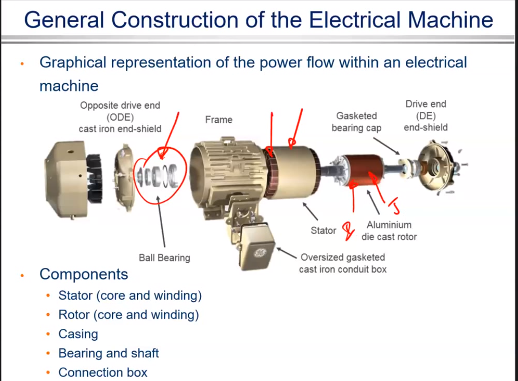
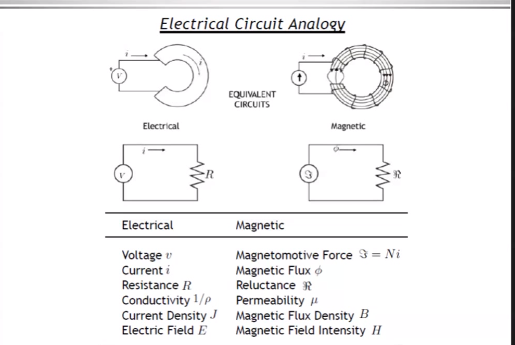
Electromagnetics Principles and Rules in electric machines
Right Hand rule
Rather than having a straight conductor we have coils, If we apply same principle there will be flux like this:
The dashed lines represent the magnetic flux
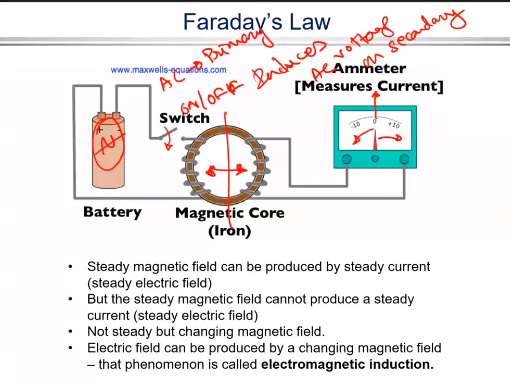
Faraday’s Law
A steady magnetic field can be produced by steady current
But the steady magnetic field cannot produce a steady current
However if the switch was constantly turned on and off there is a rate of change of flux which induces a voltage then hence a current
If the battery was changed into an AC source and the primary and secondary are not physically connected
The Primary AC Inducts an AC Voltage in the secondary.
Lenz Law
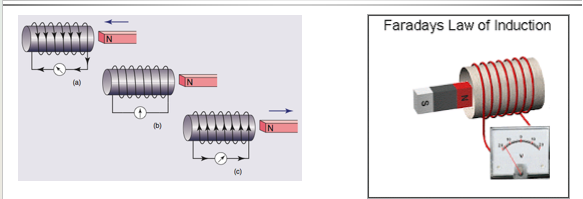
Instead of using a power supply Lenz used a magnet
A permanent magnet
He moved the permanent magnet in and out of the coil which induces a current in such a direction that the field will oppose the change of the magnetic field(produced by magnet)
The induced current wants to oppose the change in the magnetic field and that is called Lenz’s law

