KKDP 1: Roles of the Crown and the Houses of Parliament (Vic & Commonwealth) in law-making
Structure of both parliaments (Vic and Fed)
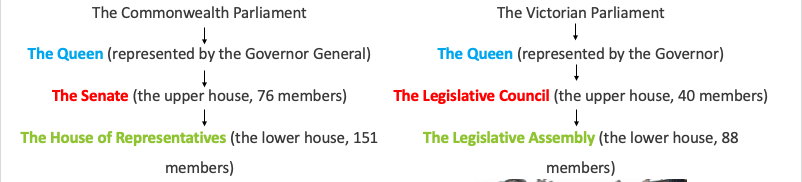
Federal/Commonwealth Parliament
House of Representatives
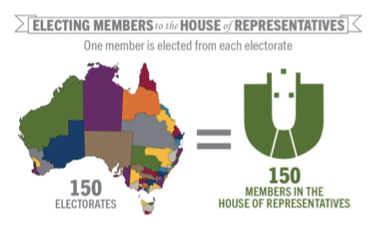
Consists of 151 members each reping an electoral division (151 electorates = 151 members in house reps
elected for a 3 year term
Sec 28 of constitution—> states elections for the HOR must be held at least every three years.
Sec 24 of constitution—> The House of Representatives shall be composed of members directly chosen by the people of the Commonwealth, and the number of such members shall be, as nearly as practicable, twice the number of the senators.
government formed in house of reps
Ministers sit on the front bench in the house
house of reps controls gov spending
Role of the House of Reps in law making
Initiate and make bills- intro of new bills to be debated & passed. Usually introduced by the gov, although any member may introduce a bill
Control government expenditure- bill must be passed through both houses before gov is able to collect taxes or spend money, but only the lower house
Determine government- the poltical party (or coalition of parties) that has the most members in the house of reps forms government. In terms of law-making, as the gov has the majority in lwr house, is able to generate the vast majority of law reform that enters the parliament
Act as a house of review- will act as the house of review in the law making process when a bill has been initiated + agreed upon in the senate.
Senate
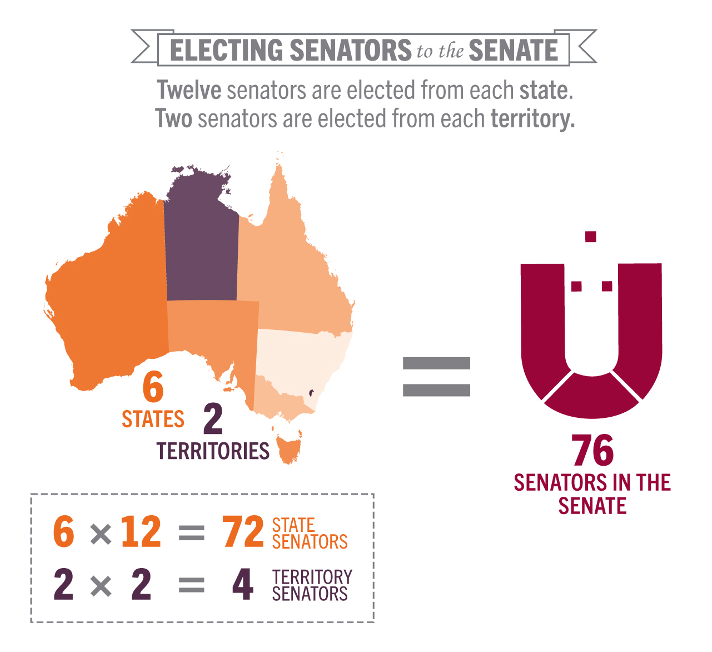
consists of 76 member
state elects 12 reps and each territory elects 2 reps
members hold office for a 6 year term, half of the members elected every 3 years
equal reps from each state
senate is decorate red
Sec 7 of the constitution states “The Senate shall be composed of senators for each State, directly chosen by the people of the State, voting, until the Parliament otherwise provides, as one electorate. The Senators will be chosen for a term of 6 years.”
Role of the Senate
House of review- bills initiated by house of reps, senates task is to review bills already passed through the lower
Act as the state’s house- sec 7 states this saying it should have equal rep from each state, regardless of size or population. In this way the senate represents the interests of the states in law-making
Scrutinise bills through the committee process- senate has a number of commitees and their role is to asses the legislative proposals to determine what effect the proposals would have individual rights, freedoms, obligations, rule of law
initiate and pass bills- senate is able to initiate bills (other than money), pass bills that hav been passed through HOR. They can pass it with, without ammendmenrs or reject it completely
Victoria Parliament
Role of the Legislative Assembly in law-making
Characteristics
Lowest House in Victoria
It consits of 88 members, they represent each electoral district throughout the state.
Members hold a 4-year term.
Roles
Goverment is formed in the legislative assembly
initiates and passes bills
provides a representative government
acts as a house of review
control gov spending
Role of the Legislative Council in law-making
Characteristics
consists of 40 members
elected from 8 regions w 5 from each region
term is 4 years
Roles
Acts as a house of review
Examine bills through its comittee
Initiate and pass bills
The Crown (Both Fed and State)
Role
grants royal assent: kings rep is required to provide royal assent. Giving approval of a bill before it goes into law
Witholding royal assent: Crowns rep has the power to withold royal assent. Its rare. Fed level, Aus Constitution has specified circumstances in which gov-gen can withold royal assent
Appoint Exec Council: the Crown's representative has the authority to appoint members to the Executive Council. comprises of the leader of the gov and senior ministers. role of this council is to give advice on gov matters as well as approve sec legislation