Unit 1 Multiple Choice Questions + Answers
Before You Begin:
Write your answers down on a piece of paper, and then check the answers + explanations when you’re done.
Groups of these questions have to do with a certain subtopic. I have public notes on each of these subtopics, so feel free to check those out for more help!
- Questions 1-15: The Constitution
- Questions 16-30: Federalism
- Questions 31-45: Theories of Democratic Government
Questions:
All of the following were weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation EXCEPT:
- the national government could not resolve state boundary disputes
- currency was not accepted outside of local areas
- the military could not put down even small rebellions
- the national government had too much power
- there was no judicial system
What was the result of the Great Compromise?
- states were represented in the upper house, and individuals were represented in the lower house.
- individuals were represented in the upper house, and state were represented in the lower house.
- individuals were given proportional representation in both the House of Representatives and the Senate.
- All members of Congress were selected by direct election
- Slaves were not counted in the census.
All of the following are part of the amendment process EXCEPT:
- a proposal accepted by a two-thirds vote of Congress
- a proposal accepted at a national convention called by Congress as requested by two-thirds of the states
- a national referendum (by popular vote) with two-thirds voter approval
- ratification by three-fourths of state legislatures
- ratification by three-fourths of states in special conventions
How does the Constitution provide an executive check on the judicial branch?
- By allowing the president to remove Supreme Court justices from office
- By permitting bureaucrats to ignore a decision of the Supreme Court
- By allowing the president to propose a bill to Congress to overturn a decision by the Supreme Court
- By allowing the president to nominate federal judges, subject to Senate confirmation
- By vesting in the president the sole power to select federal judges
How did the Antifederalists differ from the Federalists?
- The Antifederalists wanted a stronger central government.
- The Federalists wanted to protect state sovereignty.
- The Antifederalists had a more positive view of human nature.
- The Antifederalists believed that a strong central government would be too distant from the people.
- The Antifederalists were opposed to representative democracy.
Which of the following guarantees of individual liberties is found in the original Constitution?
- Freedom of speech, press, and assembly
- No official state religion
- A prohibition against double jeopardy
- No unreasonable searches and seizures
- No religious tests to hold office
Which of the following is NOT a criticism of separation of powers?
- It creates gridlock in policymaking.
- It makes it difficult for the government to act decisively in times of crisis.
- It results in prompt, but hasty, decision making.
- It makes it difficult to stimulate economic growth.
- It damages our position of international leadership.
What would be the impact of the line-item veto on the separation of powers?
- It would weaken the presidency and strengthen Congress.
- It would strengthen the presidency in relation to Congress.
- It would prevent the Supreme Court from using judicial review.
- It would strengthen the power of the states.
- It is not clear how the line-item veto would affect the separation of powers.
All of the following were arguments by the Federalists in support of the Constitution EXCEPT:
representative democracy would be preferable to direct democracy
a large republic would be preferable to a small republic
the new Constitution would eliminate factions
a diversity of interests would be represented in the new government
the majority interests would be less able to persecute minority interests
Which of the following statements best describes judicial review?
The Supreme Court may amend the Constitution.
The Supreme Court may nullify state laws if they provide more rights than are contained in the federal Bill of Rights.
The Supreme Court may remove state government officials who violate the Constitution.
The Supreme Court may recommend impeachment proceedings against the president.
The Supreme Court may nullify government acts that conflict with the Constitution
All of the following were features of the New Jersey plan EXCEPT:
equal representation in the national legislature
power to regulate interstate commerce vested in the national government
bicameral legislature
plural executive
executive elected by Congress
How can the president check the power of the other branches?
Dissolve Congress and call for new elections
Remove judges who commit serious crimes
Bypass Congress by submitting proposed Constitutional amendments to the states
Vetoing judicial decisions
Nominating federal judges
The Bill of Rights, as originally adopted in 1791, applied to:
both state and national governments
Congress and the president, but not the courts
only the national government
only the states
Congress only, but not the president and the courts
Under the original text of the Constitution, which of the following rights were protected?
Free speech
Right to a jury trial
Freedom of religion
Right to privacy
Prohibition of unreasonable searches and seizures
Which of the following institutions did the people have a right to elect under the Constitution as originally written?
