The skeletal system
Functions of skeletal system:
support and shape - support and shapes the body/ endoskeleton (inside)
Protection- Protects the organ inside
Movement- Helps make movement possible/ contraction of muscles pull on the bone causing movement
Storage of minerals and lipids- Moves quickly from blood to bones then moves slowly from bones into body
Hemopoiesis- production of red and white blood cells/ Myeloid tissue (red bone marrow) transforms into yellow marrow
VOCAB +
Yellow marrow- Lipid Reserves | Hole- A opening or a groove of the bone that allows blood vessels and nerves to enter | Rib tubercles- | |
Articulation- where the bones meet | Patella- kneecp | collagen- | |
Projection- area that is protecting the surface of your body (depression) | shial tuberosity- | calcium- |
Osseus Tissue
Contains CT (connective tissue)
between cell spaces: Hard; have minerals salts in them
67% inorganic
33% organic
Classification of Bones:
Long | long shaft curved for strength exp: humerus or femur | 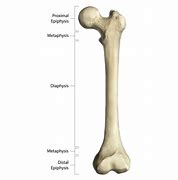 |
Short | spongy texture, small and boxy (wide) exp: 16 carpal bones (wrist) | 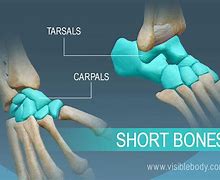 |
Flat | thin parallel surfaces, broad surface for muscle attachment exp: cranium | 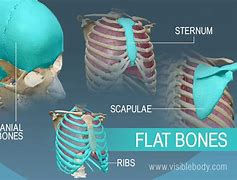 |
Irregular | complex, irregular shape exp: vertebrae or ossicles | 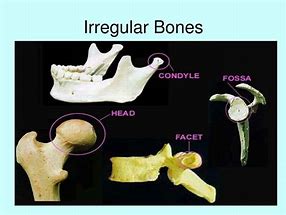 |
Sutural (Wormian) | found in the sutures of the skull, individual variations like size number, and position exp: skull lining (looks like stiches) | 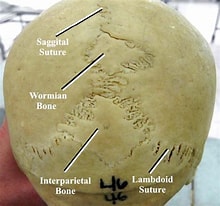 |
Sesamoid | small, flat, develops within the tendons exp: patella at the knee joint | 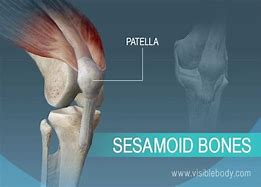 |
Bone surface features
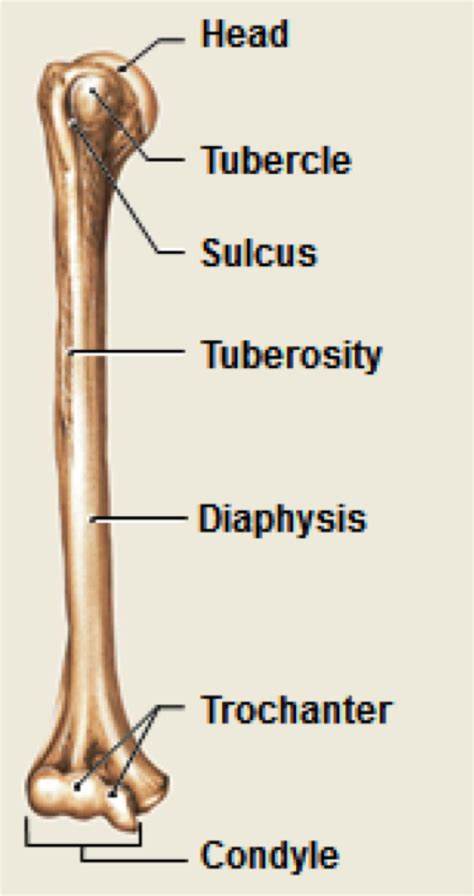
Neck- narrow part of the bone (when shaft meets end)
Ramus- extension of bone that makes an angle
Head- rounded end of bone that help form a joint/ a smooth surface
Condyle- knuckle like articular process (will be smooth)
Trochanter- large projection for a tissue attachment (rough)
Crest- raised ridge for a CT to a bone (rough + bumpy)
Spinous process- (spine) sharp and slender process, stick out away from bone.
Tuberosity- large rough projection for tissue attachment
Trochlea- smooth, grooved surface, shaped like a pulley
Tubercle- small, rounded projection (rib tubercles)
Facet- smooth and flat articular surface
Sulcus- groove for nerve, blood vessels or tendon
Bone Openings and Depressions
Foramen- Opening or a hole in the bone for the nerves and blood vessels largest in skull: foramen magnum
Meatus- tube like canal in the bone, auditory meatus- ear canal
Fissure- Narrow, irregular slit between parts of a bone
Fossa- Shallow depression on the bone surface
Sinus-(antrum) chamber within a bone and usually air filled
Bone structure
Diaphysis- long shaft
Epiphysis- articular end
Metaphysic- middle part
Medullary cavity-
Spongy bone-
Compact Bone- Dense bone
Bone Cells
Osteo blast
~ Bone that forms cells
~forms the bone matrix/ stuff around the cells (osteogenesis)
~ To remember: Bone Builders
Osteocytes
~maintain healthy bone tissue
~ To remember: Care takers
Osteoprogenitor (osteogenic)
~ found lining outside of your bone, marrow cavity, passageways, for blood vessels.
~ To remember: PRepairing to build but not there yet
Osteoclast
~bone that destroys cells
~removes and recycles bone matrix
~To remember: osteo Crash- to break
Structure of Bone
Periosteum
the outside lining (membrane) surrounding the bone
repairs the nutrients of the bone
Haversion canal
Runs length wise (up and down) the central canal
forms small blood vessels in bone
Volkmann’s canal
Runs horizontally (left-right)
canal for small blood vessels in bone
Endosteum
Membrane that lines the inside marrow cavity and central canals
Lacuna
spaces that contain osteocytes
“Little Lakes”
Canaliculus
system of canals
Lamella
concentric rings of hardened bone
Bone Marrow
Red Marrow- the production the RBC