C1
Atoms and Elements
Atoms
PEN
Atoms contain:
Protons- Relative Charge = +1 | Relative Mass = 1 | LOCATION = Nucleus
Neutrons - Charge = 0 | Relative mas = 1 | Location = Nucleus
Electrons- Charge = -1 | Mass = (negligible) | Location = Electron shells
Same amount of protons as electrons, only in ATOMS (different in ions)
Atomic number = Number of protons
Atomic Mass number = Number of protons and neutrons combined
Structure
The structure of an atom consists of:
The nucleus- A concentrated point at the centre of the atom of all its mass, protons, neutrons and positive charge.
The electrons- Shells that the electrons orbit the nucleus the volume of which determines the size of the atom, (mostly empty space), virtually no mass
Differentiations
Now of course there’s lots of different variations of atoms, this comes in the form of:
Ions- These are atoms the same number of protons different number of electrons.
Isotopes- Same number of protons different number of neutrons
Elements - A pure substance that is only made up of one type of atom
Compounds-A substance formed from two or more elements reacting
Allotropes - An element arranged in a different structure to give it different properties
Stats
Now for the annoying numbers:
Atoms have a radius of roughly 0.1 nanometres (1 × 10-10 m)
The nucleus has a radius of roughly 1 × 10-14 m, so 10,000 times smaller than the whole atom
Elements
Elements - A pure substance that is only made up of one type of atom
they have symbols blah blah blah
Isotopes
Isotopes- Elements with the same number of protons different number of neutrons
As a result of this they have a different relative atomic mass
however they still are the same element by principal
Relative atomic mass of an element therefore is calculated taking into account each isotopes abundancies
Compounds and equations
Compounds
Compounds-A substance formed from two or more elements reacting
Compounds are held together in fixed proportions
They are held together by chemical bond
These Bonds are made by the sharing or taking of an electron
These bonds are usually strong requiring chemical reactions to break
How thing react: Ionic bonds
An ionic bond is defined by- electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions arranges in a giant ionic lattice
A compound consisting of a metal and a non metal is an ionic compound
The metals lose electrons to form positive ions
and the non-metals gain electrons to form negative ions
These opposite charges are strongly attracted towards creating ionic bonds
How thing react: covalent bonds
A covalent bond is a bond formed when a pair of electrons is shared between two atoms
These bond usually take place between non-metals
Their compounds are usually totally different from the elements e.g. water is made of gasses
Symbols- The actual hard part
Ok so the thing is that compound symbols:
Have big numbers multiply the entire compound by that much
These big numbers represent the molar ratio
Small numbers only times one element in the compound by n
Small numbers next to the brackets multiply everything in the brackets by n
Oh yeah, and remember this for me lil nga:
Carbon dioxide → Co2
Ammonia → NH3
Water → H2O
Sodium chloride → NaCl
Carbon monoxide → CO
Hydrochloric acid → HCL
Calcium chloride- → CaCl2
Sodium chloride → Na2CO3
Sulfuric acid → H2SO2
Hydrogen → H2
Phosphoric acid → H2So4
Sulphate → SO4 (-2)
Nitrate → NO3 (-1)
phosphate →PO4(-3
Hydroxide → OH(-1)
Equations
Remember that you have to have the same amount if reactants as products
You can: Show chemical equations with words or symbols:
Words are so much easier, considering you don’t have to factor i- Oh wait you haven’t learned that yet L e.g:
Methane + oxygen → Carbon dioxide + water
Symbol equations:
These are the shorthand way if writing chemical equations using just their: Chemical symbols, Molar ratios, Ionic charge, Bonding configuration, oh no. e.g.
Magnesium + Oxygen → magnesium oxide
2M + O2 → 2MgO
Symbol equations must be balanced:
This is because as matter can neither be created nor destroyed, each element must be represented in equal amounts on both sides s both the products and the reactants.