President
House of Representatives
Senate
Judiciary
Bureaucracy
Which of the following is the best example of devolution?
The No Child Left Behind law, which provides states with monetary incentives for meeting national educational guidelines
The McCullouch v Maryland case, which allowed the federal government to maintain a national bank
Civil rights legislation mandating that states not discriminate
Block grants, by which money from the national government is given to the states for discretionary use with broad guidelines
The federal tax code, which provides deductions for local charities
The Founding Fathers devised a federal system for all of the following reasons EXCEPT:
Federalism is one method for checking government's power and protecting personal liberty
Concentrating power in a single entity might create tyranny.
Under the Articles of Confederation, the national government was too dependent on the states for survival
A federal system provides balance of power between the state and national governments
Federal systems were common throughout the world and were proven to be effective
Which of the following statements best describes the impact of the Tenth Amendment?
It has been effective in protecting and expanding the powers of the states.
It had little impact at first but has been expanded over time to protect state powers.
It has rarely had much practical significance.
The Supreme Court has interpreted it consistently over time.
It has protected the powers of the states, especially by significantly reducing federal mandates.
Which of the following Constitutional provisions has been interpreted as weakening the Tenth Amendment?
The full faith and credit clause
The supremacy clause
The Ninth Amendment
The necessary and proper clause
The extradition clause
The concept that the national government is supreme in its own sphere while the states are equally supreme in theirs is known as:
cooperative federalism
balanced federalism
home rule
emerging federalism
dual federalism
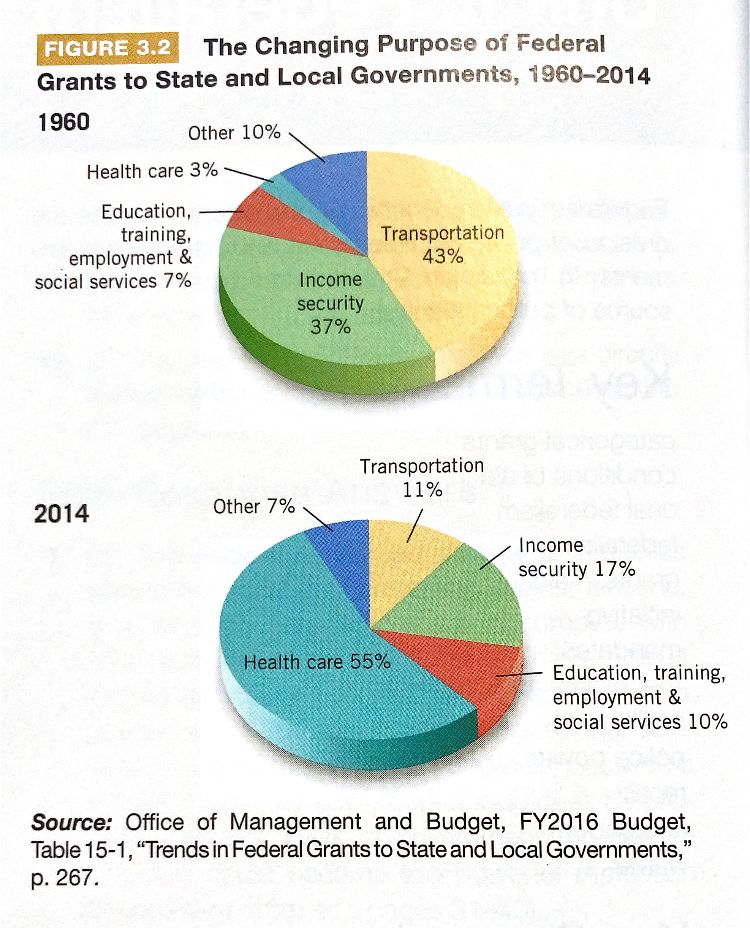
The graph above supports which of the following conclusions?
The amount of federal grant money given to states more than doubled between 1960 and 2014.
The category in which federal grant money increased the most from 1960 until 2014 is health.
Because the interstate highway system was built by 2014, spending on transportation dropped.
