the excretory system
The excretory system is responsible for removing waste products and excess substances from the body to maintain internal balance (homeostasis). The main organs involved include:
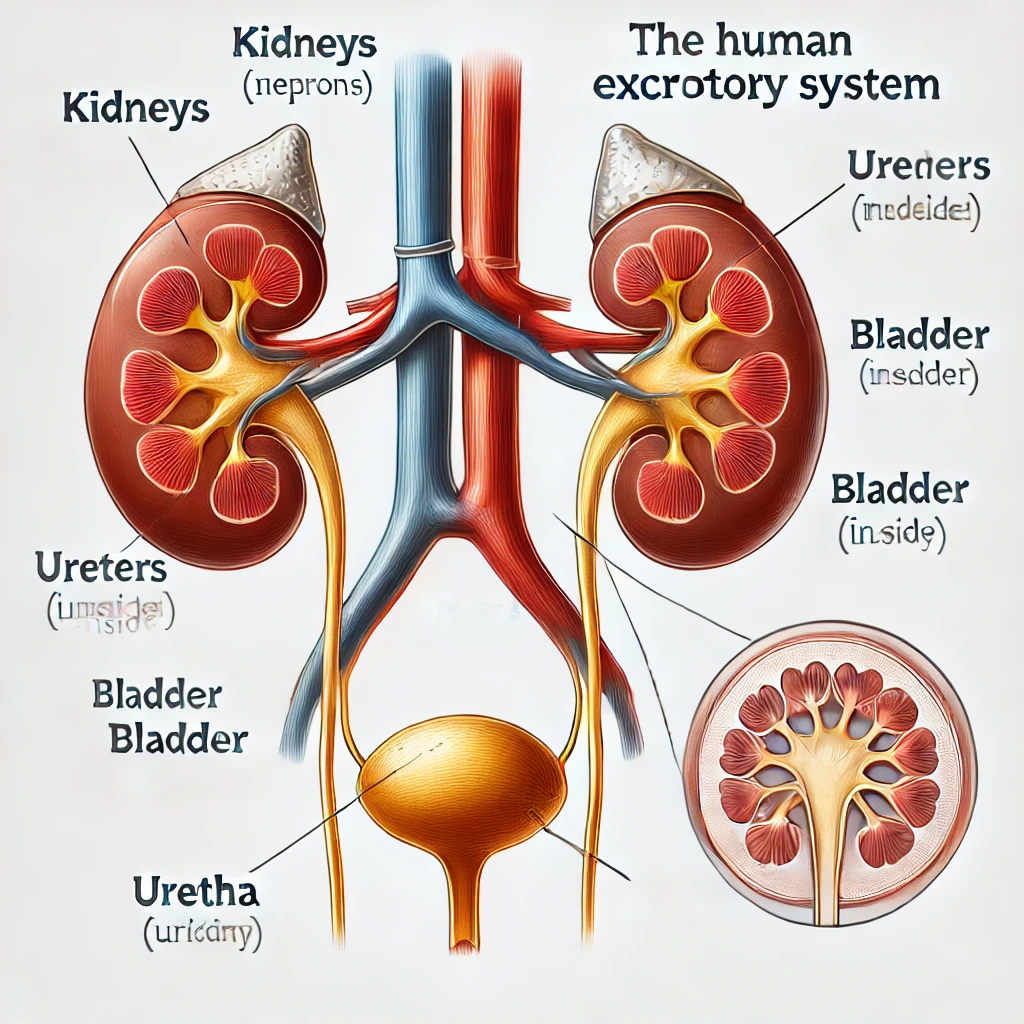
• Kidneys: Filter blood to remove waste (such as urea), excess water, and salts, forming urine.
• Ureters: Tubes that transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
• Bladder: Stores urine until it is ready to be expelled.
• Urethra: Carries urine from the bladder out of the body.
Other organs, such as the skin (through sweat), lungs (by exhaling carbon dioxide), and liver (which processes toxins), also assist in excretion. The system plays a crucial role in regulating water balance, electrolyte levels, and removing metabolic waste, ensuring the body functions properly.
1. Kidneys – Filter blood and remove waste to form urine.
2. Ureters – Transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
3. Bladder – Stores urine until excretion.
4. Urethra – Carries urine out of the body.
5. Liver – Processes toxins and waste products.
6. Lungs – Excrete carbon dioxide and water vapor.
7. Skin – Removes waste through sweat.
8. Nephrons – Functional units in the kidneys that filter blood.
9. Renal Artery – Supplies oxygenated blood to the kidneys.
10. Renal Vein – Carries filtered blood away from the kidneys.
The five main processes of the excretory system are:
1. Filtration – Blood is filtered in the kidneys (specifically in the nephrons) to remove waste, excess water, and toxins.
2. Reabsorption – Essential substances like water, glucose, and ions are reabsorbed into the bloodstream to maintain balance.
3. Secretion – Additional waste products and excess ions are actively transported from the blood into the urine.
4. Storage – Urine is temporarily stored in the bladder until it is ready to be excreted.
5. Excretion – Urine is expelled from the body through the urethra, removing metabolic waste.
1. Urea – A nitrogen-containing waste product formed in the liver from the breakdown of proteins and excreted by the kidneys in urine.
2. Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) – A waste gas produced during cellular respiration and expelled from the body through the lungs.
3. Nitrogenous Waste – Waste products containing nitrogen, such as urea, uric acid, and ammonia, which result from the metabolism of proteins and nucleic acids.
4. Waste – Unwanted or excess substances produced by the body’s metabolic processes that need to be excreted to maintain homeostasis.
 Knowt
Knowt