AP Bio Unit 6
Evidence that DNA is the Genetic Material (Scientific Contributions to DNA)
Frederick Griffith
Transformation principle—change in genotype and phenotype due to assimilation of external DNA by a cell
Experiment showed that living R bacteria transformed into deadly S bacteria by unknown heritable substance
Avery, McCarty, MacLeod
Discovered the transforming agent was DNA
Tested DNA, RNA and proteins in heat-killed pathogenic bacteria, only when DNA was destroyed did transformation not occur
Hershey and Chase
Proved DNA is the genetic material
Used bacteriophages found that when bacteriophage DNA entered hosts it affected the cells but the proteins did not
Edwin Chargaff
*Chargaff’s Rules
Ratios of Adenosine = Thymine and Guanine = Cytosine are THE SAME (pairs)
DNA composition varies between species
Rosalind Franklin
Provided images of the structure of DNA using X-ray crystallography
Provided measurements on chemistry of DNA
James Watson and Francis Crick
Discovered the double helix structure of DNA by building models of DNA confirming Franklin’s X-ray data and Chargaff’s rules
Discovered semiconservative model of DNA replication
DNA Structure
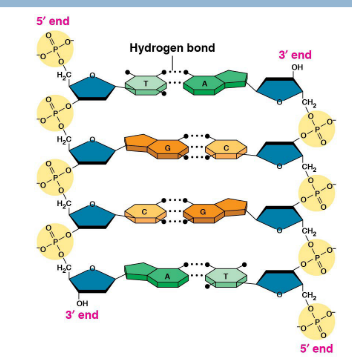
Double helix sugar (deoxyribose) + phosphate backbone
Phosphodiester bonds- bonds connecting phosphate group to sugar (Deoxyribose—DNA; Ribose—RNA)
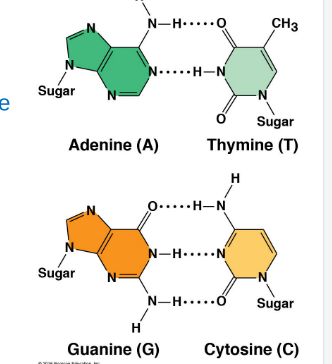
Nitrogenous bases rungs
Adenine—Thymine (2 hydrogen bonds)
Guanine—Cytosine (3 hydrogen bonds)
Adenine + Guanine are purines (larger); Thymine and Cytosine are pyrimidines (smaller)
Antiparallel strands
One strand (leading) runs from 5’ → 3’ (phosphate group on top)
Other strand (lagging) runs upside-down in the opposite 3’ → 5’ direction (phosphate group on the bottom)
Eukaryotic DNA | Prokaryotic DNA |
|
|
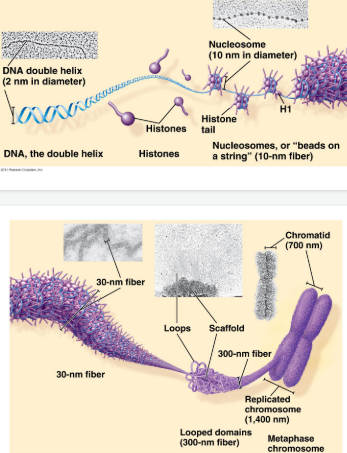
How DNA is packaged
DNA starts as a double-stranded molecule
DNA coils around histone proteins to form nucleosomes (like beads on a string)
Nucleosomes coil into chromatin structures
Chromatin further condensed into chromosomes during cell division
DNA Replication
Semiconservative model- Two strands of parental DNA separate with each serving as a template for synthesis of a new complementary strand

Steps of DNA Replication:
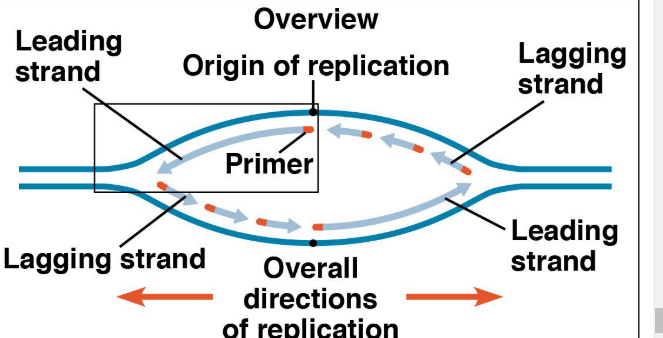
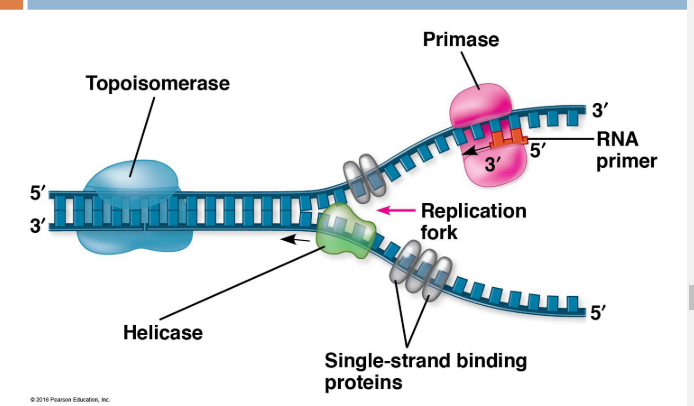
Helicase- unwinds DNA at the origins of replication (breaks Hydrogen bonds), creating a replication fork (binds AT replication fork)
