Space Exploration Section 3 + 4
Section 3.0
Section 3.1
Telescopes → Allow us to see distant objects with more detail than just using our eyes
Types of Telescopes → Optical, Refracting, Reflecting
Optical Telescopes → Use a series of lenses and mirrors to gather and focus light (“light collectors”)
Refracting Telescopes → Use two lenses to Gather and focus light (Bends light as it goes through the lenses)
Reflecting Telescopes → Use mirrors, One side has a large concave mirror (Light bounces off the mirror onto another, then into the eye piece lens)
Segmented Mirrors → several mirrors used together to create a bigger mirror (Able to gather large amounts of light)
Interferometry → Combining telescopes for greater power (Quality is improved)
Hubble Space Telescope → A reflecting telescope that makes it easy to observe without light and air pollution \n Reflecting = Mirrors & Refracting = Lenses
Section 3.2
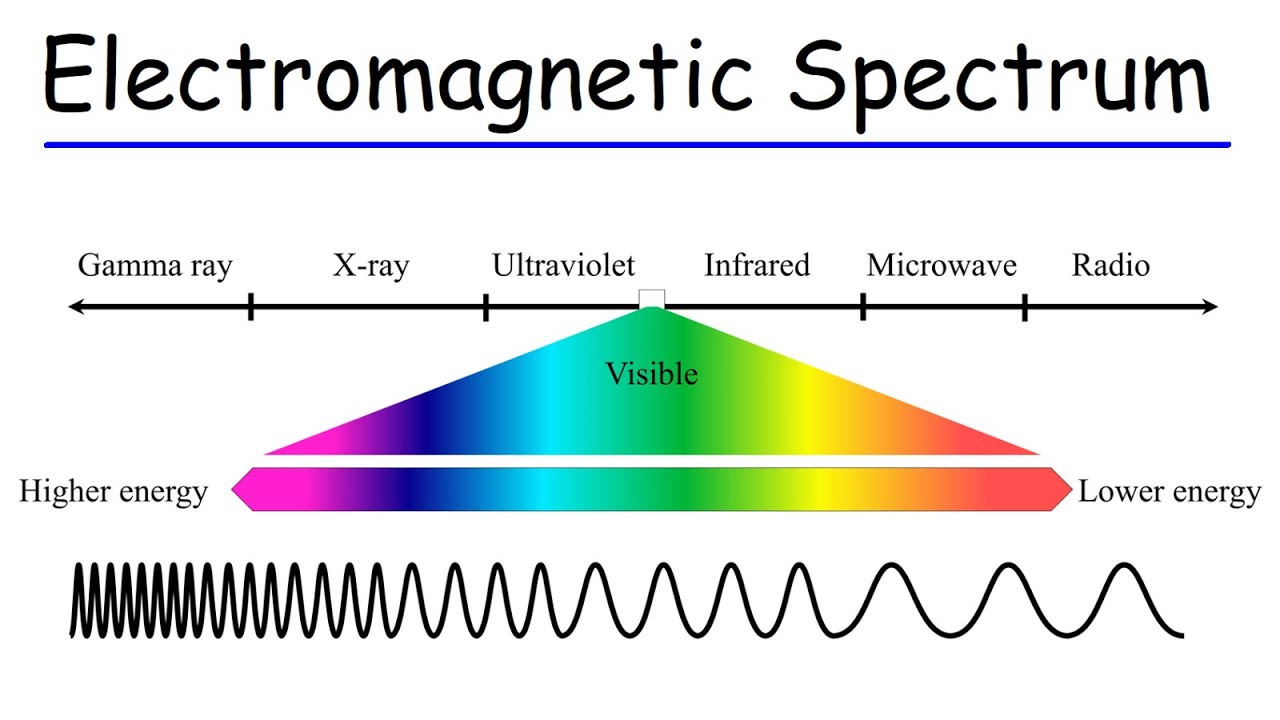
Electromagnetic Energy → radiated energy that travels at the speed of light but has different wave lengths and frequencies
Wavelength → Measured from one point on the wave to the same point on the next wave
Frequency → Number of waves that pass a point in a second (high frequency=short wavelength)
Electromagnetic Spectrum → Covers the whole range of electromagnetic energy
Radio Telescopes → Used to study radio waves emitted from objects in space (Signals are mapped through electronics and computers)
Radio Interferometry → Extreme detail in the radio maps (multiple telescopes)
Array → Group
Space Probes → unmanned space crafts that send the equipment directly to the object you want to study
Section 3.3
Triangulation → Used to indirectly measure distance (Based on the geometry of a triangle)
Parallax → Apparent shift of an object when it is viewed from two different places (Longer base line = more accurate result)
Visible Light → White light is actually a combination of all the colors of the rainbow (visible spectrum)
Determining a Star’s Composition → Astronomers use a spectrometer to compare the known spectra of elements to stars (happens because various elements absorb light in different ways)
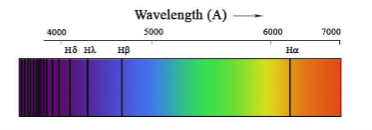
Doppler Effect → Apparent changes in frequency of waves as the observer and the wave source move towards or away from one another
Determining a Star’s Direction of Motion → An approaching star: bands move towards the blue end, A moving away star: bands move towards the red end
Section 4.0
Section 4.1
Apollo 1 (1967) → Had an accident where a fire broke out during a training exercise
Challenger (1986)→ Catastrophic explosion shortly after take-off
Columbia (2003) → Disintegrated upon re-entry to the Earth’s atmosphere