When balancing an equation:
You must not Change the small numbers as that changes the away the elements are bonded
This means you can only change the large numbers and their molar ratio
Until there is the same amount of Products as reactants
This means that if there was 5 gold reactant atoms and 3 oxygen reactant atoms
There will be 5 gold product atoms, and 3 oxygen product atoms

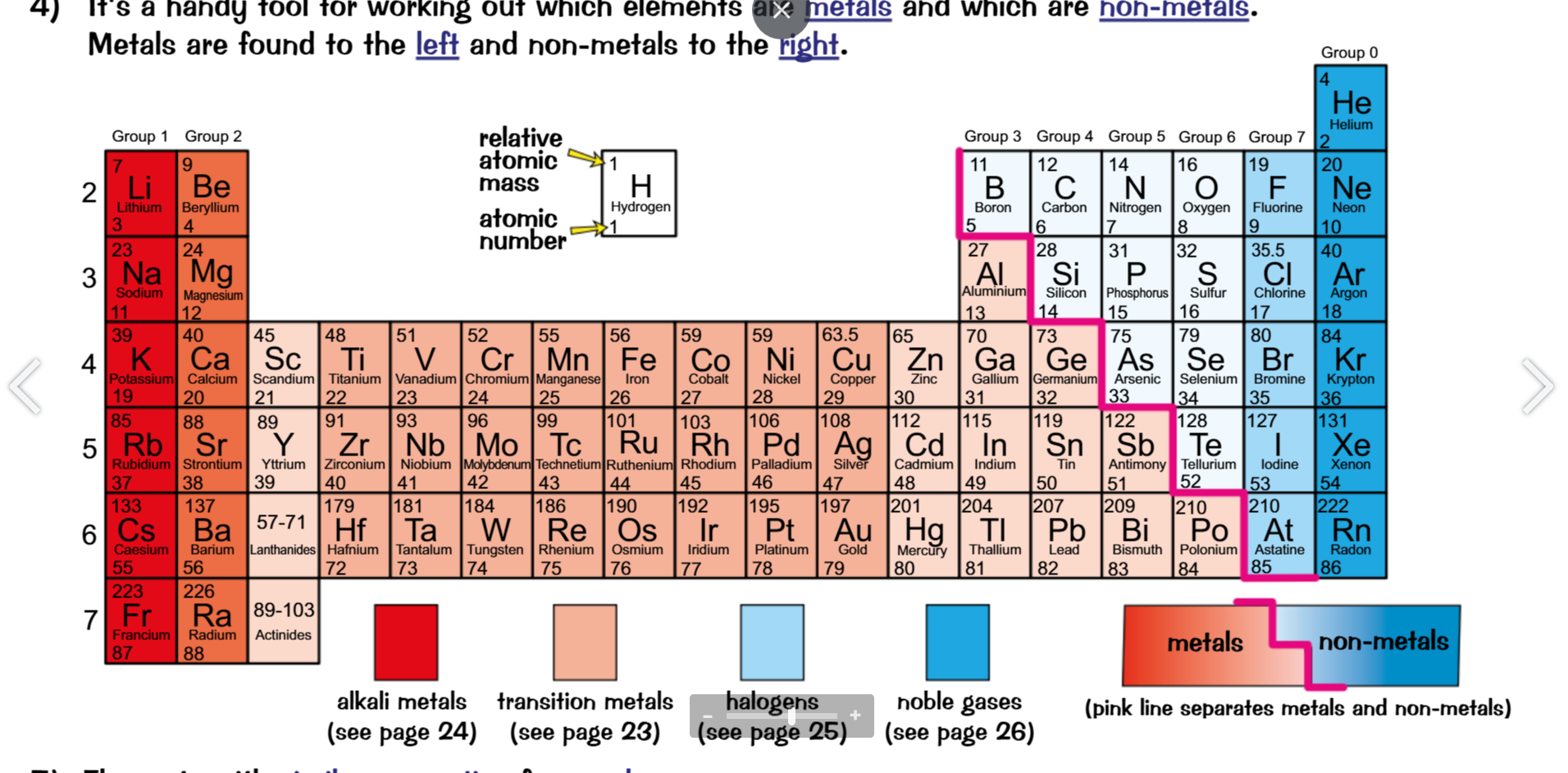
The modern periodic table
Order
The periodic table is ordered in multiple ways
in order of proton number, going across from left to right
Non- metals on the right, metals on the left
Vertical columns are groups (that’s on the y axis)
Each group has the same number of electrons on their outer most shell
The group number increases going from left to right
This corresponds with their overall group number
E.g. group 1 has 1 electron on its outermost shell etc.
