Molecular Shape, Hybridization, Polarity, Dipoles, Metallic/Ionic/Covalent Bonds
Molecular shape (Lewis, VSEPR, Mol. Orbital)
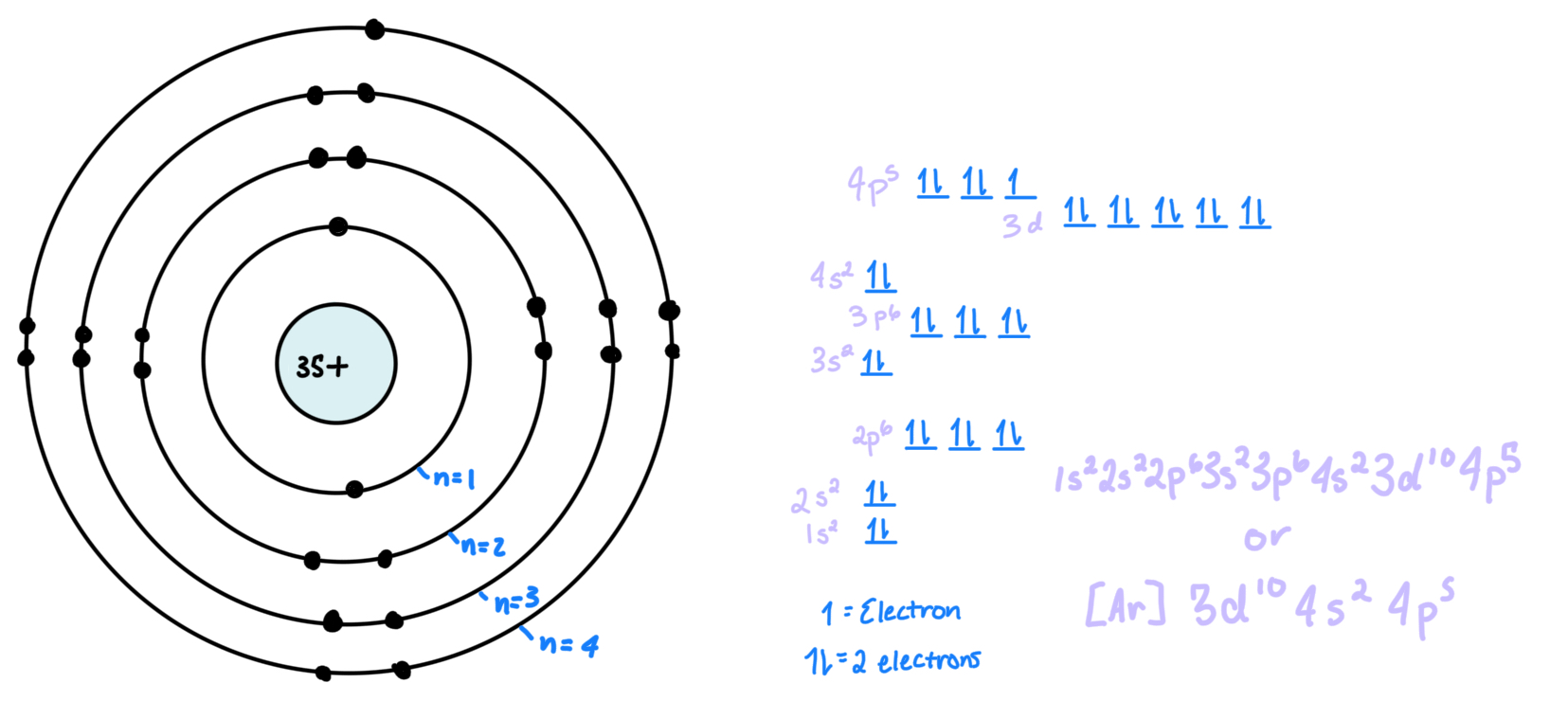
Electron: is a negatively charged subatomic particle
Electron shell: orbit/rings around a nucleus, represented by n = a number
Subshell: space where electrons are, giving info about where they are and what they are doing. There is an s, p, d, and f orbital
s holds 2 electrons (holds 1 atomic orbital)
p holds 6 electrons (holds 3 atomic orbitals)
d holds 8 electrons (holds 4 atomic orbitals)
f holds 14 electrons (holds 7 atomic orbitals)
atomic orbitals hold 2 electrons
Covalent bond: is when two atoms share an electron in order to fill its octect
Ionic bond: is when one atom transfer electrons to another, creating cation and anion
Cation: when an atom loses an electron, it forms a positive cation (pawsitive!)