Apollo 11: it’s original landing site too rocky so the crew had to find a new spot (Only had enough fuel for one landing, Had to do it right the first time)
Dangers of Manned Space Travel → tons of explosives, Smallest error could be catastrophic, cosmic radiation, meteoroids, debris, Re-entry is highly dangerous
Space Junk → Pieces of debris that have fallen off spacecraft, rockets and satellites and \n remain in space
Micrometeorites → tiny pieces of space debris, if these pierced a space craft could be catastrophic
Hazards on Earth → Space Junk, crashes, radioactive debris \n
Section 4.2
First Magnetic Observatory (1839)→ Established by Sir Edward Sabine, Discovered aurora borealis
Alouette 1 (1962) → First Canadian Satellite in space
Anik 1 (1972) → Gave the whole country telecommunications coverage (Made Canada the first country in the world to use satellites to broadcast television)
Apollo 11 (again) → Ensured safe touch down for the first manned mission to the moon
Canadarm (1981) → Manipulated by remote control, Launched several satellites, Launched and fixed the Hubble Space Telescope, Put together pieces of the ISS (on Space Shuttle)
First Canadian in Space (1984) → Marc Garneau
First Canadian Female in Space (1992) → Dr. Roberta Bondar
First Canadian to Walk in Space (2001) → Chris Hadfield (Helped deliver the Canadarm 2 to the \n International Space Station)
Canadarm2 → Improved Canadarm with more joints and more capabilities
Dextre (2008) → “Handy man” on ISS
Section 4.3
Pros of Space Exploration → Space is the last great frontier, so we must explore it to find ways to improve earth, Demand for natural resources may increase to the point we need to look elsewhere
Cons of Space Exploration → Many problems here on earth, why don’t we solve those first?, Money should go to relieving suffering on our own planet
Space Resources → Solar energy, Asteroids could be mined for precious metals, building spacecraft in space
Moon Resources → Hydrogen and oxygen can be produced from moon rock, Hydrogen could be used as fuel, Oxygen could be used for life support
Three types of issues → Political, Ethical, Environmental
Political Issues → Who owns space?, Who has the right to use the resources in space?, Who will determine how space will be used?
Ethical Issues → Is it right to spend money on space exploration rather than solving problems on Earth?, Do we have a right to alter materials in space to meet our needs?, How can we ensure space resources will be used for good?
Environmental Issues → Who is responsible for protecting space environments from alteration?, Who is responsible for cleaning up space junk and who should pay for doing it?