Initiation proteins attach to DNA to separate them, creating a replication bubble
Single-strand binding proteins (SSBs) bind to unpaired DNA strands to prevent strands from re-pairing (prevents Hydrogen bonds)—binds after replication fork
Topoisomerase- Reduces/relieves strain caused by unwinding ahead of replication forks by breaking, swiveling, and rejoining parental DNA (breaks COVALANT bonds in DNA backbone)
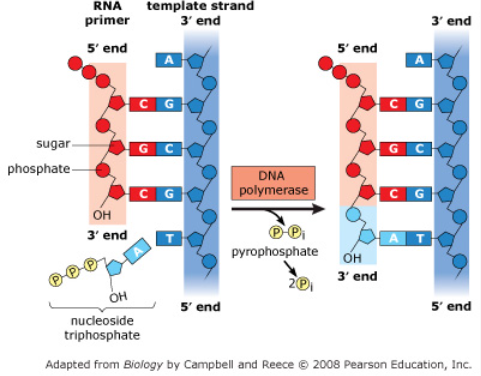
Primase synthesizes RNA primers (5-10 nucleotides long) to provide a starting point for replication of the new DNA strand (starts at 3’ end of RNA primer)
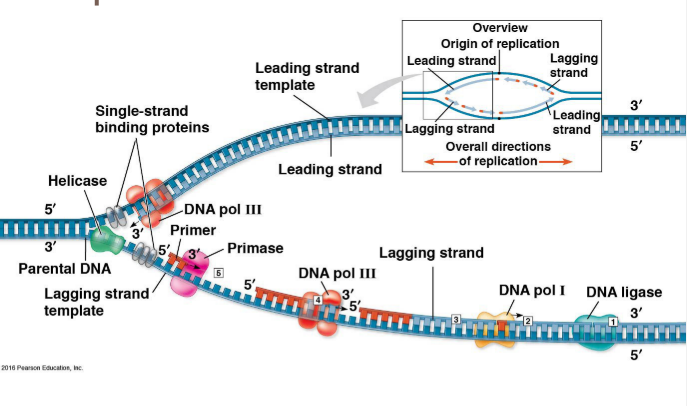
DNA polymerase III- Synthesize new DNA by adding complimentary bases to with the new DNA made in 5’ → 3’ direction for Primer (new bases added to the 3’ end)
Adds bases to the lagging strand with the addition of Okazaki fragments- short sections of DNA formed due to discontinuous synthesis of the lagging strand
*From the perspective of the DNA strand moves from the 3’ end towards the 5’ end;
Adds bases to the 3’ end of the PRIMER
Replication of leading strands moves TOWARDS the replication forks; Replication of lagging strand (Okazaki fragments) moves AWAY from replication forks
Order: Both leading strands synthesized first then each segment of lagging strand closest to the leading strand
DNA polymerase I- Replaces RNA primers (at the ends) with DNA nucleotides
DNA ligase- joins all Okazaki fragments into a continuous strand
Proofreading and Repair
DNA polymerases proofread each nucleotide against template, removing any incorrect nucleotides
Mismatch repair- other enzymes remove and replace incorrectly paired nucleotides from replication errors (evaded proofreading)
Nucleotide Excision Repair- Nucleases cut damaged DNA; DNA polymerase + ligase fill in missing nucleotides/gaps
Telomeres
Since DNA polymerase only adds nucleotides to the 3’ ends, no way to complete 5’ ends of the daughter strands → DNA strands grow shorter and shorter over many replications
Telomeres: Repeated units of short nucleotide sequences (TTAGGG) at the ENDS of DNA serve to “cap” the ends of DNA to postpone erosion of genes at the ends
Telomerase: Enzyme that lengthens/extends telomeres in eukaryotic germ cells to restore to their original length (not active in most somatic cells shows inappropriate activity in some cancer cells)
Gene Expression
Gene Expression- process by which DNA directs the synthesis of proteins/RNA