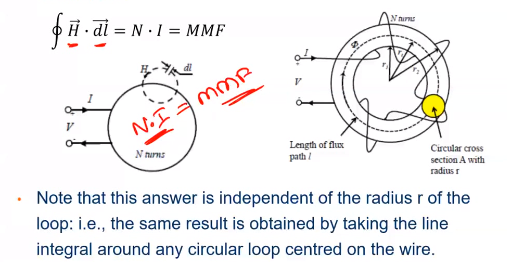
Ampere’s Law
For the average Path at the mean radius r , the magnitude field intensity H is related to its source N * I by ampere’s circuital law.
Magnetic Flux density
Magnetic flux phenomena
Fringing
Air Gap Fringing
The flux across an air gap will not be confined to the surface area of the iron core
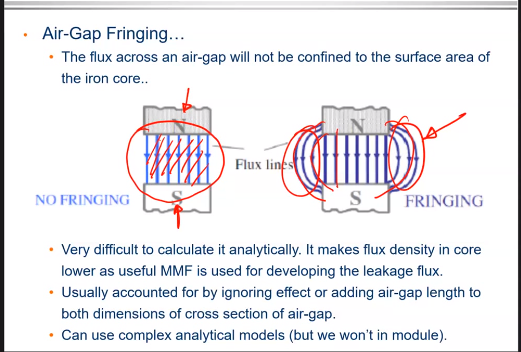
We can quantify the left region but not right (image)
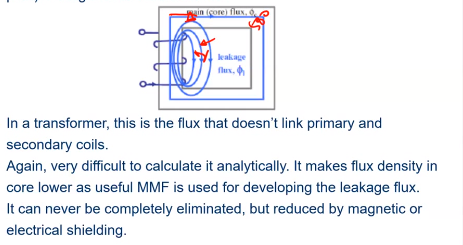
Leakage
Flux behave non usefully (usually as it passes through the air regions or non preferred magnetic paths instead of the desired path.
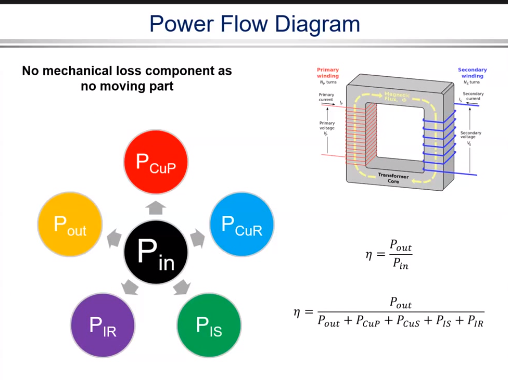
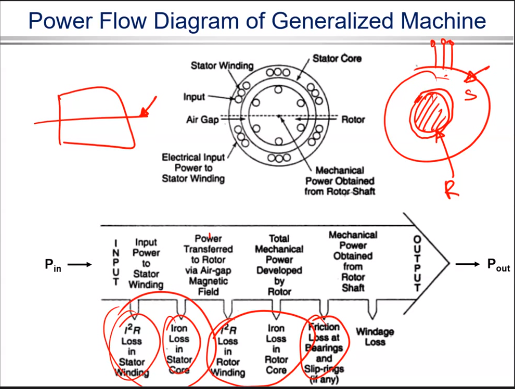
Power Flow Diagram
the input power is ideal so there will be joules lost in primary maybe in coil There is also losses in the iron core called iron losses then the remaining power goes to secondary where there is also secondary losses and finally the remaining power goes to output .
Efficiency is given by:
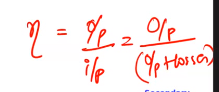

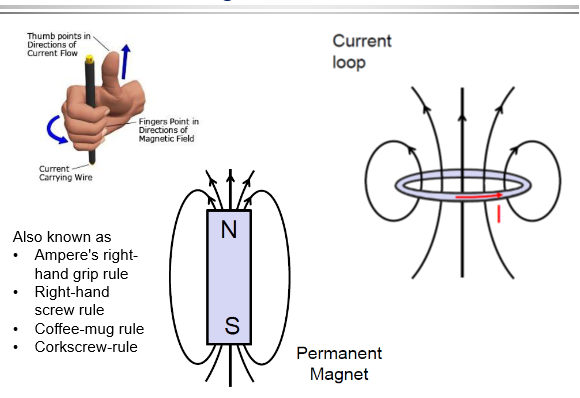 Rather than having a straight conductor we have coils, If we apply same principle there will be flux like this:
Rather than having a straight conductor we have coils, If we apply same principle there will be flux like this: The dashed lines represent the magnetic flux
The dashed lines represent the magnetic flux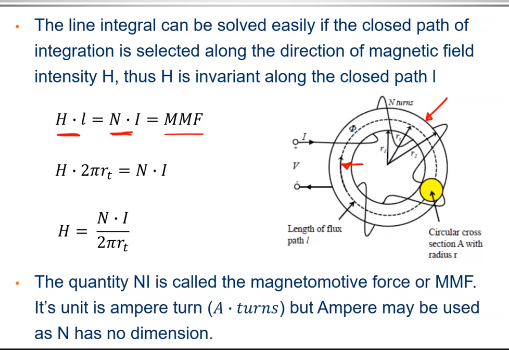

 Magnetic Flux density
Magnetic Flux density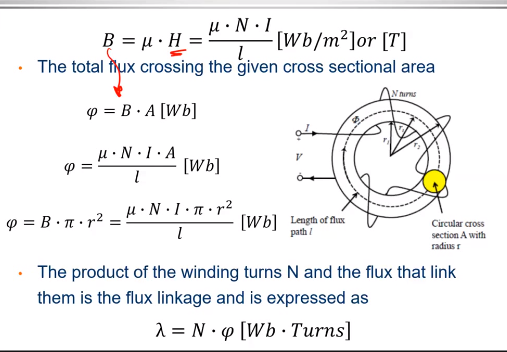 Magnetic flux phenomena
Magnetic flux phenomena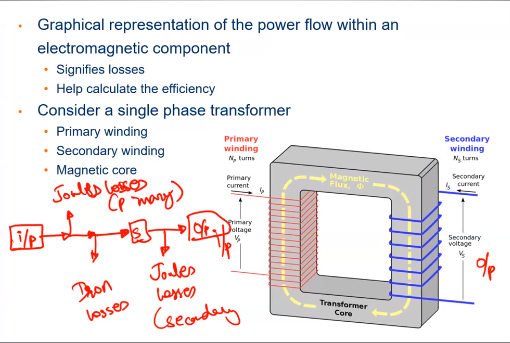 Efficiency is given by:
Efficiency is given by: