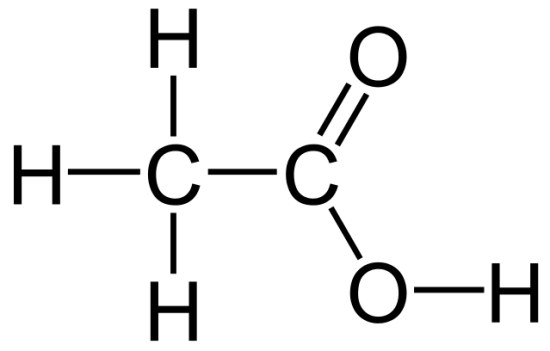
1.1: Chemistry in Living System
Elements of Life
92 naturally occurring elements
carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur, phosphorus
carbon and hydrogen are backbone
other 4 give molecules specific properties
atom=smallest particle that retains the properties of the element
protons, electrons, neutrons
#protons defines the element
electrons jump and allow atoms to bond
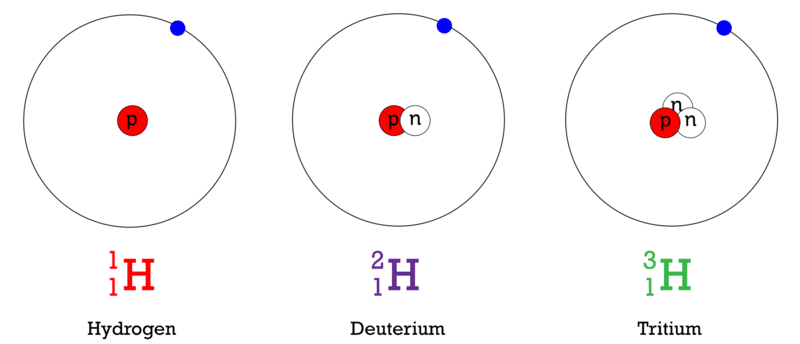
Isotopes
of neutrons in an element can vary
same element, differs in neutrons
depends on atomic mass
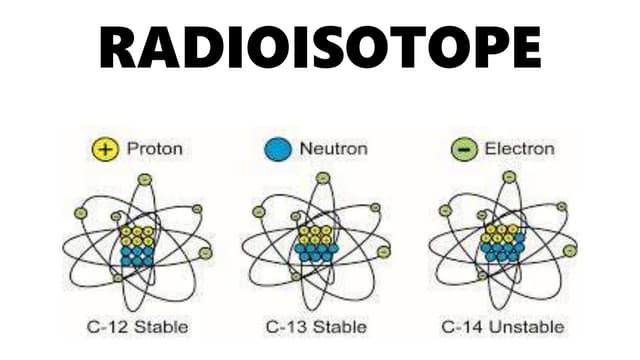
Radioisotopes
unstable isotopes, nucleus decays
ex. carbon 14→ nitrogen 14
nuclear decay emitting radiation in the form of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves
Molecules
molecule = group of 2 or more atoms held together by chemical bonds
covalent = shares electrons
ionic = transfers electrons
disassociates in water
organic = contains carbon and hydrogen, use covalent bonds
proteins, carbs, lipids, nucleic acids
inorganic = ionic or covalent, no CH groups
water, oxygen gas, nitrogen gas, salt
Interactions Within Molecules
intramolecular forces = hold atoms together within a molecule
covalent bonds
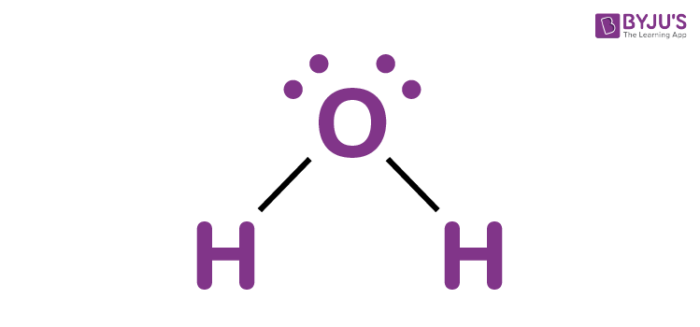
ex. water
Electronegativity
some atoms attract electrons stronger than others
ex. H2O
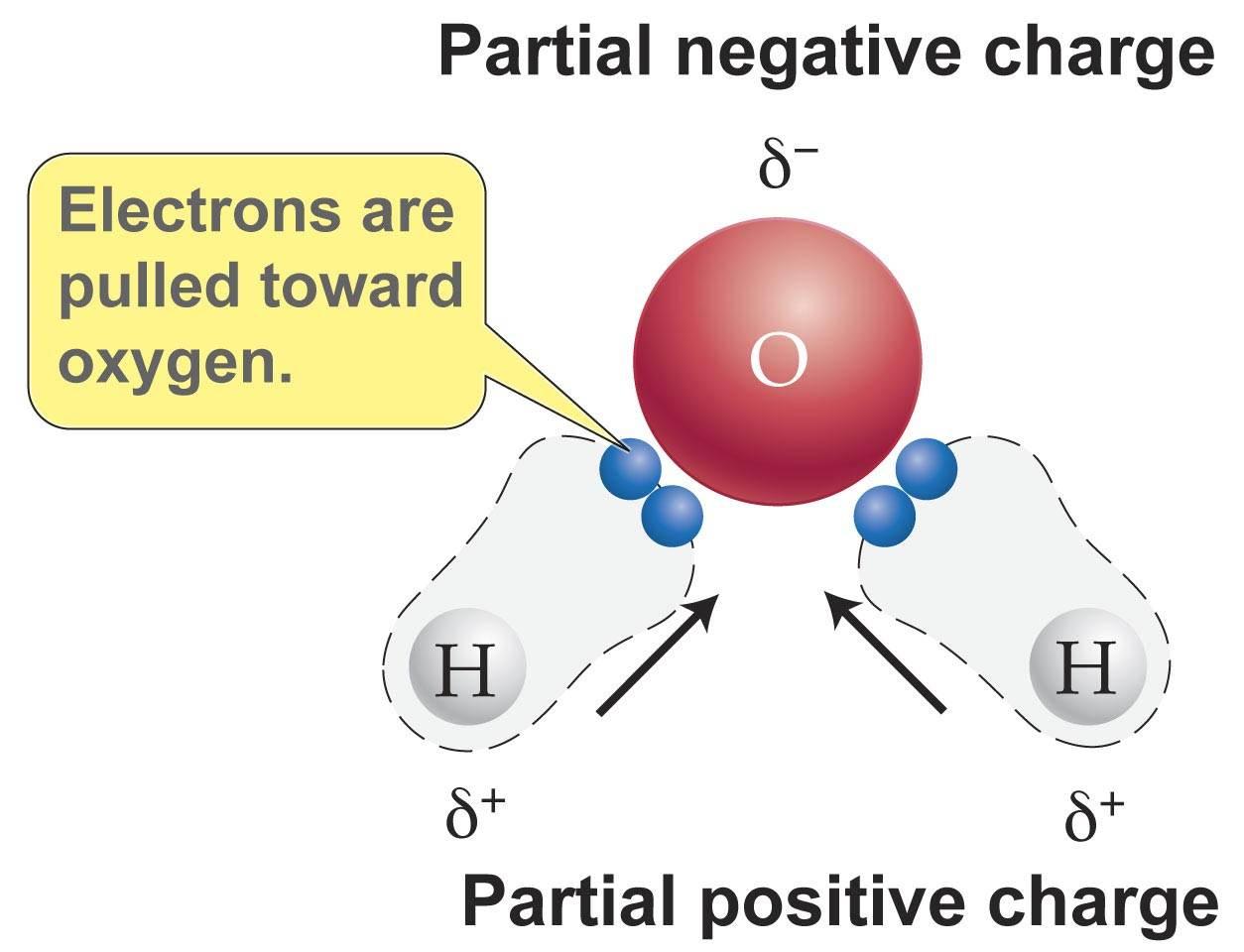
electronegativity increases from left to right on periodic table
Polar Covalent Bonds
two atoms with different electronegativities share electrons
electrons are imbalanced, more attracted to atom with higher electronegativity
causes atom to have a slight negative charge
Interactions Between Molecules
intermolecular forces = hold molecules together
weak bonds
broken easily, with sufficient energy
responsible for physical properties of substances