One gene-one RNA molecule (which can be translated into a polypeptide)
Flow of Genetic Information
Central dogma: DNA → RNA → Protein
Transcription- Process of transcribing DNA sequence into RNA (DNA → RNA)
Translation: Translation sequence of mRNA into amino acids during protein synthesis (RNA → proteins)
DNA | RNA |
|
|
Roles/Types of RNA
mRNA- carries code from DNA that specifies amino acids
tRNA- carries specific amino acid to ribosome based on its anticodon to mRNA codon
pre-mRNA- precursor to mRNA newly transcribed and not edited
rRNA- makes up 60% of the ribosome and the site of protein synthesis
ribozyme- RNA that functions enzymes
RNAi- interference RNA a regulatory molecule
srpRNA- signal recognition particle that binds to signal peptides
snRNA- small nuclear RNA part of a spliceosome has structural and catalytic roles
miRNA/siRNA- micro/small interfering RNA; binds to mRNA or DNA to block it for regulating gene expression/cutting it up
Genetic Code
One DNA strand (3’ → 5’) serves as the template strand
mRNA is complimentary to template (5’ → 3’)
mRNA codons/triplets code for amino acids (read in groups of 3)
ALWAYS starts with the start codon (AUG) and ends with 3 possible end codons (UAA, UAG, UGA)
Transcription steps
Transcription unit: Stretch of DNA that codes for a polypeptide or RNA (i.e. tRNA, rRNA)
RNA Polymerase
Separates DNA strands and transcribes mRNA
mRNA elongates in 5’ → 3’ direction
Attaches to promoter (start of gene) and stops at the terminator (end of gene)
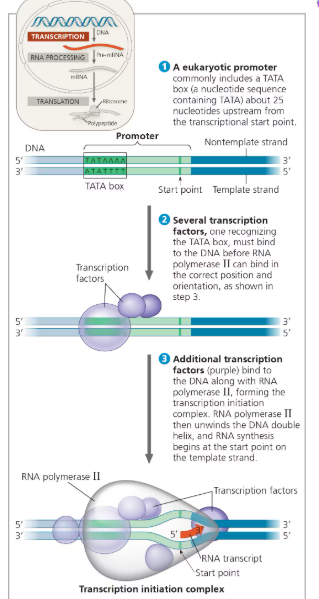
1. Initiation-
After RNA polymerase BINDS to the promoter, polymerase unwinds the DNA strands and initiates RNA synthesis at the start point of the template strand
Promoter- DNA sequence where RNA polymerase attaches and initiates transcription; in bacteria, the sequence signaling the end of transcription is the terminator
Transcription unit- the stretch of DNA downstream from the promoter that is transcribed into an RNA molecule
In Prokaryotes:
Bacteria: RNA polymerase binds DIRECTLY to promoter in DNA
Eukaryotes:
TATA box- DNA sequence (TATAAAA) in the promoter region upstream from transcription start site
Transcription factor recognize the TATA box before RNA polymerase binds to the DNA promoter
Transcription factors + RNA polymerase = transcription initiation complex
2. Elongation
RNA polymerase moves downstream, unwinding DNA and elongating the RNA transcript by adding RNA nucleotides to the 3’ end of the growing chain
