Note
0.0(0)
Explore Top Notes Note
Note Studied by 826 people
Studied by 826 people Note
Note Studied by 81 people
Studied by 81 people Note
Note Studied by 6 people
Studied by 6 people Note
Note Studied by 1 person
Studied by 1 person Note
Note Studied by 19 people
Studied by 19 people Note
Note Studied by 8 people
Studied by 8 people
AP PSYCH 1.1 Introducing Psychology
4.7(17)
Unit 9: Period 9: 1980-Present
5.0(1)
Photosynthesis
4.0(1)
ATP-Dependent Chromatin Remodeling Complexes Change Nucleosome Structures
5.0(1)
Chapter 2: States
5.0(1)
Chapter 7
5.0(1)
Chapter 14:Salt and identification of Ions
Salt
A salt is a compound that is formed when the hydrogen of an atom in an acid is replaced by a metal.
It is formed by the neutralisation reaction between an acid and a base
[ ] Precipitation
[ ] Titration
Reactions
- Metal and acid➡️ salt and water
- [ ] zinc + sulphuric acid➡️ zinc sulphate+ Hydrogen
2. Metal oxide + acid ➡️ salt and water
- [ ] Copper(II) oxide + sulphuric acid➡️ copper sulphate+ water
3• Metal hydroxide + acid ➡️salt and water
- [ ] Potassium hydroxide+ hydrochloric acid ➡️ potassium chloride + water
4• Metal carbonate + acid ➡️salt+water+ carbon dioxide
- [ ] Zinc carbonate+ nitric acid ➡️ zinc nitrate +water+ carbon dioxide
Solubility
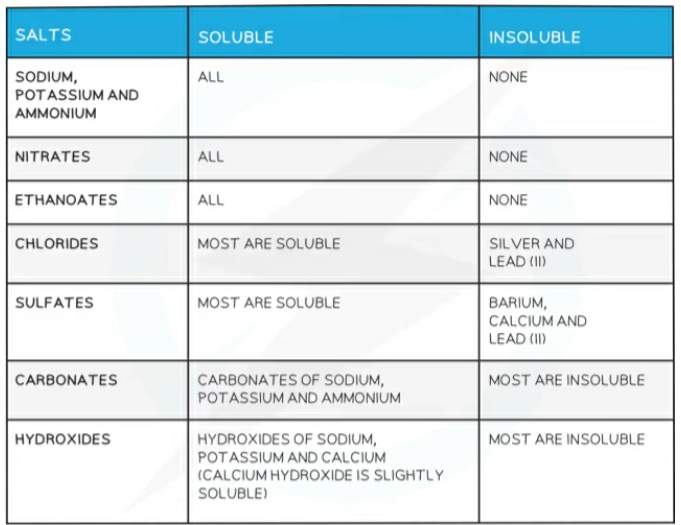
Preparation of soluble salts
- Metal and acid
- Metal oxide and acid
- Metal hydroxide and acid(titration)
- Metal carbonate and acid
Preparation of insoluble salts
Precipitation
[ ] Soluble salt+ soluble salt ➡️ insoluble salt
Identification of ions
Cations (postive ions) they travel to the negative terminal Cathode during electrolysis.
Anions (negative ions) they travel to the positive terminal Anode during electrolysis
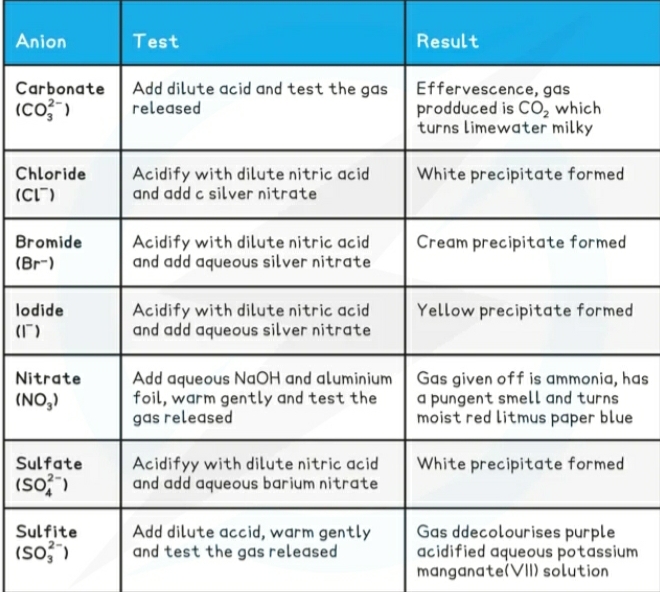
Identification of gases
| Hydrogen | Pops with a lighted splinter |
|---|---|
| Oxygen | Relights a glowing splinter |
| Carbon dioxide | Turns limewater milky |
| Chlorine | Turns moist blue litmus red and then bleaches it |
| Ammonia | Turns moist red litmus paper blue |
| Sulphur Dioxide | Turns acidified potassium dichromate from yellow to green |
Note
0.0(0)
Explore Top Notes Note
Note Studied by 826 people
Studied by 826 people Note
Note Studied by 81 people
Studied by 81 people Note
Note Studied by 6 people
Studied by 6 people Note
Note Studied by 1 person
Studied by 1 person Note
Note Studied by 19 people
Studied by 19 people Note
Note Studied by 8 people
Studied by 8 people
AP PSYCH 1.1 Introducing Psychology
4.7(17)
Unit 9: Period 9: 1980-Present
5.0(1)
Photosynthesis
4.0(1)
ATP-Dependent Chromatin Remodeling Complexes Change Nucleosome Structures
5.0(1)
Chapter 2: States
5.0(1)
Chapter 7
5.0(1)