Each row going across is a period
Each period has one more shell of electrons
The properties of these elements can be predicted based off of these factor
a
The rule of nuclear attraction
The further away electrons are from the nucleus the less attraction there is. This means on the outermost shell is the weakest nuclear attraction. For lower grouped elements this is a good thing because it means it makes it much easier to lose their electrons and gain a full outermost shell. Which is an application of this rule of nuclear attraction which happens in the inverse for high group elements
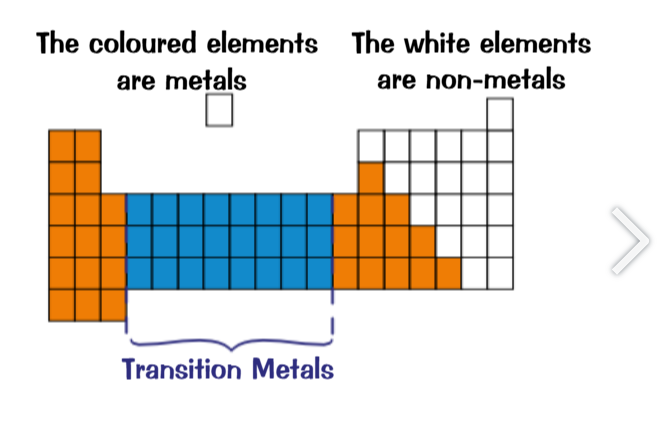
Metals and nonmetals
What are they?
Metals are elements which can form positive ions.
Most elements are metals
Non-metals don’t usually form positive ions
How things react
Atoms usually react in order to form a full outer shell
whether it be through gaining losing or sharing electrons
Mixtures and separation
A mixture is a combination 2 elements or compounds that are not chemical joined together
Solvent- a liquid that can dissolve certain solutions
Solute- a substance dissolved in a solvent
Solution- the mixture of the solvent and solute
Aqueous- The state a solute is in when it is dissolved in a solute
Soluble- can dissolve in solvent e.g. liquid