After mRNA is made, DNA strands are retwisted to reform a helix
3. Termination
RNA polymerase transcribes a terminator sequence (prokaryotes) OR polyadenylation signal sequence (eukaryotes) then mRNA and polymerase detach
Becomes pre-mRNA for eukaryotes, and ready-to-use mRNA for prokaryotes
RNA transcription is released and polymerase detaches from DNA
RNA processing (Eukaryotes)
Alternations to pre-mRNA ends for eukaryotes after transcription
5’ cap (modified guanine nucleotide) and a 3’ poly-A tail (long string of adenine nucleotides) are added to pre-mRNA
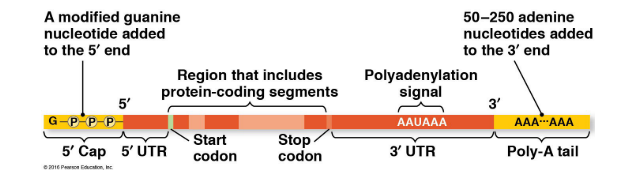
Functions:
1. Export from nucleus
2. protect mRNA from enzyme degradation
3. Attach mRNA to ribosomes
RNA Splicing:
Introns (noncoding sequences) are CUT OUT while exons (code for amino acids) are joined together
Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs) are made of snRNA + protein
snRNPs recognize splice sites and join with other proteins to form a spliceosome—catalyze the process of removing intros/joining exons
Ribozyme- RNA acts as enzyme (ribosomes are one big ribozyme)
Introns-
Serve to regulate gene activity
Alternative RNA Splicing- produce different combinations of exons
Translation
Takes place inside ribosomes
tRNA (transfer RNA)
Transcribed in the nucleus
Specific to each amino acid and transfers amino acids to ribosomes based on Anticodons- pairs with complementary mRNA codon
Wobble- base-pairing rules between THIRD base of codon and anticodon not as strict (different nucleotide for third codon can code same amino acid)
Anti-codon Calculations:
Anti codons are ANTIPARALLEL to the codon in the 3’ to 5’ direct → reverse pairing of codons
Aminoacyl-tRNA-synthetase- enzyme that binds tRNA to specific amino acid
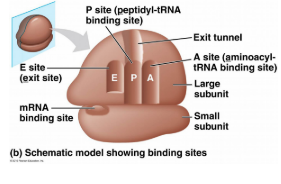
Ribosomes-
rRNA + proteins; Made in the nucleol; Comprised of 2 subunits
Actives Sites
A site: Holds the Amino Acid (AA) to be added
P site- Holds growing polypeptide chain
E site- Exit site for tRNA
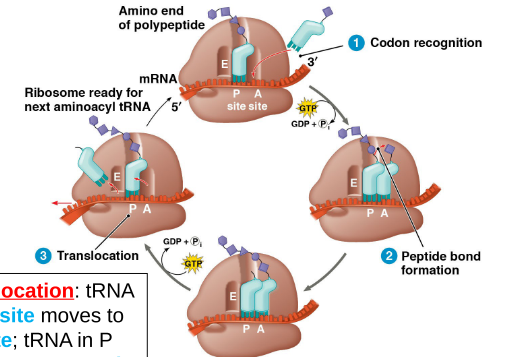
3 Steps of Translation (similar to transcription)
1. Initiation
Small ribosomal subunit binds to the start codon (AUG) on mRNA
tRNA carrying met (start amino acid)/initiator tRNA attaches to P site
Large ribosomal subunit attaches to the complex forming the Translation Initiation Complex
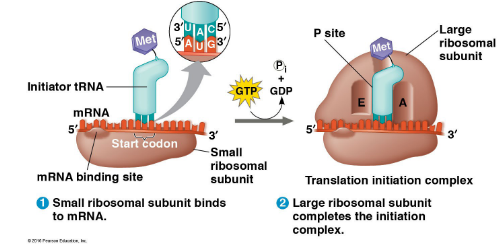
2. Elongation
Codon recognition- tRNA anticodon matches codon in A site
