6.1.2(a) factors affecting phenotypic variation
sources of variation
From Meiosis
Crossing over (chiasmata) formation at prophase I results in the exchange of alleles between non-sister chromatids, so new combinations of alleles are formed on these chromosomes.
Independent assortment of homologous chromosomes at metaphase I (in humans resulting in 223 combinations of chromosomes)
Independent assortment of chromatids at metaphase II (crossed over chromosomes)
From sexual reproduction
Random mating
Random fertilisation (all sperm and eggs are genetically different)
New variation
Mutations (gene or chromosome)
types of variation
All organisms of the same species show differences between each other this is called variation.
Some of this variation is due to genetic changes during gamete formation (and subsequent fertilisation) and some of it is due to the environment..
There are 2 types of variation:
Discontinuous
Continuous
discontinuous variation
This shows clear cut, qualitative differences.
Variation falls easily into different categories
Caused by different alleles of a single gene locus.
Individual alleles have a large effect on phenotype.
Different gene loci have different effects on phenotype
E.g.: Mendel’s tall and short peas, Horned and polled cattle, Vestigial and normal winged fruit flies, ABO Blood group
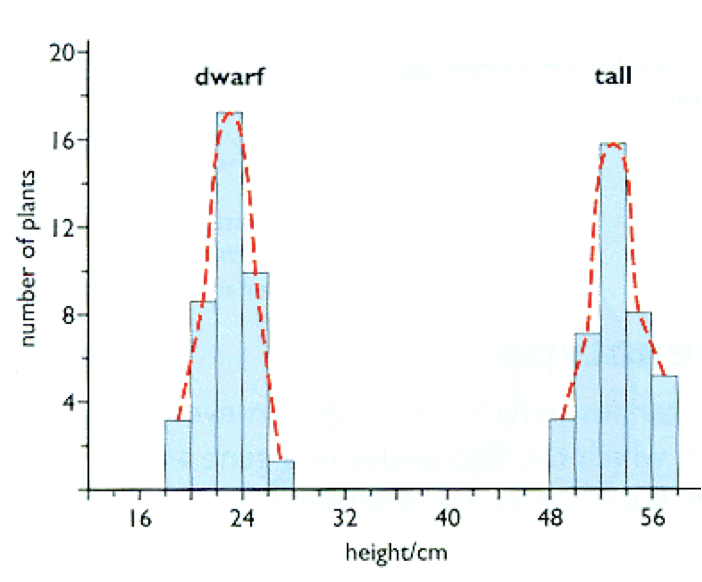
continuous variation
Tend to show quantitative differences.
Can’t put large groups into easy classes as differences between individual values may be small.
You get a range of values.
A large number of loci may have combined effect on a phenotype (this is called a polygenic effect/ polygenic inheritance)
Different alleles at a gene locus have small effect.
Different gene loci have the same/ additive effect on phenotype.
Genes are on different chromosomes (unlinked).
