Blood Lab - Differential White Blood Cell Count
Key Concepts
Leukocytes, or white blood cells (WBCs), can be divided into two subgroups depending on whether or not their cytoplasm contains granules that are visible using a brightfield microscope.
Agranulocytes do not have visible granules.
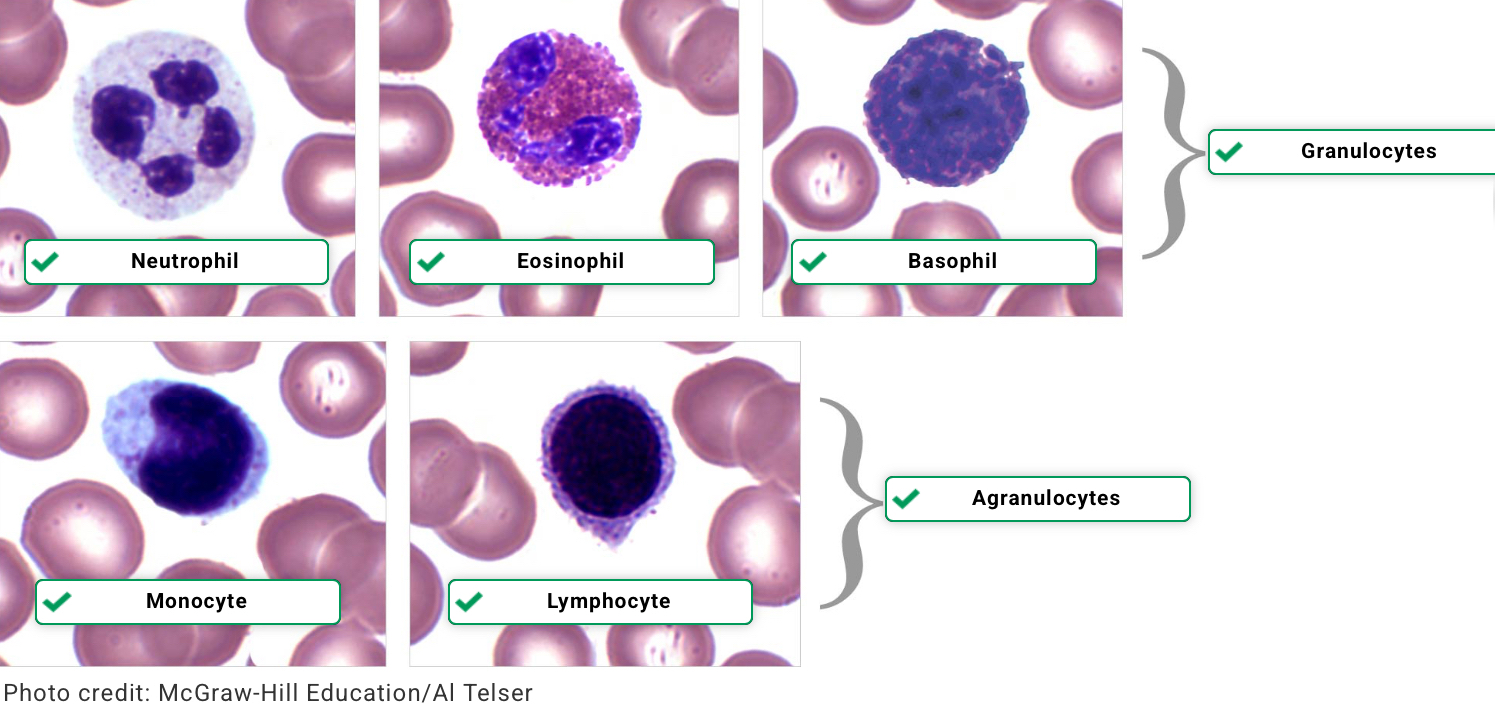
Lymphocytes: Small cells with a round nucleus taking up most of the volume of the cell.
Monocytes: Large cells with a bean-shaped nucleus taking up half to nearly all the volume of the cell.
Granulocytes contain granules that stain characteristic colors.
Basophils: Contain dark purple or black granules. The nucleus is usually bilobed (two lobes).
Eosinophils: Contain bright red granules. The nucleus is usually bilobed (two lobes).
Neutrophils:Contain light pink and/or purple granules. The nucleus is multilobed (multiple lobes).
A differential white blood cell count (DIFF) determines the percentage of the various types of white blood cells (WBCs), also known as leukocytes, in a blood sample.
