1.4 - CompTIA A+ Core 2
1.4a - Task Manager: Professor Messer
Task Manager
Task Manager: Windows utility that provides a real-time view of important system processes and performance metrics, allowing users to monitor application status.
Can be accessed via multiple methods:
Ctrl + Alt + Del→ select Task ManagerRight-click → select Task Manager
Ctrl + Shift + EscWin + R→taskmgr
Services
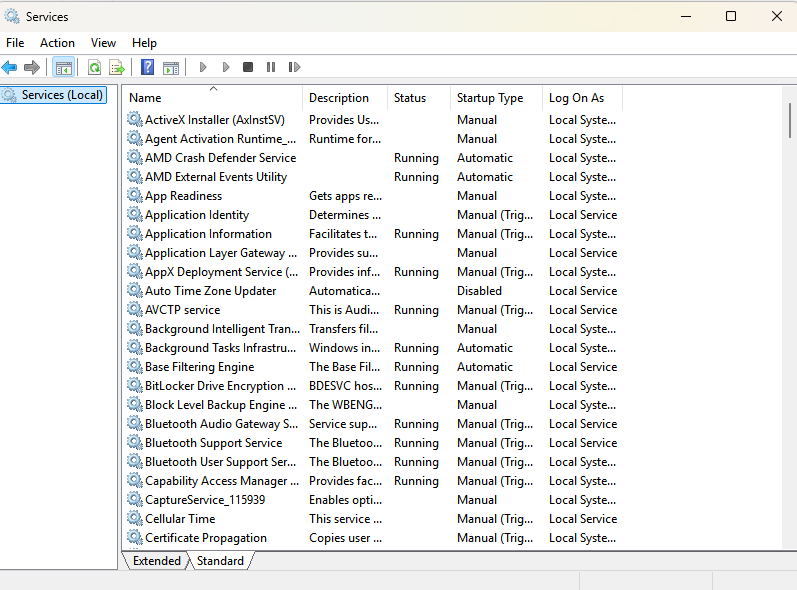
Services (Task Manager): Lists non-interactive applications and background processes - Task Manager provides a single point of management for these services, enabling users to start, stop, or configure system services as necessary.
Startup
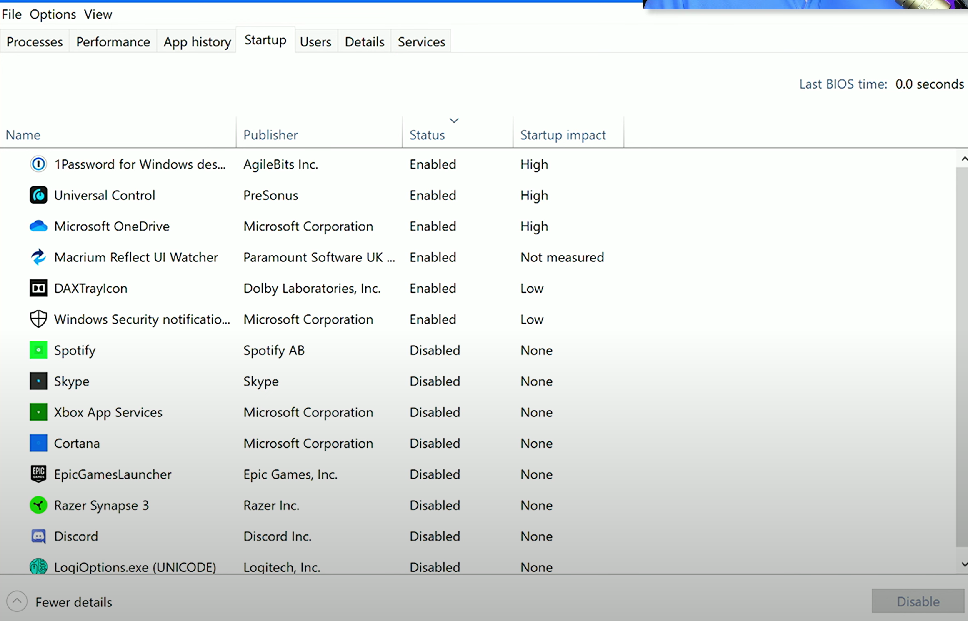
Startup (Task Manager): Allows users to manage which programs start on Windows login and provides options to toggle these on and off.
