Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Life
2.1 The Nature of Matter
Atoms
- Atoms are the basic unit of matter and are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons
- Protons and neutrons have the same mass but different charges
- Protons have a positive charge (+)
- Neutrons carry no charge at all
- An electron is a negatively charged particle (-)
- The nucleus is the center of the atom
Elements and Isotopes
- An element is a pure substance that consists entirely of one type of atom
- Each element has a one- or two-letter symbol (C for carbon or Na for sodium)
- An element’s atomic number is the number of protons in the atom
- Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are isotopes
- Protons + neutrons = mass number
- Isotopes are named using their mass number
- Some isotopes are radioactive
Chemical Compounds
- A compound is a substance formed by the chemical combination of two or more elements in definite proportions
- The number of each element in a compound can be shown using chemical formulas
- Ex: Since water has 2 atoms of hydrogen and 1 atom of oxygen, the chemical formula for water is H2O
Chemical Bonds
@@The 2 main chemical bonds are ionic and covalent bonds@@
- An ionic bond is formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another
- An atom that loses electrons becomes positively charged, while an atom that gains electrons has a negative charge
- Oppositely charged ions attract one another
- A covalent bond is a bond between atoms in which the electrons are shared and is formed when the electrons travel around the nuclei of both atoms
- Single covalent bond: atoms sharing 2 electrons
- Double bond: atoms sharing 4 electrons
- Triple bond: atoms sharing 6 electrons
- @@Covalent bonds form structures called molecules@@
- The molecule is the smallest unit of most compounds that displays all properties of that compound
- In a water molecule, each hydrogen atom shares 2 electrons with the oxygen atom. So, each hydrogen atom is joined to the oxygen atom by a covalent bond.
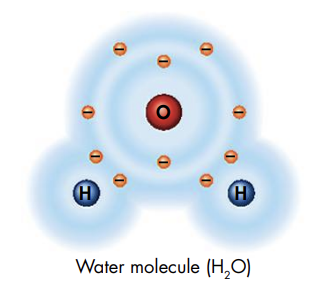
2.2 Properties of Water
The Water Molecule
- @@Water is a polar molecule@@
- A molecule in which the charges are unevenly spread out is said to be “polar”
- The pull between a partially positive hydrogen atom on one molecule and a partially negative oxygen atom on another is known as a hydrogen bond
- @@Hydrogen bonds give water special properties such as cohesion, adhesion, and a high heat capacity@@
- Cohesion: the attraction between molecules of the same substance
- Adhesion: the force of attraction between different kinds of molecules
- Heat capacity: the amount of energy needed to increase a substance’s temperature
Solutions and Suspensions
- Water is often part of a mixture
- A mixture is made up of elements or compounds that are combined but not bonded together
- Two kinds of mixtures made with water are solutions and suspensions
- A solution is a type of mixture in which all the components are evenly distributed. Contains one or more solutes in a solvent
- A solute is what is dissolved
- A solvent is what does the dissolving
- A suspension is a mixture of water and non-dissolved material
Acids, Bases, and pH
- The pH scale is used to show the concentration of H+ ions in a solution
- The scale ranges from 0 to 14
- A solution with a pH of 7 is considered neutral
- Solutions with a pH below 7 are acidic
- Solutions with a pH above 7 are basic
- An acid is a compound that releases hydrogen ions in a solution; has a pH of less than 7
- A base is a compound that releases hydroxide ions in a solution; has a pH of more than 7
- A buffer is a compound that prevents sharp, sudden changes in pH
2.3 Carbon Compounds
The Chemistry of Carbon
- Carbon atoms have 4 electrons available for bonding, including @@hydrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur, and nitrogen@@ to form life’s molecules
- Carbon atoms can bond with one another
- Carbon-carbon bonds can be single, double, or triple and can even close up on themselves to form rings
Macromolecules
- Macromolecules are made from thousands or even hundreds of thousands of smaller molecules called monomers
- Monomers join to form polymers
- The four major groups of macromolecules are:
- Carbohydrates: compounds made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms; a type of nutrient that is the main source of energy for the body
- Simple sugars such as monosaccharides and disaccharides
- Complex carbohydrates are the large macromolecules formed when simple sugars join together
- Lipids: macromolecules that generally do not dissolve in water and are made mostly of carbon and hydrogen atoms; used to store energy and are parts of membranes and waterproof coverings
- Common lipids include fats, oils, and waxes
- Saturated and unsaturated
- Nucleic acids: macromolecules containing hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, and phosphorus; function to store and transmit genetic information
- Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) contains the sugar deoxyribose
- Ribonucleic acid (RNA) contains the sugar ribose
- Proteins: macromolecules that contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen; needed by the body for growth and repair
- Amino acids are compounds with an amino group on one end and a carboxyl group on the other end
2.4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes
Chemical Reactions
- A chemical reaction is a process that changes or transforms one set of chemicals into another set of chemicals
- Reactants are the elements or compounds that go into a chemical reaction
- Products are the elements or compounds that come out of a chemical reaction
Energy in Reactions
- Chemical reactions that give off energy often happen on their own, while chemical reactions that take in energy will not happen without a source of energy
- Activation energy is the energy that is needed to get a reaction started
Enzymes
- A catalyst is a substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction by lowering a reaction’s energy rate
- Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts in living things
- The reactants of enzyme-catalyzed reactions are known as substrates
- The substrates bind to a site called the active site
- Temperature, pH, and other molecules can affect how enzymes work