Anion: when an atom gains an electron, it forms a negative anion
Cations and anions are attracted to each other (opposite charges)
Lewis Structure/Lewis Dot Structure: is a simplified drawing of how the valence electrons of an element bond with the other valence electrons of another element, and if there are any lone pairs
Central atom: is typically the atom in the middle, forming the most bonds
Electrons are negatively charged, and negatives repel. So, when forming molecules, the electrons make a shape to maximize the distance between themselves and other electrons.
Electron domains/Steric number: region where electrons are most likely to be found, bonding and non bonding. Note: a bond, double bond, triple bond, or lone pair, all count as only 1 electron domain
VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Repulsion) Theory: model to predict 3D shape of a molecule based on number of electron bonds around the central atom
AXE notation: a way to count electron domains and predict what the shape of the molecule will be. A is the central atom, with a subscript of 1. X is the amount of bonds the central atom is forming to other atoms. E is the amount of lone pairs of electrons on the central element. The steric number is the sum of X and E.
Different shapes form based on steric number and the amount of lone pairs
Typically molecules will have 2-6 electron domains, flashcards here: https://knowt.com/flashcards/5797fac8-0f6e-493f-91eb-3ef80e2a443b
2 electron domains: linear
3 domain electron domains: trigonal planar (AX3), bent (AX2E1)
4 electron domains: tetrahedral (AX4), trigonal pyramidal (AX3E), bent (AX2E2)