Environmental influence is often quite large.
It includes characteristics such as:
Height
Weight
Shape
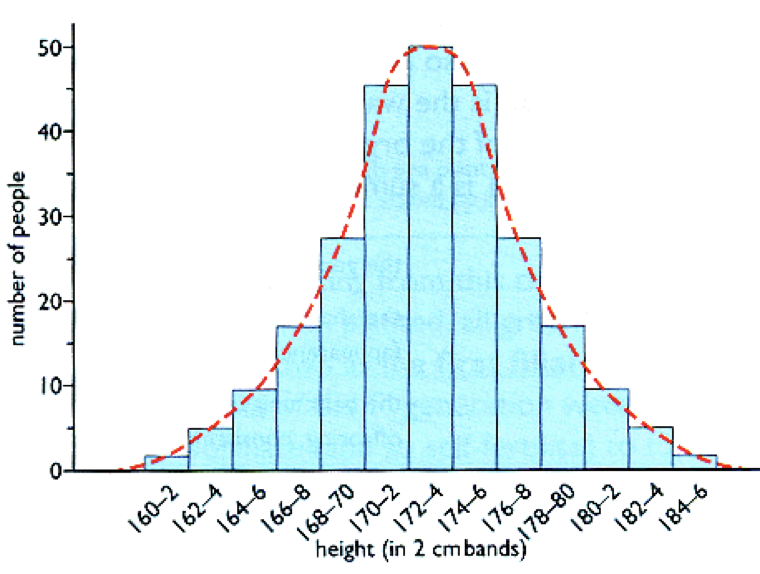
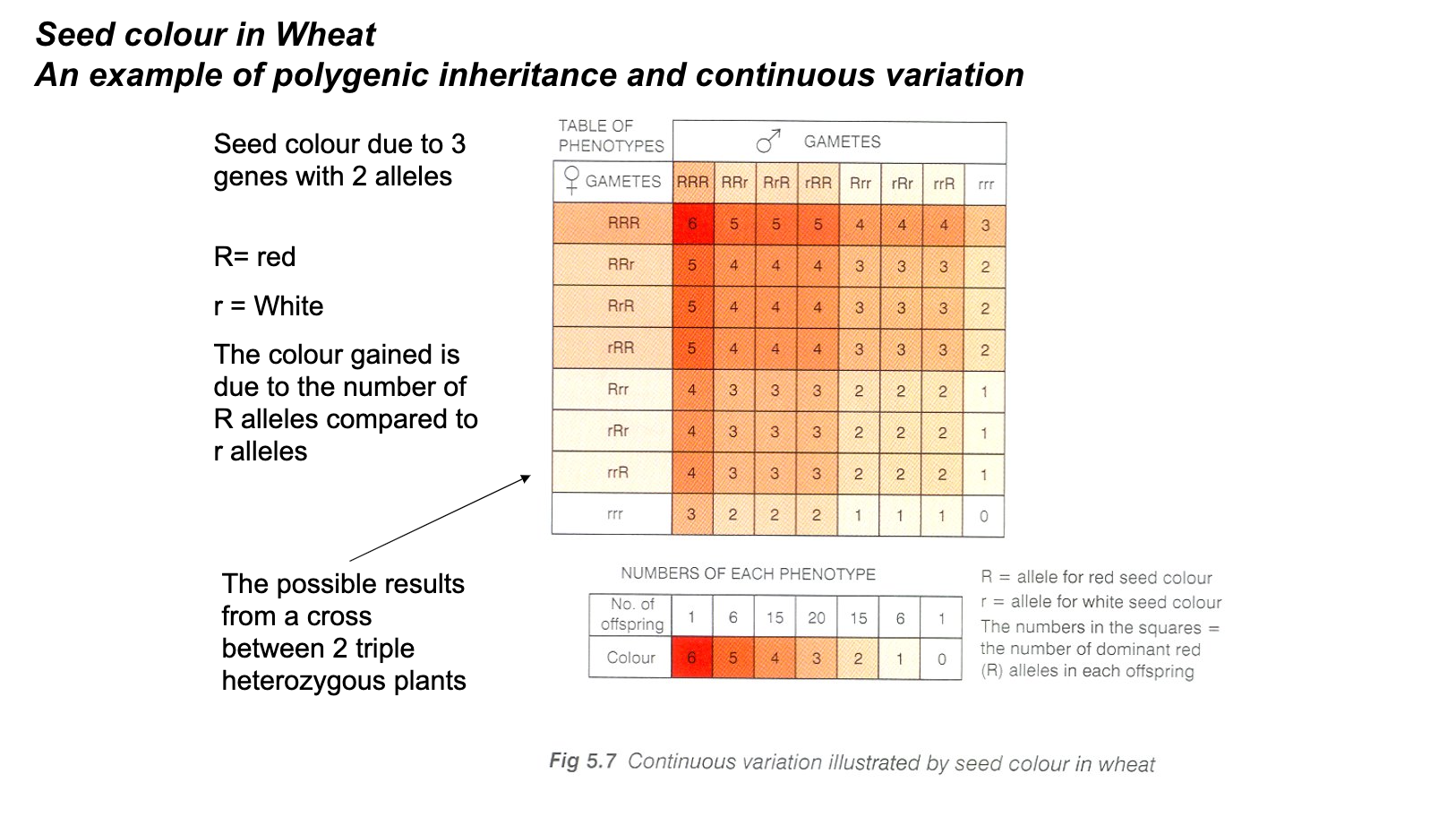
variation in wheat with 2 heterozygous parents
variation in sweetcorn
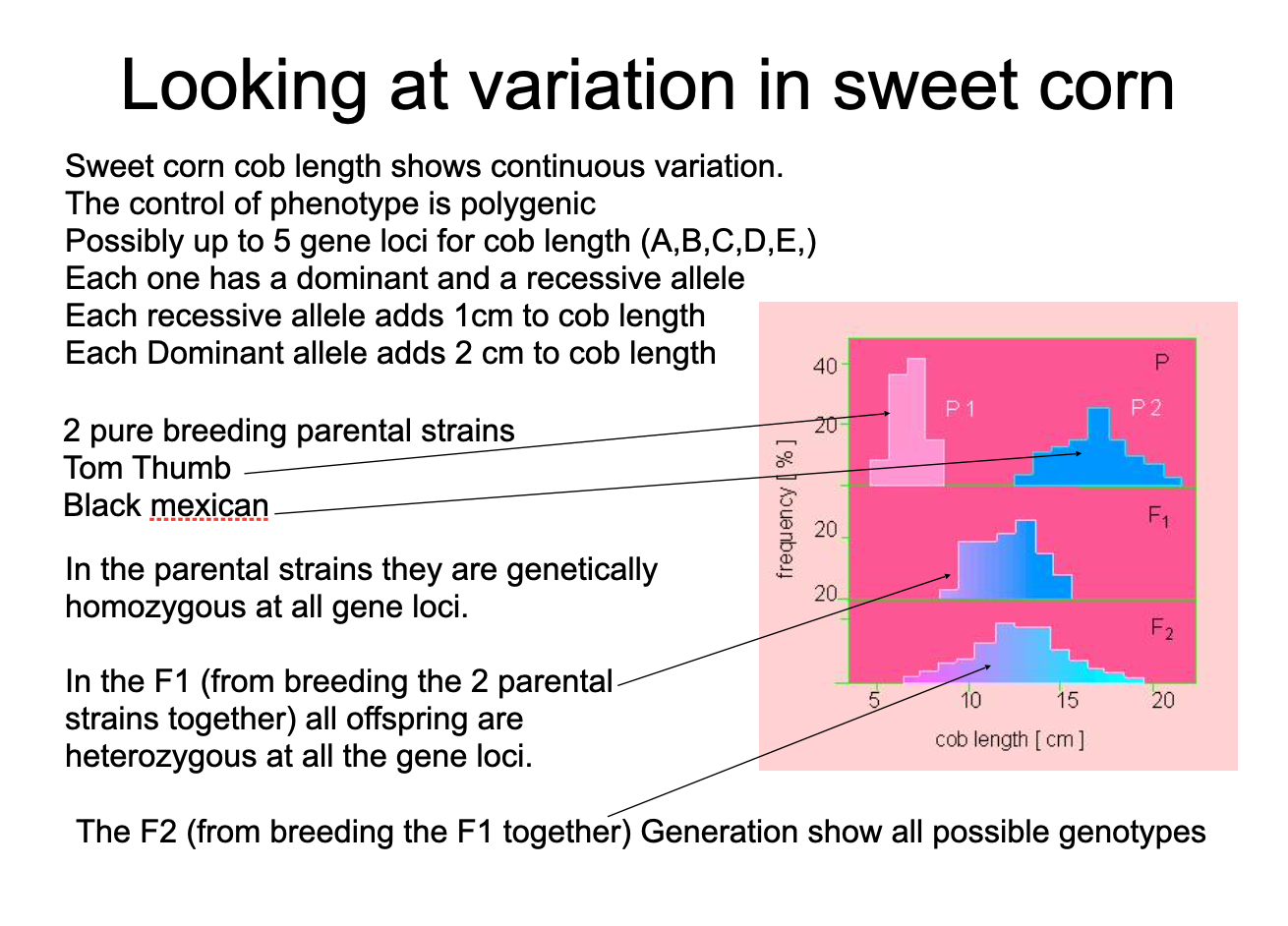
The Tomb Thumb plant genotype is aabbccddee (recessive at all gene loci)
The Black Mexican plant genotype is AABBCCDDEE (dominant at all gene loci)
What is the theoretical maximum cob size of
a) Tom Thumb Plants? 10cm
B) Black Mexican plants? 20cmWhat will the genotype for the F1 be and what is its potential size?
AaBbCcDdEe, 15cm
F1 is always heterozygous if pure breeding parents
None of these 3 strains show any genetic variation within their strain (they all have the same genotype.
Explain why they still show variation in cob length.environmental factors e.g. light intensity, water availability, pH of soil