A complete blood count (CBC) with DIFF is often run in the lab on a machine that counts with an algorithm to match cells. However, many clinicians request a manual count from a trained lab tech's perspective when highly accurate counts are necessary or if cells are expected to be irregular, such as in leukemias.
It is important to learn this technique, as the values that come back from this test are important to clinical diagnosis and evaluation of how/what the immune system is doing in the patient.
Normal DIFF counts are approximately as follows:
Neutrophils 40-70%
Lymphocytes 20-40%
Monocytes 2-8%
Eosinophils 1-4%
Reference ranges can vary by age, sex, methods of testing, and other factors. There are no nationally established reference ranges for DIFF values; instead, each laboratory tests a population and establishes its own reference ranges. Therefore, the reference ranges quoted are only approximate.
Reference ranges can vary by age, sex, methods of testing, and other factors. There are no nationally established reference ranges for DIFF values; instead, each laboratory tests a population and establishes its own reference ranges. Therefore, the reference ranges quoted are only approximate.
Overview
In this simulation, you complete a differential white blood cell count (DIFF) manually using a prepared blood slide and a brightfield microscope. It is helpful to understand the manner in which this process works and to further familiarize yourself with WBC appearance.
To prepare for the count, you will first identify the 5 types of WBCs and the lab equipment used to perform the DIFF.
Next, you will prepare your own wet mount of blood using the Wright stain technique.
A DIFF can only be performed using high magnification so the types of WBCs can be distinguished.
Take a moment to reflect on personal safety precautions. Working with blood is a potentially hazardous situation. In real life, you should:
Wash the laboratory lab benches before and after the procedures with an appropriate disinfectant.
Wear disposable gloves, lab coat, and goggles when handling blood samples.
Wash your hands after the laboratory.
Only use a blood lancet once.
Dispose of used lancets, pipettes, and other blood contaminated items in the appropriate hazardous waste container, never a regular trash container.
Before you begin
Knowledge of the operation of a brightfield microscope is assumed for this simulation.
A good blood smear is necessary for accurate counts.
You will slowly move the slide top to bottom to identify and count 50 WBCs, then calculate the percentage of each type of WBC.
Only count the middle of the blood smear where the red blood cells just nearly touch each other and there is little white space.
Near the edges of the smear, the cells will either overlap or be spread out too much for an accurate count.
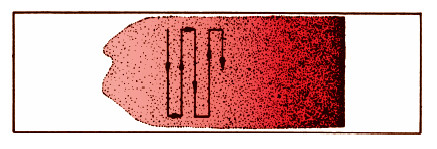
How to move the slide: Make sure to only count each area once by moving the slide in a straight line through one field of view at at time.
Laboratory Simulation
Methods
Phase 1: WBC identification
Identify different WBCs (leukocytes)
Phase 2: Lab equipment
Identify lab equipment
Phase 3: Preparation of blood smear
Place microscope slide on staining rack
Add drop of blood to slide using pipette. Dispose of pipette
Take another slide from box and use it to smear blood drop by sliding it from right to left. Let air dry for 1 minute. Dispose of slide
Add Wright stain to smear. Wait 2 minutes
Add distilled water to smear. Wait 4 minutes
Wash slide with filtered water. Wait 1 minute
Place slide on microscope stage
Phase 4: Microscope differential count
Focus slide at 4X using the coarse focus, then the fine focus
Turn objective to 10X and focus again
Move to upper-left corner of slide
Open Lab Data. Count each type of WBC in each region of slide by clicking corresponding buttons in Lab Data.
Count 50 WBCs in total by using arrow buttons to move through regions of slide.