Peptide bond formation- Amino acids in A site bonds with peptide in P site
Translocation- tRNA in A site moves to P site while tRNA in P site moves to E site to exit (process of sliding down one codon on the mRNA)
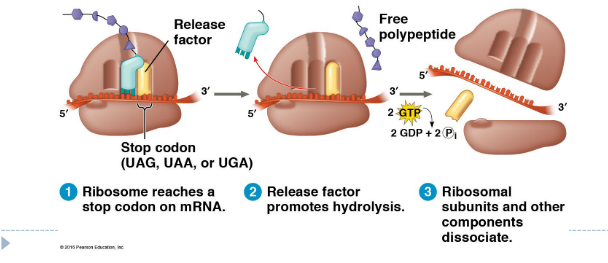
3. Termination
Stop codon reached to stop translation
Release factor binds to stop codon and polypeptide released
Ribosomal subunits dissociate
Protein Folding
During synthesis, polypeptide chain coils and folds spontaneously
Chaperonin: protein that helps polypeptide fold CORRECTLY
Post-Translational Modifications
Attaches sugars, lipids, phosphate groups, etc.
Remove amino acids from ends
Cut into several pieces
Subunits come together
Phosphorylation
Types of Ribosomes:
Free ribosomes: synthesize proteins that stay in cytosol and function there
Bound ribosomes (attached to ER) make proteins for secretion and proteins of the endomembrane system (nuclear envelope, ER, Golgi, lysosomes, vacuoles, plasma membrane)
Uses signal peptide- 20 amino acids at the leading end of polypeptide to determine location
Signal-recognition particle (SRP) brings the ribosome to the ER
Polyribosomes- a single mRNA can be translated by several ribosomes at the same time
Prokaryotes can transcribe + translate at the SAME TIME
Mutations:
Changes in the genetic material of a cell
Chromosomal mutations- large-scale, causes disorders or death
i.e. Nondisjunction (extra chromosomes), translocation, inversion, duplication, large deletions
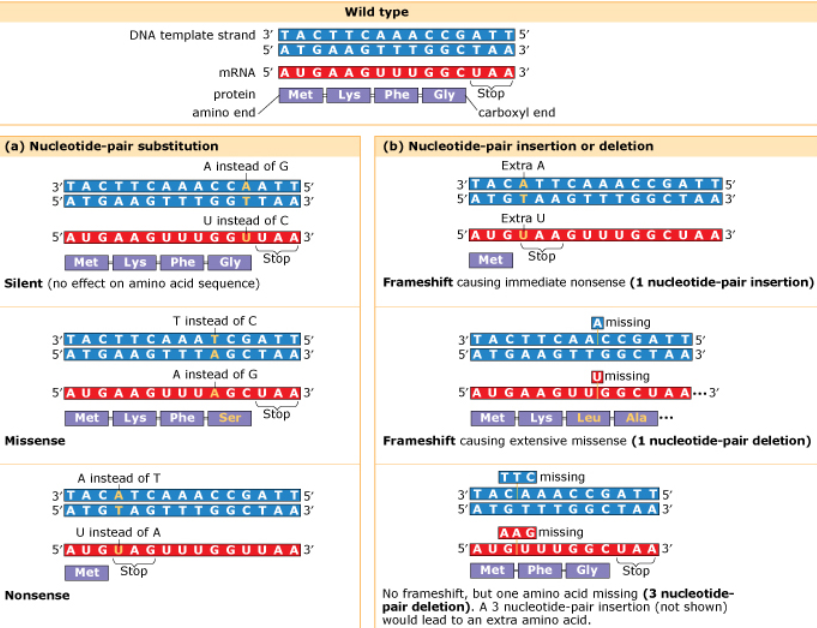
Point mutations- alter a single nucleotide pair of a gene
Substitution- replacing one with another
Silent- same amino acid (often when last codon is altered but still codes for same amino acid)
Missense- amino acid replaced by different amino acid
Nonsense- stop codon instead of amino acid
*Sickle cell disease is caused by a point mutation resulting in the VAL mutant protein instead of GLU
Frameshift (insertion/deletion)- mRNA read incorrectly leads to nonfunctional proteins
*The insertion or deletion of three nucleotide pairs does not cause a frameshift mutation; Insertion/deletion of one nucleotide causes frameshift
Mutagens- substances of forces that cause mutations in DNA (radiation, chemicals, infectious agents)
Prokaryotes | Eukaryotes |