Most of the money given to states for education and training comes in the form of block grants.
Devolution has taken place for all categories of federal grants.
States have found federal funding attractive for all of the following reasons EXCEPT:
in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, the national government had surplus money to spend on the states
in the late 20th century, the income tax provided a flexible source of federal grant money
the federal government can print money when it is needed to fund programs
federal grants rarely come with strings attached
state politicians can get federal money without having to take the unpopular political position of supporting expanding government
Why do states prefer block grants to categorical grants?
Categorical grants require the states to spend matching funds.
Block grants allow states to spend funds on any governmental purpose.
Categorical grants are often rescinded.
The amounts given in block grants are stable from year to year.
Block grants allow local officials to satisfy the needs of interest groups.
Suppose the state of Nevada receives federal money to renovate McCarran International Airport. The money must be used for this purpose and there are additional requirements that must be met by Nevada. What term best describes this?
A categorical grant
A formula grant
A block grant
A condition of aid
A mandate

The table above supports which of the following conclusions?
Most federal grant money goes to support infrastructure, such as roads and bridges.
States spend very little of their own money on health care.
Federal grants for Medicaid are more than double the spending on any other program.
States with a high percentage of poor citizens are more likely to receive federal grant money.
Federal grant money is distributed unevenly, with a few states receiving the bulk of the funds.
What is the significance of United States v Lopez and United States v Morrison?
There is a limit to the power of the national government to claim "interstate commerce" as a justification for a policy.
The fundamental supremacy of the national government was upheld.
Congress may use the commerce clause as a justification for the expansion of national power if it demonstrates a "compelling government interest."
States are prohibited from interfering in a primary function of the national government.
The doctrine of "dual sovereignty" is fundamentally enshrined in the original text of the United States Constitution.
Federalism has what impact on the cost of political participation?
It tends to increase the cost of political participation at the national level.
It tends to increase the cost of political participation for large groups.
It tends to lower the cost of political participation for most all groups.
It tends to lower the cost of political participation for minority groups only
It tends to increase the cost of political participation at the state level.
Under the United States Constitution, cities and other municipalities are:
protected by the Ninth Amendment and the Tenth Amendment
creatures of the states
created by the national government and subject to its direct control
sovereign creations of the people
accountable only to their residents
Which of the following is the best example of an intergovernmental lobby?
The mayor of New York City filing a law- suit challenging the constitutionality of a national law.
The governor of Oklahoma negotiating with the governor of Arkansas an interstate compact regulating the water usage on the Arkansas River.
The mayor of Philadelphia arguing before a congressional committee for increased fund- ing for transportation.
The secretary of education encouraging Congress to increase funding for afterschool programs.
The president of the United States delivering his state of the union message to Congress.
Which of the following is most clearly a condition of aid?
The Supreme Court ordering school desegregation.
Congress requiring the Defense Department to purchase a new weapons system.
The president issuing an executive order establishing affirmative action in the awarding of government contracts.
Congress requiring states to set their drinking age at 21 in exchange for highway funding
The Food and Drug Administration prohibiting the sale of untested drugs
All of the following statements about the beliefs of the framers of the Constitution are true EXCEPT:
They favored representative democracy over direct democracy.
They believed that most citizens did not have the time, information, and expertise to make informed choices.
They believed that government decisions should mirror popular viewpoints.
They recognized that representative democracy would proceed slowly.
They insisted on the protection of civil rights and civil liberties.
Which of the following statements best represents the pluralist view of politics?
The class that dominates the economy also controls the government
The most important policies are set by a loose coalition of three groups: corporate leaderstop military officers, and key political leaders.
Leaders outside of the government structure dominate government.
Unelected bureaucrats who run agencies dominate the government.
There are so many groups that none of them can dominate the political process.
Which of the following views holds that public policy is heavily influenced by morally impassioned elites?
Pluralist view
Marxist view
Creedal passion view
Elitist view
Bureaucratic view
What is one of the best barometers for measuring changes in who governs?
A public opinion poll
An analysis of the topics covered in campaign speeches
An examination of the amount of coverage given by the media
An analysis of the policy process and changes in the laws
There is no real way of measuring political change
What is the most basic definition of democracy?
