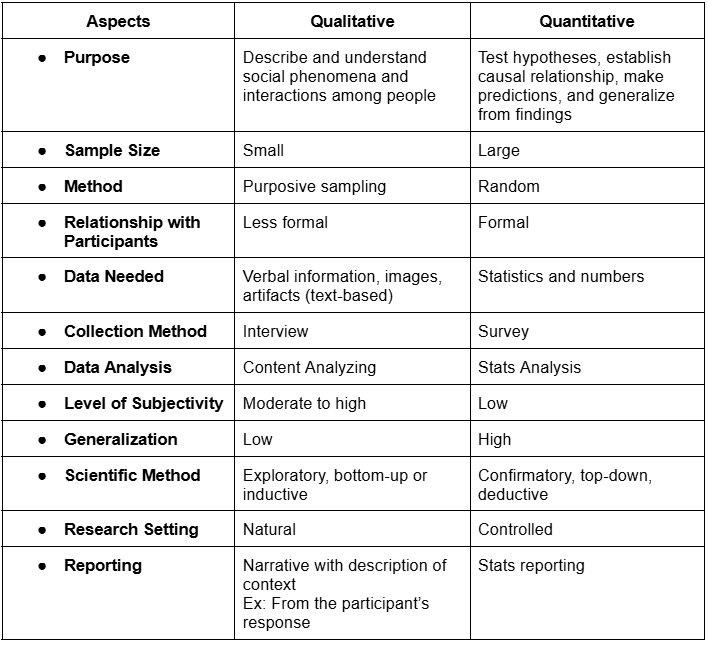
Quanti vs Quali Research
Qualitative
Used in exploring new ideas
Explaining concepts in greater depth
Focuses on phenomenon, person, community, or reality in its natural and everyday state
Analysis should be grounded on the experience of the people
Quantitative
Understanding the magnitude of a phenomenon
Testing hypothesis about relationship between variables
Predictions about human behavior
Extent and measurement of a phenomenon
analysis = quantifiable factors
Mixed Methods (Qualitative + Quantitative)
Literature Review Tips
Treat the literature review as a series of mini essays
Decolonize references by citing studies from the Global South
Apply “One Thing” principle
What I learned from the article that I never knew of until I read this specific article
Global South
Latin America, Asia, Africa, Oceania
Third World Countries
Periphery
Developing
Decentralization
Not just a metaphor for poor
Challenges in PH research
important to discuss own country
Acknowledge
Influence of foreign
Globalization
Economy
Politics
Migration