Transcription and translation BOTH in cytoplasm DNA/RNA in cytoplasm RNA polymerase binds DIRECTLY to promoter Transcription makes mRNA directly No introns Can do both translation and transcription AT THE SAME TIME Do not have membrane bound organelles | Transcription- nucleus; Translation- cytoplasm (ribosomes) DNA in nucleus; RNA travels in/out of nucleus RNA polymerase binds to TATA box and transcription factors Transcription makes pre-mRNA → RNA processing → final mRNA Cuts out intros, joins exons Transcription/translation occurs separately |
Directionality:
DNA replication:
Leading 5’ → 3’; Lagging 3’ → 5’;
New DNA strands synthesized from 5’ → 3’ direction
RNA transcription
Template strand 3’ → 5’
Coding strand 5’ → 3’
mRNA 5’ → 3’
RNA translation
mRNA 5’ → 3’
tRNA anticodons 3’ → 5’
Practice Problems:
The -OH group on the 3' carbon of the sugar unit is the attachment site for the nitrogenous base. False
Complementary base pairing relies on the number of hydrogen bonds that each base can make. True
In a single nucleotide, the phosphate group is attached to the 5' carbon of the sugar unit. True
The antiparallel arrangement of double-stranded DNA is due to the phosphate group being bonded to the 3' carbon on one strand and the 5' carbon on the complementary strand. False
The phosphate attached to the 5' carbon of a given nucleotide links to the 3' -OH of the adjacent nucleotide. True
FRQ
Gibberellin is the primary plant hormone that promotes stem elongation. GA 3-beta-hydroxylase (GA3H) is the enzyme that catalyzes the reaction that converts a precursor of gibberellin to the active form of gibberellin. A mutation in the GA3H gene results in a short plant phenotype. When a pure-breeding tall plant is crossed with a pure-breeding short plant, all offspring in the F1 generation are tall. When the F1 plants are crossed with each other, 75 percent of the plants in the F2 generation are tall and 25 percent of the plants are short.
The wild-type allele encodes a GA3H enzyme with alanine (Ala), a nonpolar amino acid, at position 229. The mutant allele encodes a GA3H enzyme with a threonine (Thr), a polar amino acid, at position 229. Describe the effect of the mutation on the enzyme and provide reasoning to support how this mutation results in a short plant phenotype in homozygous recessive plants. (2 points)
This mutation that alters the amino acid from polar to nonpolar would alter the structure specifically the tertiary structure and thus the function of the protein thus could decrease or stop the production of gibbrellin resulting in short plants
wild type gene is dominant so in heterozygous the gene would be expressed still expressing prodcution of