Hydrogen Bonds
weak association between an atom with a partial - charge and a hydrogen atom with a partial + charge
ex. water
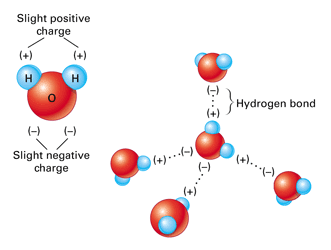
many hydrogen bonds together can be very strong
backbone of DNA
Hydrophobic Interactions
non polar molecules (oils) do not form hydrogen bonds
non polar + polar = non polars clump, don’t mix with polar
hydrophobic = non polar molecules do not have attractive interactions with water molecules
hydrophilic = polar molecules that have attractive interactions with water molecules
Ions in Biological Systems
anion = negative ion (gains electrons, non metals)
cation = positive ion (loses electrons, metals)
cells are aqueous environments, ions become dissociated
ex. Li+, Na+, K+
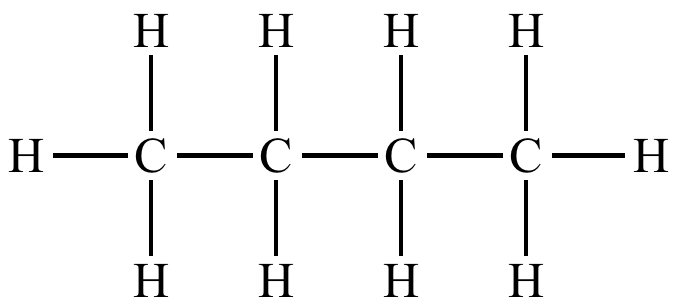
Hydrocarbons
long chains of carbon backbone with hydrogen
non-polar, do not dissolve, low boiling point, flammable, energy-rick
ex. methane, propane, butane, octane, benzene
Functional Groups
functional groups = a cluster of atoms that always behaves in a certain wat
contains oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, or sulfur
attached to carbon-based structure
functional group | class of compounds | structural formula |
|---|---|---|
hydroxyl | alcohols | R-OH |
aldehyde | aldehydes | R-CHO |
keto | ketones | R>CO |
carboxyl | carboxylic acids | R-COOH |
amino | amines | R-NH2 |
phosphate | organic phosphates | R-OPO32- |
sulfhydryl | thiols | R-SH |
Structure and Shapes of Molecules
molecular formula = shows the # of each type of atom in an element or compound
ex. H2O, C3H7NO2, C6H12O6
isomers=same formula, different structure
structural formula=shows how atoms are bonded together
C6H14 | molecular |
|---|---|
C3H7 | emperical |
H3C-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3 | condensed |
| structural |
/\/\/\/\/\/\ | skeletal |