Processes
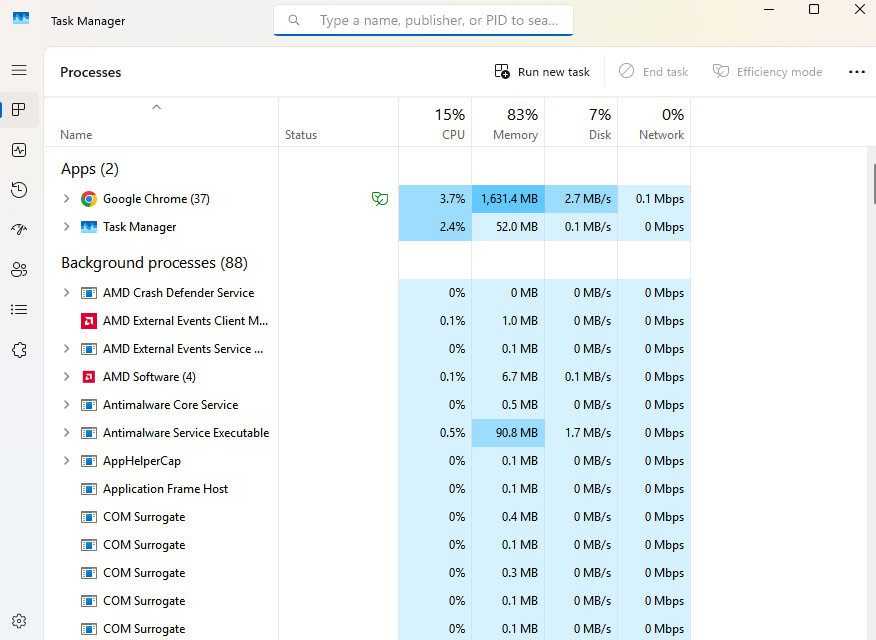
Processes (Task Manager): Allows users to view/manage all active programs, including system tray apps and processes from other accounts.
Performance
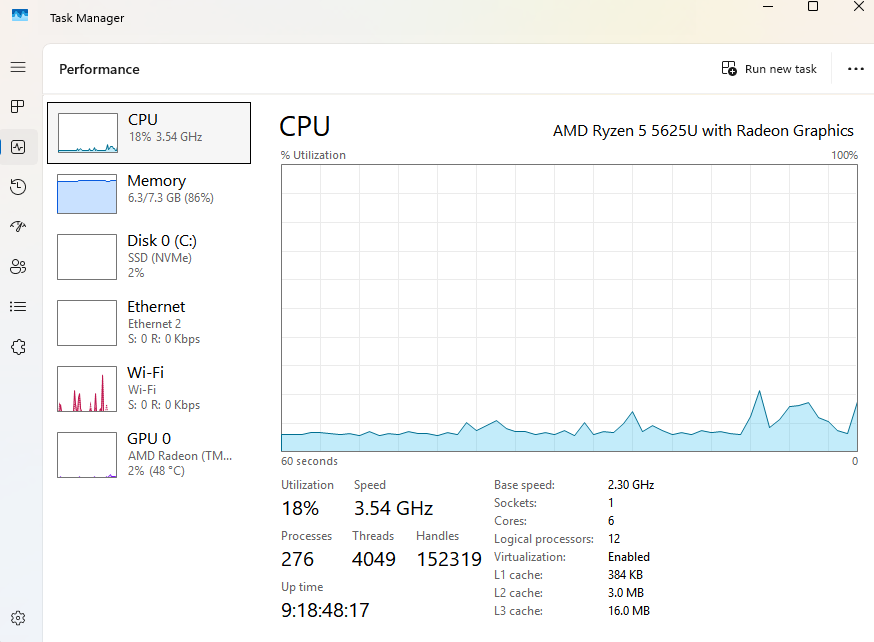
Performance (Task Manager): Provides real-time monitoring of CPU, memory, disk, and network usage, helping users to identify resource-hogging applications and optimize system performance.
