WORLD HISTORY 8 REVIEWER
LESSON 1: 5 THEMES OF GEOGRAPHY
LOCATION: place or position of a certain thing
Absolute - exact location
Relative - location using nearby land/waterforms
PLACE: physical features of a place, its landforms, climate, and resources
HUMAN-ENVIRONMENT INTERACTION: man’s contact with his environment
dependence to environment (relying, tied)
adaptation to environment (adapting, getting used to)
modification to environment (modifying, changing)
MOVEMENT: movement of someone or something from one place to another
(Immigration: leaving, Emigration: entering)
movement of goods/products
movement of migration
movement of ideas
REGION: group of places with at least one common characteristic
LESSON 2: IMAGINARY LINES
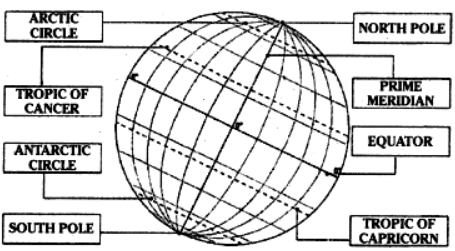
ARCTIC CIRCLE: line around the frigid zone
NORTHERN POLE: very top of globe
SOUTHERN POLE: very bottom of globe
PRIME MERIDIAN: VERTICAL line that separates east and west (GREENWICH OBSERVATORY)
EQUATOR: HORIZONTAL line that separates north and south
LONGITUDE: VERTICAL LINES
LATITUDE: HORIZONTAL LINES
GRID: network of latitudes and longitudes
TROPIC OF CANCER: line above the tropical zone (north)
TROPIC OF CAPRICORN: line below the tropical zone (south)
NORTHERN HEMISPHERE: top half of the globe
SOUTHERN HEMISPHERE: bottom half of the globe
EASTERN HEMISPHERE: right half of the globe
WESTERN HEMISPHERE: left half of the globe
LESSON 3: LANDFORMS AND WATERFORMS
> LANDFORMS
Mountains: high landforms above 1k ft.
Hills: low landforms below 1k ft.
Deserts: desolate land, little water
Loess: muddy or clay deposits of slits
Plateau: high landform, flat top
Plains: flat areas made from eroded soils from hills/mountains
Islands: land fully surrounded by water
Valleys: low areas of land between mountains or hills
> WATERFORMS
Oceans: biggest form, 71% of the Earth
Sea: almost surrounded by land
Glaciers: slow moving bodies of ice
Strait: between land, narrow
Lake: fully surrounded by land
Cove: small sheltered inlets
Bay: semi-circle shape along the shore
Waterfall: falling from a river or stream from elevated lands
Gulf: large bay
Rivers: natural flowing stream of freshwater
LESSON 4: RENEWABLE AND NONRENEWABLE RESOURCES
> RENEWABLE - are physical or biotic resources, can be replaced
forest
fish
water products
agricultural products
> NONRENEWABLE - limited amount
fossil fuels (REMAINS OF PLANTS AND ANIMALS)
coal
oil
natural gas
iron, copper, aluminum, uranium, gold (IMPORTANT MINERALS)
> BIOTIC: living
> ABIOTIC: nonliving
LESSON 5: CLIMATE ZONES
> Aristotle was the first to come up with climate zones
Low: hottest, near equator
Medium: warm, in temperate zone
High: coldest, in frigid/polar zone
> TEMPERATE ZONE: middle latitude, perfect temperature with seasons
> POLAR/FRIGID ZONE: high latitude, near poles, coldest (north: subarctic, south: subantarctic)
> TORRID/TROPICAL ZONE: low latitude, hottest, near equator (includes SUBTROPICS)
> SUMMER SOLSTICE: sun passes farthest north, JUNE 22
> WINTER SOLSTICE: sun passes farthest south, DEC 22
> EQUINOX: sun crosses equator, day and night are equal length almost everywhere on Earth, MAR 21, SEPT 23
LESSON 6: CONTINENTS OF THE WORLD
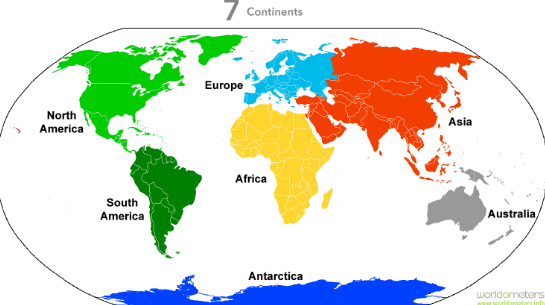
NORTH AMERICA: top left (has all biomes, 3rd largest)
SOUTH AMERICA: bottom left (4th largest)
EUROPE: middle top (2nd smallest, no desert biome, EURASIA)
AFRICA: middle bottom (54 countries, 2nd largest)
ASIA: top right (1st largest, most people living there)
AUSTRALIA: bottom right (smallest, includes islands in the Pacific)
ANTARCTICA: very bottom (least populated, covered in ice/TUNDRA)
LESSON 7: HUMAN GEOGRAPHY
the study of populations
demography is a special focus (birth, marriage, migration, death)
> PEOPLE AND ENVIRONMENT:
Population Density: number of people living per km²/m²
Population Growth: effects: famine, disease, natural resource depletion
> CULTURE:
Material: objects/things that people created
Non-Material: ideas of people, religion, language, beliefs, patterns of behavior
> LANGUAGE: cornerstone of culture
> RELIGION: important feature of a culture. Helps answering basic questions about the meaning and purpose of life
Buddhism: (Buddha, Sacred texts, Nirvana, eliminating worldly things)
Christianity: (God, Jesus Christ, Bible, There is only one God)
Hinduism: (Brahma, Vishnu and Shiva, Sacred texts, rebirth)
Islam: (God(Allah), Muhammad, Qur’an, Five Pillars)
Judaism: (God(Yahweh), Abraham, Hebrew Bible, Torah)
Confucianism: (Confucius, Analects, Five Classics, Social Order)
> CUSTOMS AND TRADITIONS: rules of behavior (wearing clothes, eating, how to be polite)
> RACE AND ETHNIC GROUP: race refers to a group of people who share similar and distinct physical characteristics
CAUCASIAN: Europe, North Africa, Eastern Africa, Western Asia, Central Asia, South Asia
MONGOLOID: Eastern Asia, Southeast Asia, Arctic region of North America
NEGROID: Central Africa, Southern Africa
AUSTROLOID: Aborigines of Australia
 Knowt
Knowt