Insoluble- Something that can’t be dissolved by a substance
They can be separated by:
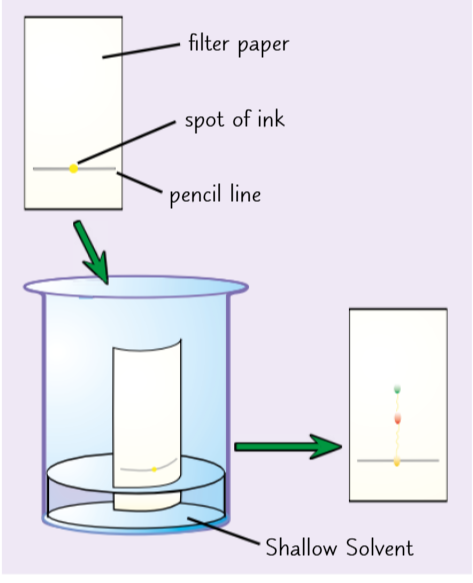
Chromatography
Draw a line near the bottom of the paper (as pencil marks are insoluble)
Add a spot of ink to the line
Place it in a beaker with a solvent (e.g. water or ethanol)
Make sure the ink isn’t touching the solvent
Place a lid on top of the container to stop it from evaporating
The water moves up the paper
Different dyes move at different rates so they will separate out as they move up
Take it out once the water has almost reached the top
And the finished result: A chromatogram
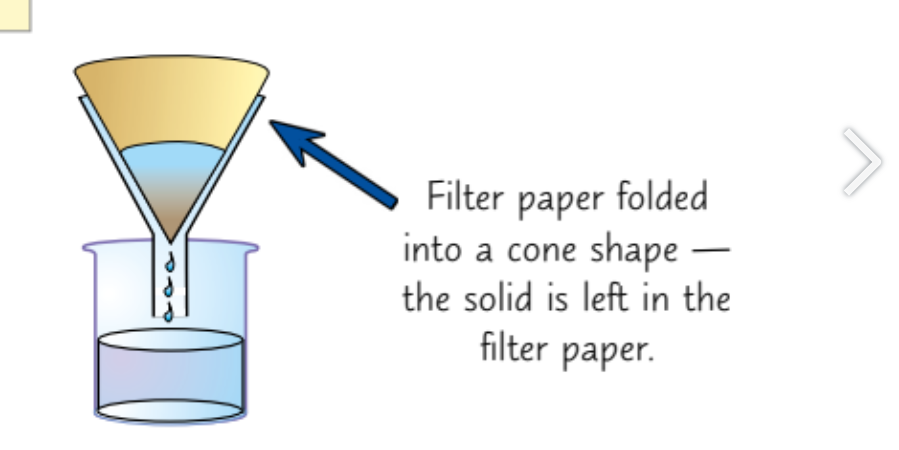
Filtration
Use this to filter and insoluble solvent from a liquid e.g. sand from water
Its done by using filter paper folded into a cone
Connecting it to a funnel
And placing a beaker under it
Evaporation e.g. (Salt and water)
Pour solution into evaporating dish
Heat slowly until the solution get concentrated enough to form crystals
Keep heating evaporating dish until all you have left are crystals
This can only be used when the salt doesn’t decompose when heated
Crystallisation e.g. (Salt and water)
Pour solution into evaporating dish
Heat slowly until the solution get concentrated enough to start forming crystals