Users
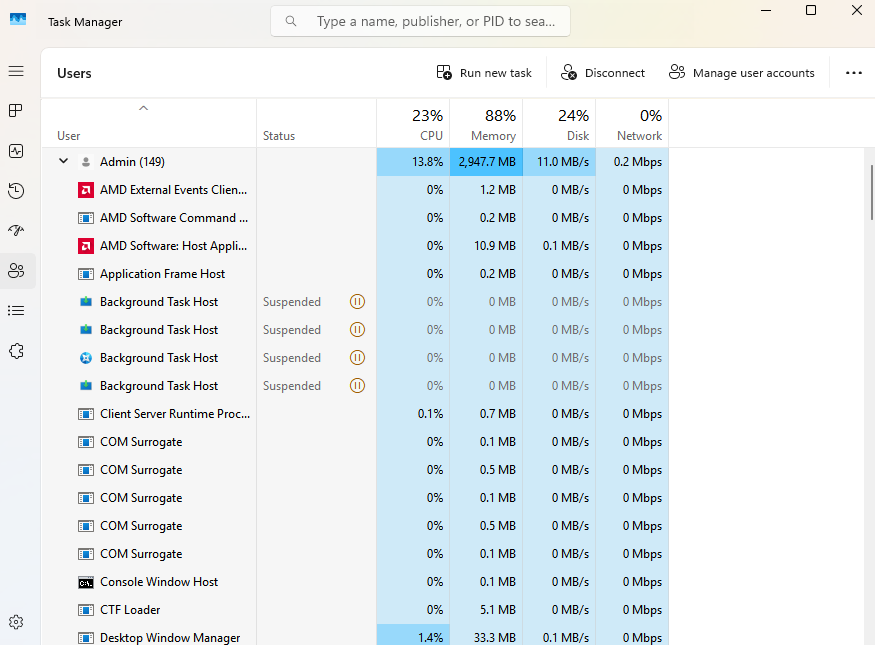
Users (Task Manager): Provides information on individual users’ sessions and the resources used by each particular user. Also allows the owner of the laptop/workstation to revoke access (if they’re an Administrator).
1.4b - The Microsoft Management Console: Professor Messer
Microsoft Management Console (MMC) snap-in
Accessible via
mmc.exe.Allows users to build their own console to show particular system utilities, used to help with troubleshooting.
Initially empty on first startup - system utilities (e.g., Event Viewer, Task Scheduler, Disk Management) are added via File → Add/Remove Snap-in…
Event Viewer (eventvwr.msc)
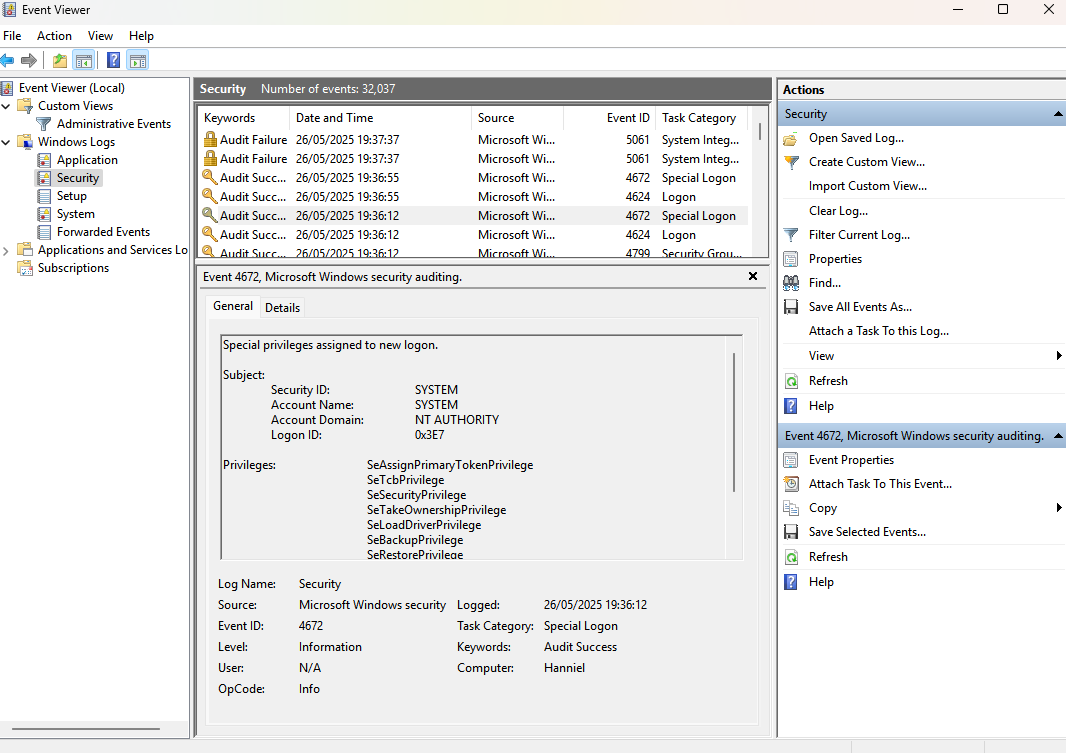
Event Viewer (
eventvwr.msc): Provides a centralized view of events/logs generated by the system and applications. Split into different categories (Application, Security, Setup, System), and different severity levels (Information, Warning, Error, Critical, etc).