5 electron domains: trigonal bipyramidal (AX5), seesaw (AX4E), T-shaped (AX3E2), linear (AX2E4)
6 electron domains: octahedral (AX6), square pyramidal (AX5E), square planar (AX4E2)
Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT): a way to explain atoms bonding together and a molecules’ shape using quantum mechanics (no, we’re not talking about that).
In MOT, electrons are described as “delocalized” through out the entire molecule, in electron clouds (space where electrons could be). (Compared to VSEPR and Lewis)
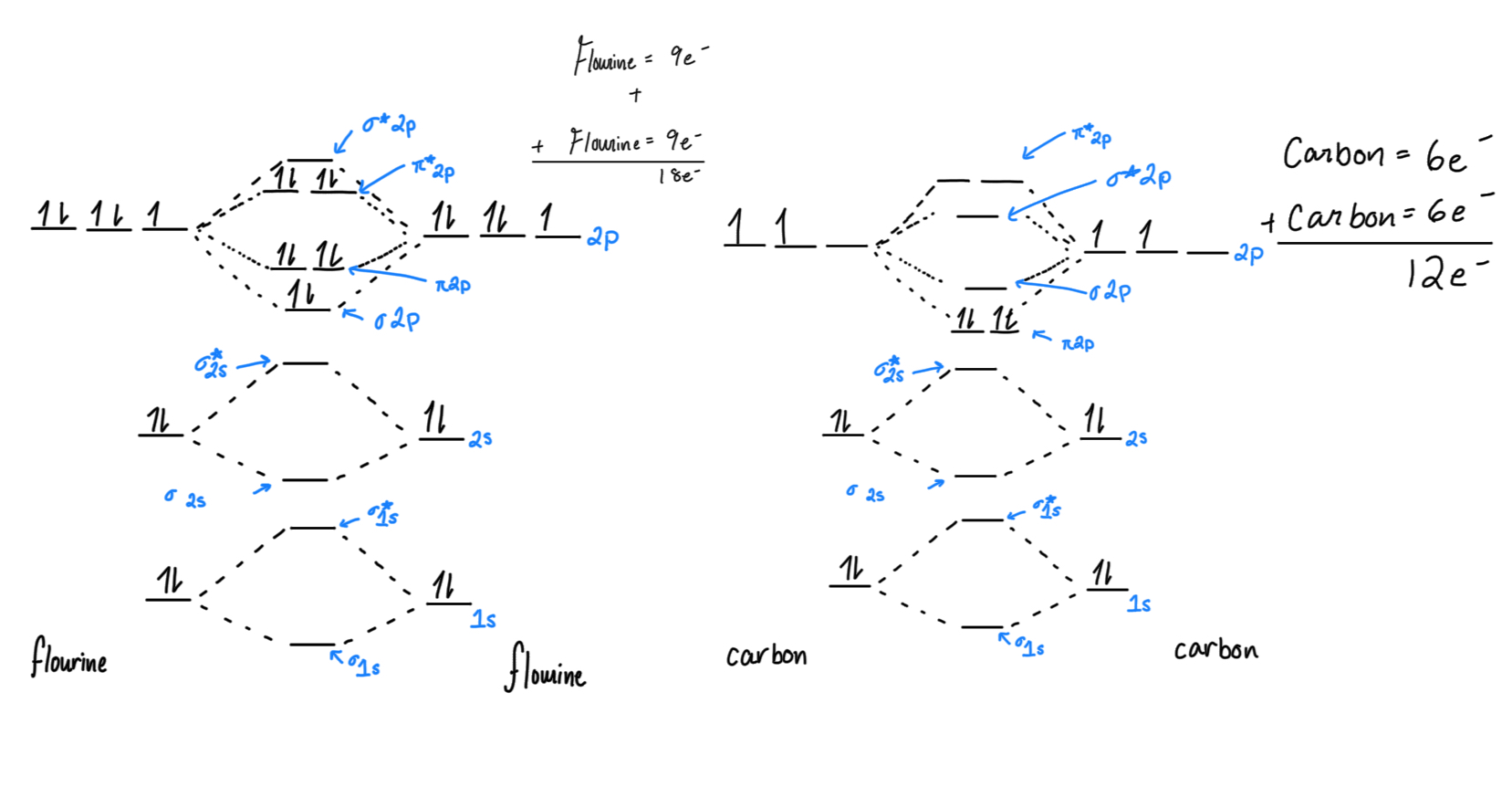
Sigma bond: generally, one bond, where the electron clouds overlap. it takes less energy to be here, so these fill up first. These are usually stronger than pi bonds.
Sigma*/Sigma star: bonding two elements means you have another orbital you need to maintain, so that is the anti-bonding orbital.
Pi bond: when there is more overlap of electron clouds (p orbitals), pi bonds form (psst… pi is two letters, and has two slots)
Pi*/Pi star:
Bond Order: (bonding e - antibonding e)/2
Paramagnetic
Diamagnetic
HOMO: Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital (higher energy than LUMO)
LUMO: Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital (lower than HOMO)
Valence Bond Theory (VBD):
Lewis Dot Structure Weakness:
Depicts molecules as 2D
MOT Weakness:
Predicting Shape
VBD Weakness:
Predicting magnetic properties
Hybridization
Hybridization: low energy state is preferably for elements, so you can hybridize atomic orbitals (s,p,d,f) into hybrid orbitals (like sp) which is a new shape!