Let the solution to cool down slowly, during this time the solution will form crystals
Filter out the crystals and let them dry in a warm place e.g. oven or desiccator
Filtration and crystallisation can be used to separate rock salt, a mixture of sand and salt
Grind the rock salt down
add water
Stir it
Filter it
Crystallise it
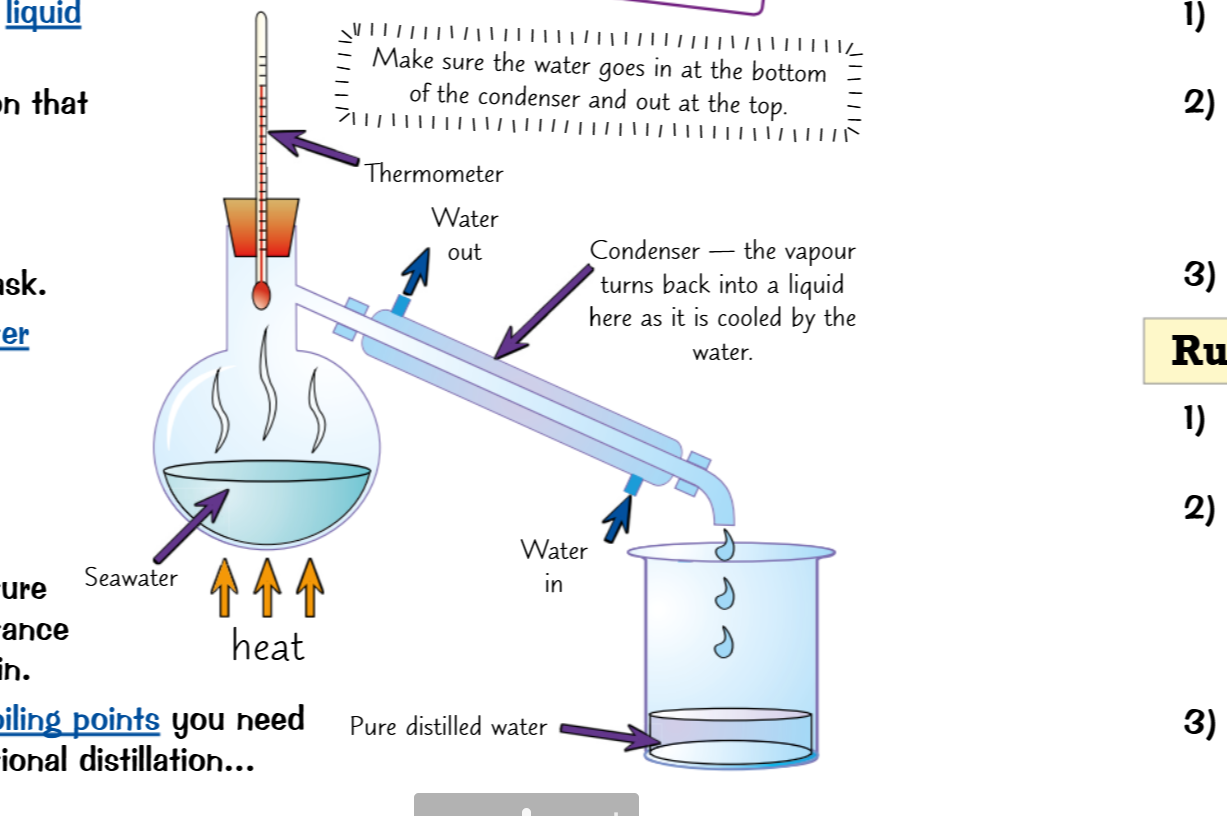
Simple distillation Distillation: 2 liquids (far boiling points)
The solution is heated at a particular heat,
The part with the lowest boiling point is heated first
It travels into a condensation tube
Where cold water flows through adjacent tubes to keep it cool
Then the condensed water is collected in a beaker next to the tube
This only works for liquids with a boiling points far away from each other
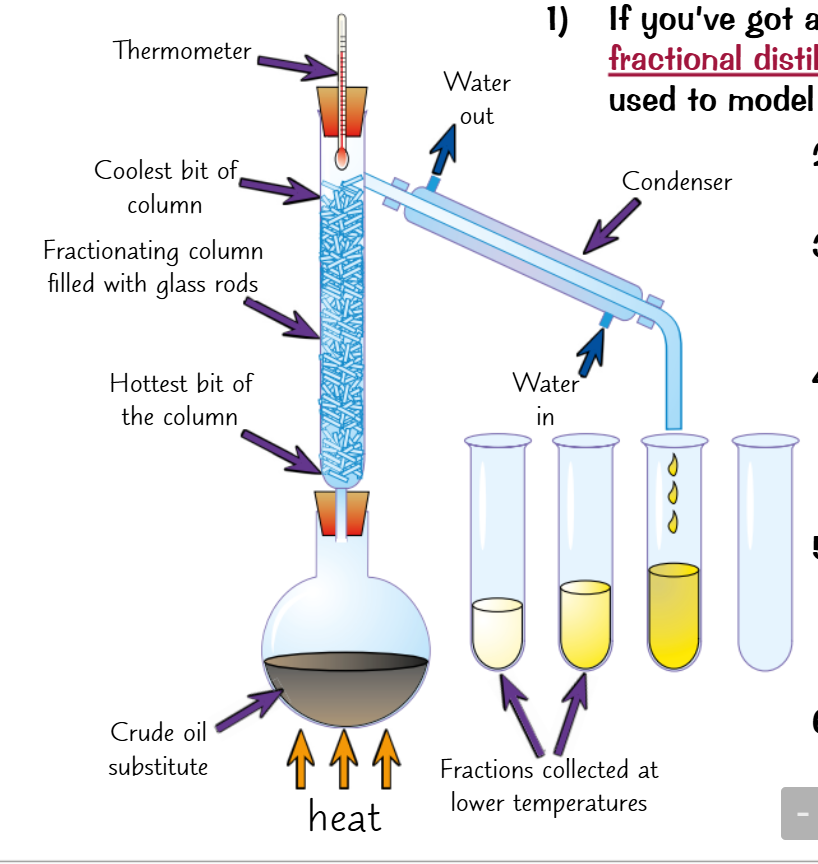
Fractional distillation: Close boiling points e.g. oil refinery
The only difference is a fractionating column
This is a bunch of convoluted tubed which slow gasses down
By the time the temperature reaches the lowest boiling point
the corresponding liquid will already be at the top
And whilst the other liquids may start rising
They will cool down before they reach the top
Ensuring only one substance distillates at a time