Phase 5: Lab wrap-up
Select your answer to the question
Phase 6: Save Lab Data
Relevant Lab Data is available to be saved for personal reference. Data will be available if you return to this laboratory simulation
White Blood Cells
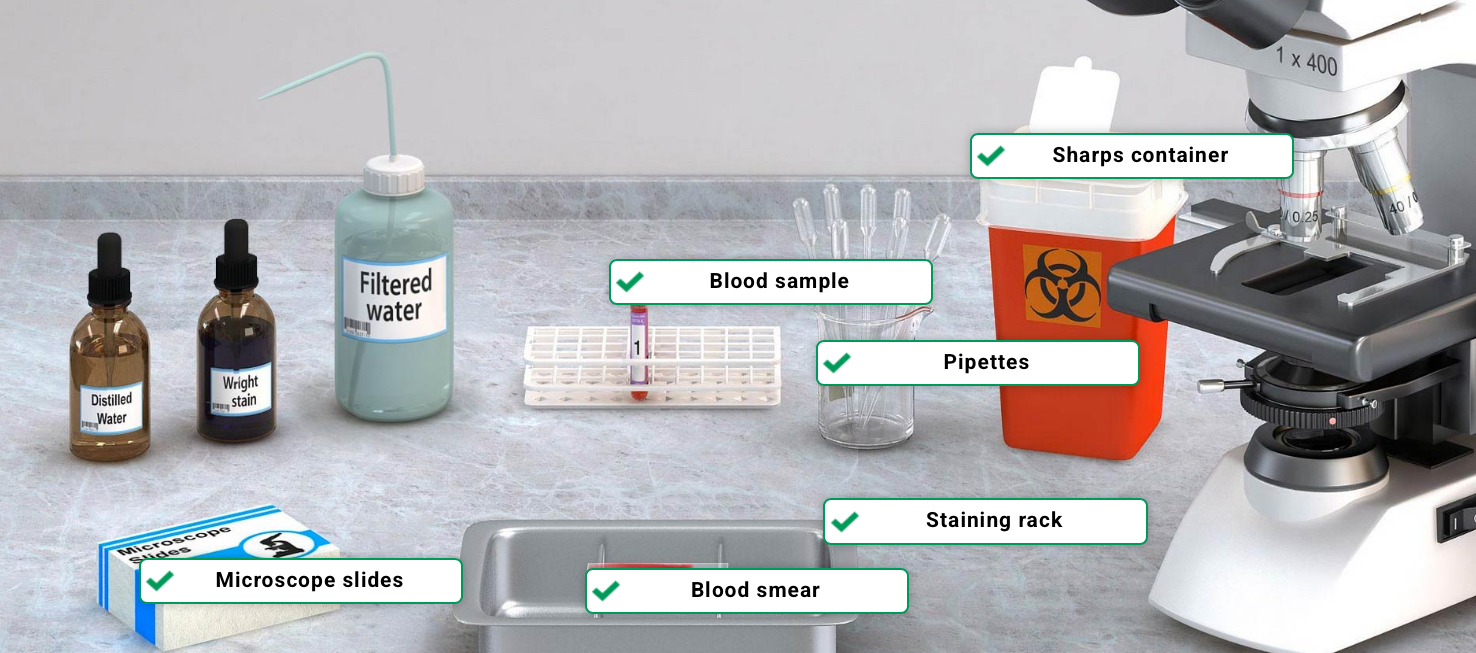
Supplies
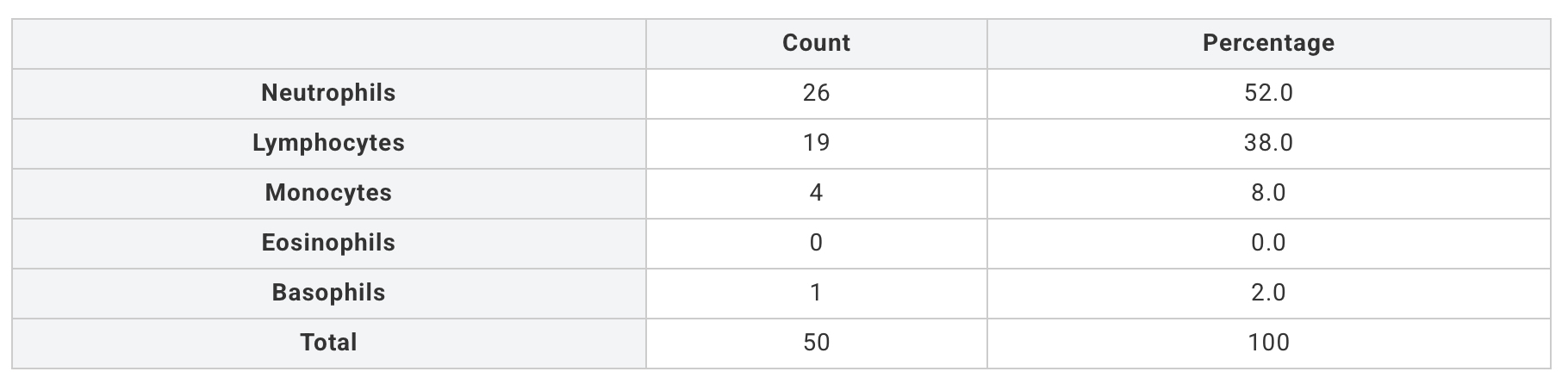
Collected Data
 Knowt
Knowt