To find hybridization: consider number of electron domains, if it is 2 then the hybridization is sp, if it is 3 then the hybridization is sp2, if it is 4 then it is sp3, if it 5 then it is sp3d, if it is 6 then it is sp3d2
Ex: a hybridized is a new shape, so CH4 has 4 sp3
Polarity
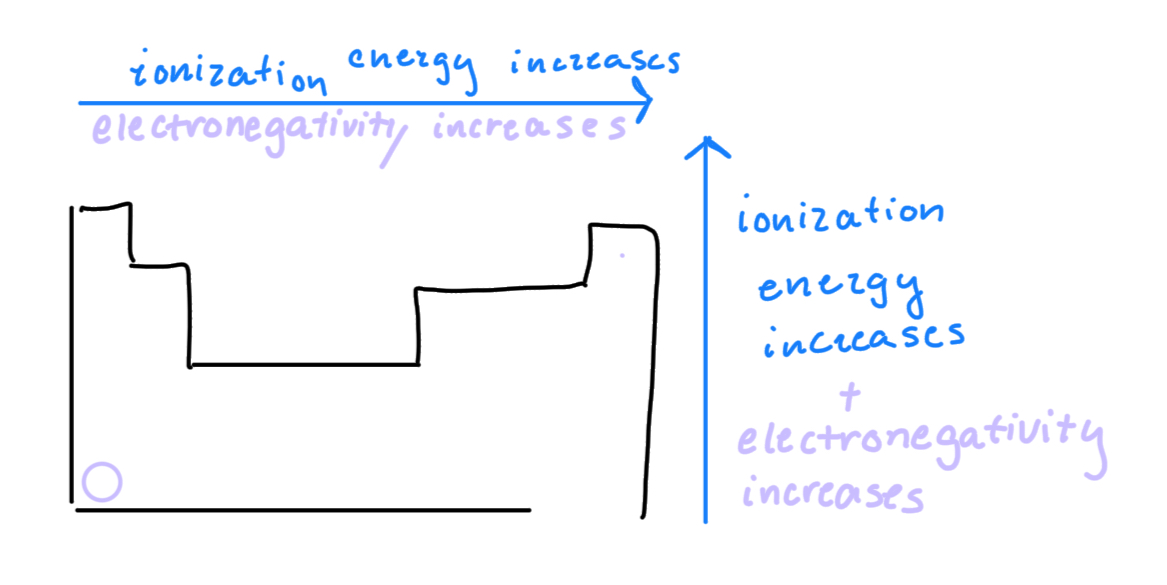
Electronegativity: measure of how strong an element is pulling electrons towards itself. Smaller elements tend to be more electronegative.
Polarity: when differences of electronegativities happen, there is an uneven distribution of electron density. in essence, the electrons aren’t being evenly shared
