Resonance
Definition
Resonance is a phenomenon that occurs when an object or system is driven at its natural frequency, resulting in an increase in amplitude of oscillation.
Example of Using a Swing
A swing has a natural frequency based on its length and the force of gravity.
When you push the swing at this natural frequency, each push aligns with the swing's natural movements, adding energy efficiently.
This synchronization leads to larger and larger swings, demonstrating resonance.
If you push the swing at a different frequency, the energy transfer is less effective, resulting in smaller swings and less amplitude.
Resonance Curve
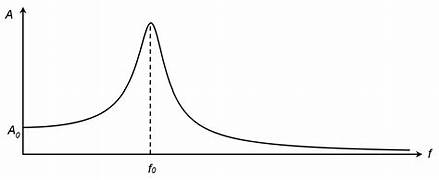
f0 = resonance frequency
Adding energy to a system
Effects of damping on a Resonance Curve
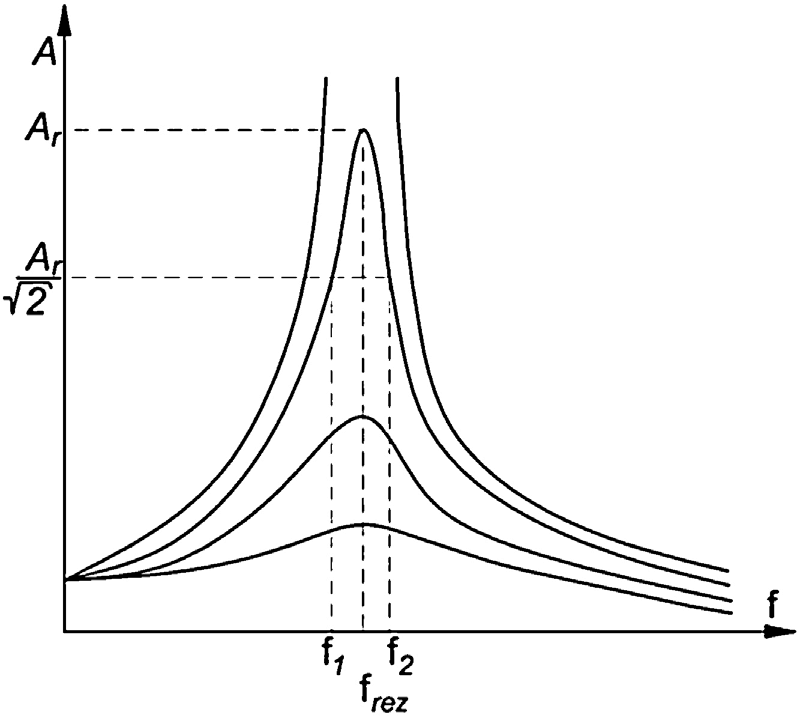
Comes in front, frequency decreases
Resonance energy decreases
Peak becomes less defined
Uses of Resonance
1. Microwave Ovens
Use: Resonance is used to heat food by exciting water molecules.
Example: Microwaves resonate with water molecules, causing them to vibrate and generate heat.
2. Communication Systems
Use: Resonance is used in radio, television, and mobile communication to select specific frequencies.
Example: Radio tuners use resonance circuits to filter and amplify signals at desired frequencies.
3. Sensors and Detection
Use: Resonance increases sensitivity in sensors.
Example: Quartz crystal microbalances use resonance to measure mass changes on their surface with high precision.
4. Energy Harvesting
Use: Resonance can capture and utilize ambient energy.
Example: Piezoelectric materials resonate to convert vibrations into electrical energy for powering small devices.
Problems with Resonance
1. Structural Damage
Problem: Resonance in structures can amplify vibrations, leading to catastrophic failure.
Example: The collapse of the Tacoma Narrows Bridge in 1940 occurred due to wind-induced resonance that caused excessive oscillations.
2. Mechanical Fatigue
Problem: Machinery components subjected to resonant vibrations can experience fatigue and eventually fail.
Example: A poorly designed engine mount can resonate at the engine's operating frequency, causing bolts or welds to weaken over time.
3. Damage to Electronics
Problem: Resonance in electronic circuits can lead to overheating or malfunction.
Example: Resonance in an electrical transformer can cause voltage spikes, damaging equipment connected to the system.
4. Aviation and Spacecraft Issues
Problem: Resonance can cause destructive oscillations in aircraft or spacecraft.
Example: Resonant frequencies in an aircraft wing can lead to dangerous fluttering and possible structural failure.
5. Hearing Damage
Problem: Acoustic resonance can amplify sound to harmful levels.
Example: Standing near a large speaker producing sound at a resonant frequency can damage hearing.
 Knowt
Knowt