Rule by the many
Rule by representatives who are directly elected
Any system of government with elections
Any system of government with a written constitution
Any system where citizenship is widely extended by most adults
Multiple policymaking institutions impact daily life in the United States. According to the bureaucratic view of governmentwho holds most of the power in the American government?
Congress, because it makes laws that are then translated into regulations by the bureaucracy
State governments, because they make most of the rules that impact a citizen's daily life
Appointed officials and career government workers because they translate public laws into administrative actions.
No one, because our government is so tangled in red tape it is difficult to determine who holds power.
The courts because they make policy and are unelected and serve for life
What best explains the legitimacy of the United States government?
The government has been in existence for more than 200 years.
Elections are frequent, and their outcome is rarely in doubt.
Citizens may use the initiative process to change the law.
The Constitution is widely accepted as the source of authority
All citizens have the right to vote and hold office
Some argue that the government is dominated by business owners. Which of the following terms does this best describe?
Power elite view
Class view
Pluralism
Bureaucratic view
Prestige view
All of the following are arguments against direct democracy EXCEPT:
most people are not interested in government or politics
it is impractical because of limited time, information, and energy
most people do not have enough expertise to make good decisions on complicated policies
direct democracy leads to bad decisions because people act according to their passions
people might fall under the influence of charismatic speakers
Some argue that appointed officials actually run the government, despite the efforts of elected officials to control them. This belief is consistent with which theory of government?
Bureaucratic view
Pluralism
Class view
Indirect democracy
Power elite view
Which view of government would hold that public policy is the product of the clash of special interests?
Bureaucratic
Class
Elitist
Pluralist
Creedal passion
Which of the following is true of the political agenda?
It is controlled exclusively by the political elite.
It is composed of issues of concern to citizens.
The Constitution restricts its consideration during wartime.
Presidents use it to manage the states.
It is set at the national conventions of the two major political parties.
Making appeals to large segments of society is an example of:
general politics
majoritarian politics
distributed politics
interest-group politics
client politics
Entrepreneurial politics is characterized by:
distributed benefits, concentrated costs
concentrated benefits distributed costs
limited benefits, concentrated costs
limited benefits, limited costs
concentrated benefits, limited costs
The primary source of legitimacy in the United States political system is derived from:
state constitutions
the U.S Constitution
popularity
the Bible
congressional acts
Answers with Explanations:
- D. Most of the power under the Articles of Confederation was given to the states.
- A. The House of Representatives is proportional and elected directly, and there are two senators per state .Senators were originally chosen by state legislators; they are now chosen by direct election
- C. A proposed amendment must receive a thirds vote in Congress or in a specially held national convention. It must then be approved by a three- fourths vote in state legislatures or through special state ratifying conventions.
- D. The president nominates federal judges. Judges must be confirmed by the Senate.
- D. The Antifederalists argued that a strong national government would be too distant from the people and would take away powers that belong to the states.
- E. Under the original Constitution, there may be no religious qualification or test to hold office. The rest of the protections are contained in the Bill of Rights.
- C. Separation of powers results in slow and deliberate decision making. This can make it difficult to act quickly regarding foreign affairs, crises, and the economy.
- B. The line-item veto would strengthen the president by allowing him to veto a part of a bill. The president does not have line-item veto power
- C. The Founders argued in favor of representative democracy and large republics. While they did not believe the Constitution would eliminate factions, they believed that it was structured to control the "mischiefs of faction".
- E. Judicial review is the Supreme Court's power to interpret the Constitution and nullify state and federal laws that conflict with it.
- C. The New Jersey plan only called for minor amendments to the Articles of Confederation. The plan retained the idea of equal representation in a unicameral legislature.
- E. The president has the power to nominate federal judges with the "advice and consent of the Senate".
- C. The Bill of Rights was only intended to restrict the actions of the national government. States were restricted by their bills of rights. Only later, through the process of selected incorporation, did the Bill of Rights become binding upon the states and even then not in its entirety.
- B. The right to a jury trial in criminal cases is protected in the original text of the Constitution. It is augmented by the Sixth Amendment.