Polar covalent: when 2 elements bond and share an electron, but one pulls harder because of the higher electronegativity
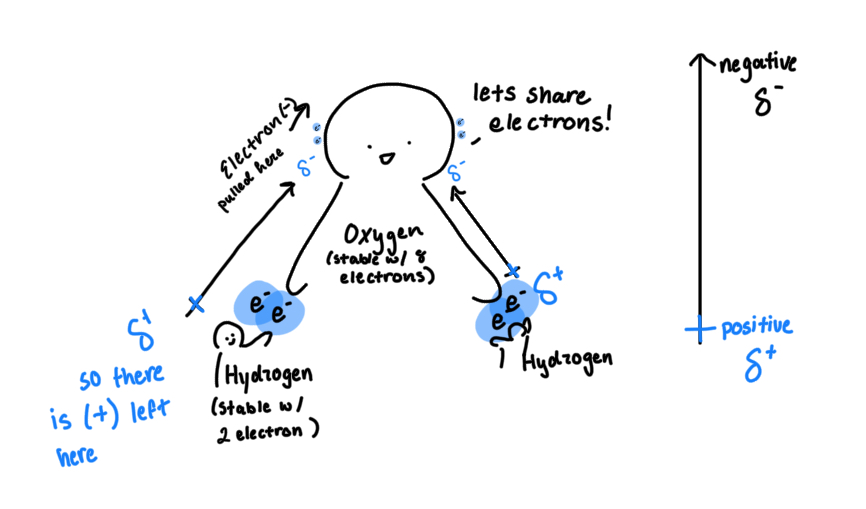
Dipole moment: measures separation of positive and negative charge within a molecule
Polar bonds
Polar molecules
Non-polar covalent: when two atoms share atoms equally, so there is no dipole moment. this occurs between bonds of the same element, or when the electronegative difference is small (>0.4
Metallic/Ionic/Covalent Bonds
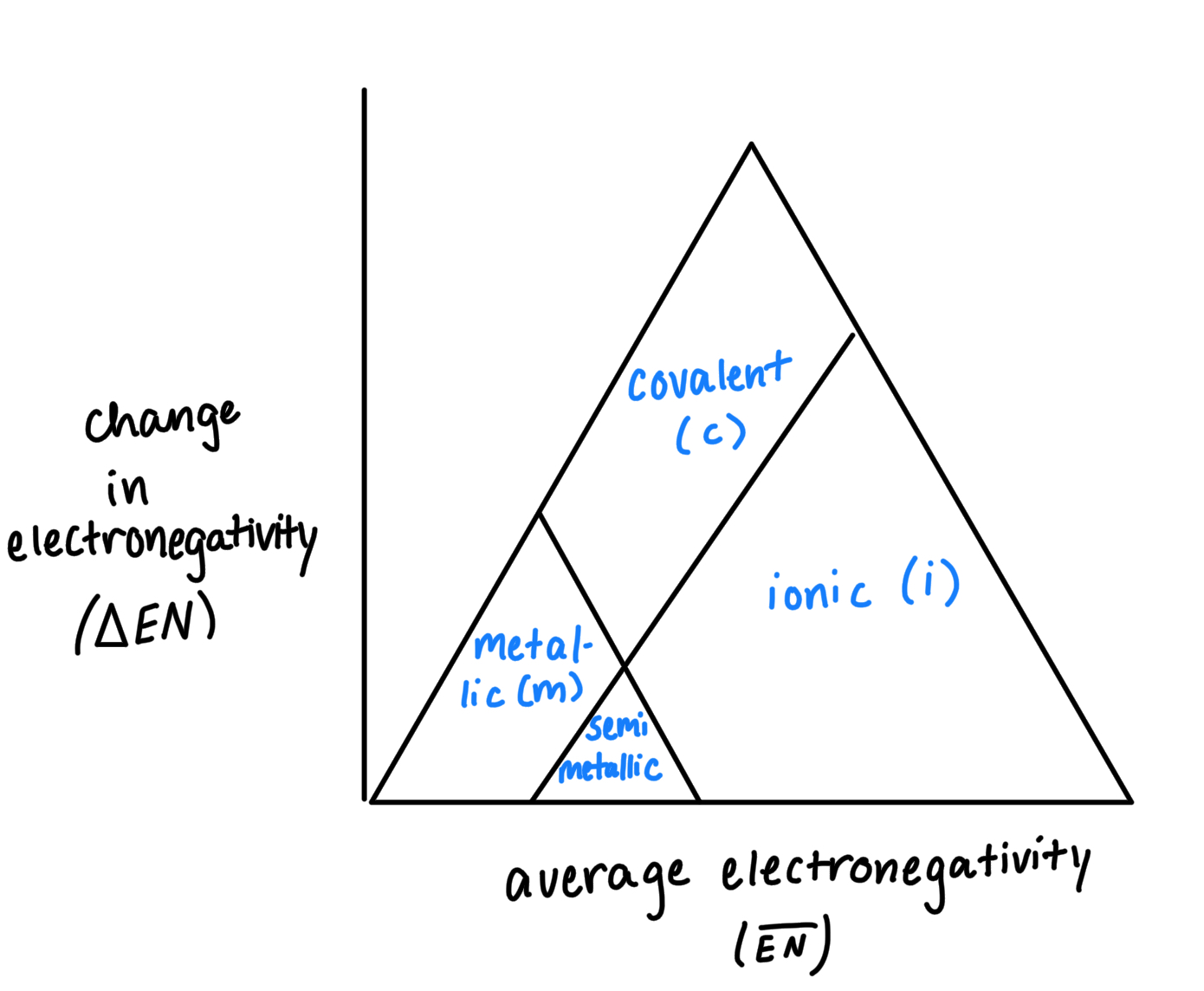
Covalent Bonds: are typically between a non metal and a non metal
Ionic Bonds: are typically between and non metal and a metal
Metallic Bonds: are usually between a metal and a non metal