- B. Only the House of Representatives was directly elected by the people.
- (D) Devolution is an effort by the national government to return some powers to the states. Block grants, which allow states to spend federal money using some discretion, are an example of devolution
- (E) Federal systems were uncommon when the Constitution was written and they are relatively rare today. There are only 11 countries with federal systems
- (C) The Supreme Court has tried to interpret the Tenth Amendment as giving the states certain powers beyond the reach of the federal government, but there is a pattern of contradictory decisions by the Supreme Court over time. As a result, the Tenth Amendment has rarely had much practical significance
- (D) The necessary and proper clause, also known as the elastic clause gives to the national government any power important for carrying out its expressed powers. As a result the power of the national government was expanded relative to state power
- (E) Dual federalism is the idea that the national and state governments are supreme in their own respective spheres. This has been replaced with cooperative federalism, with each level of government sharing overlapping powers
- (B) In 1960, about 3 percent of federal grants to state and local governments were for health care. In 2014, heath care accounted for 55 percent of all federal grants to the states
- (D) While federal funding has historically provided states with significant resources it often comes with provisions regarding how the money must be spent
- (B) Block grants allow states to spend federal money on any governmental purpose, although lately, they are coming with more strings attached categorical grants require the states to spend the money on a specific purpose, like building an air- port
- A. Categorical grants are used by states for specific purposes, like building an airport.
- (C) Grant money for Medicaid which provides health care for the poor, amounts to $276.2 billion. This is more than double the $116.4 billion spent on income security programs and more than triple the amount spent on other programs
- (A) From the 1930s until the 1990s the Supreme Court allowed Congress to use the commerce clause as a justification for increased national power. United States v. Lopez and United States v Morrison signaled an end to this policy
- (C) Federalism tends to decrease the cost of political participation because it decentralizes the decision making in policy areas to the states
- B) Cities and towns are entirely creatures of the states. They derive their legal authority from the state and are subject to its regulation (American Government, 15th ed., page 62).
- C) Intergovernment lobbying is when state and local officials pressure the national government for increased resources and favorable policy. There has been an increase in intergovernmental lobbying since the New Deal. However, the success of these efforts has been limited since the 1980s
- D) A condition of aid is a requirement imposed on the states by the national government as a prerequisite to the distribution of funding. In the 1980s the national government required states to raise their drinking age to 21 or be subject to a reduction in highway funding
- (C) The framers believed that government should mediate, not mirror, popular views
- (E) Pluralism is the belief that competition among all affected interests shapes public policy
- The creedal passion view, advanced by political scientist Samuel Huntington posits that political change is the product of those who act with a moral passion to reform. He offers as examples leaders of the American Revolution and American Civil Rights movement
- (D) One of the best barometers of changes in who governs is the policymaking process
- (A) Aristotle's basic definition of democracy is "rule of the many"
- (C) The bureaucratic view is that the government is dominated by appointed officials who have a significant amount of power to make policy. The bureaucracy will typically publish over 3,000 rules per year.
- (D) The Constitution today is widely accepted as a source of legitimate authority
- (B) The class view emphasizes the power in government of the rich or of multinational corporations. This view is inspired by the philosophy of Karl Marx. It is similar to the elite view. However, the elite view encompasses other elites such as military officials, labor union officials, and the leaders of other large special-interest groups
- (A) Those opposed to direct democracy argue that citizens are limited by time, information, energy, and expertise and might fall under the influence of fleeting passions or demagogues
- (A) The bureaucratic view first set forth by Max Weber, contends that in modern states appointed bureaucrats manage complex government affairs and actually make policy
- (D) Political scientist David Truman believed that politics resources were held by so many people that no single group can control policymaking. As such in the pluralist view public policy is the product of the interaction and competition of various interests in a political system
- (B) The political agenda are those issues that citizens believe should be addressed by govern- mental action
- (B) Majoritarian politics involves convincing large segments of society that an issue or cause is worthy of support
- (A) Entrepreneurial politics are described to be in play when a large segment of society benefits from a policy, but the costs are borne by a much smaller segment of society
- (B) The US Constitution is the source of legitimate political power in the United States as it draws its authority from the people