Disk Management (diskmgmt.msc)
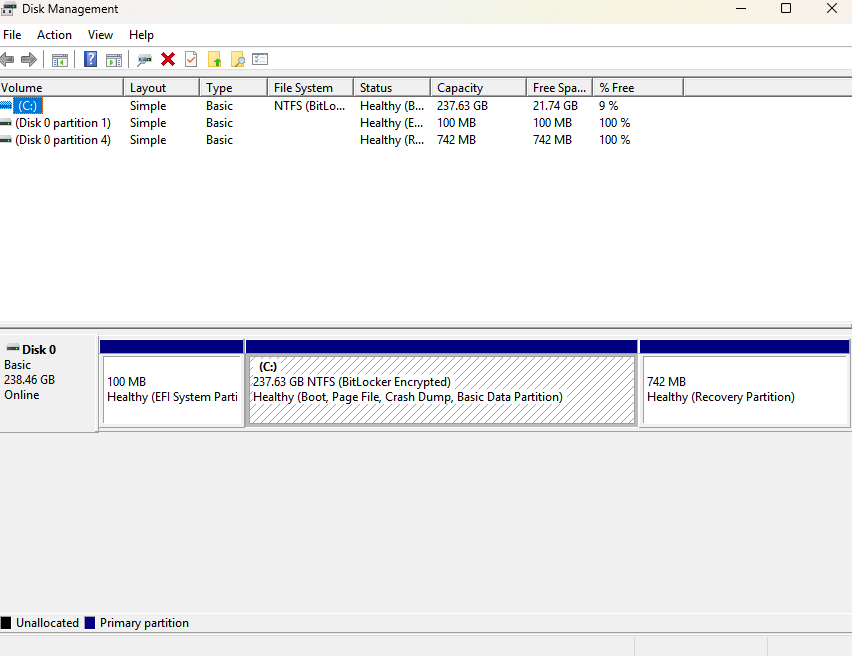
Disk Management (
diskmgmt.msc): Provide disk drive management functionality, including for partitions, and the filesystems used for those partitions. ALWAYS HAVE A BACKUP WHEN WORKING WITH DISK DRIVES - YOU CAN ERASE DATA.
Task Scheduler (tasksch.msc)
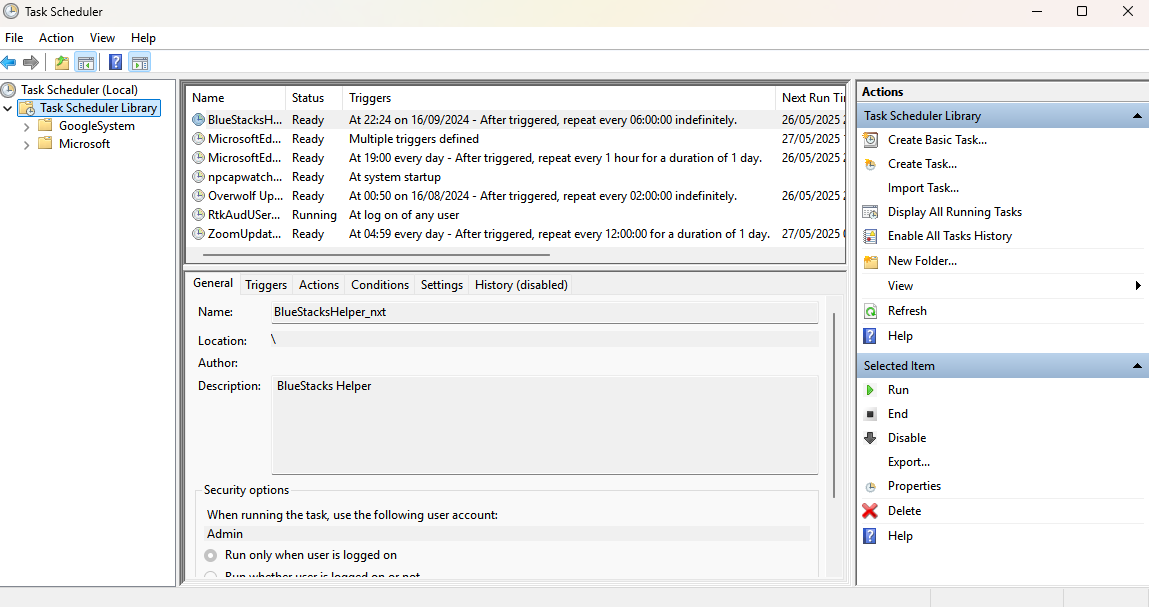
Task Scheduler (
tasksch.msc): Allows users to automate tasks on a local or remote computer, enabling scheduled execution of applications, scripts, and system maintenance tasks. Includes predefined execution schedules and organizes similar tasks into folders.
Device Manager (devmgmt.msc)
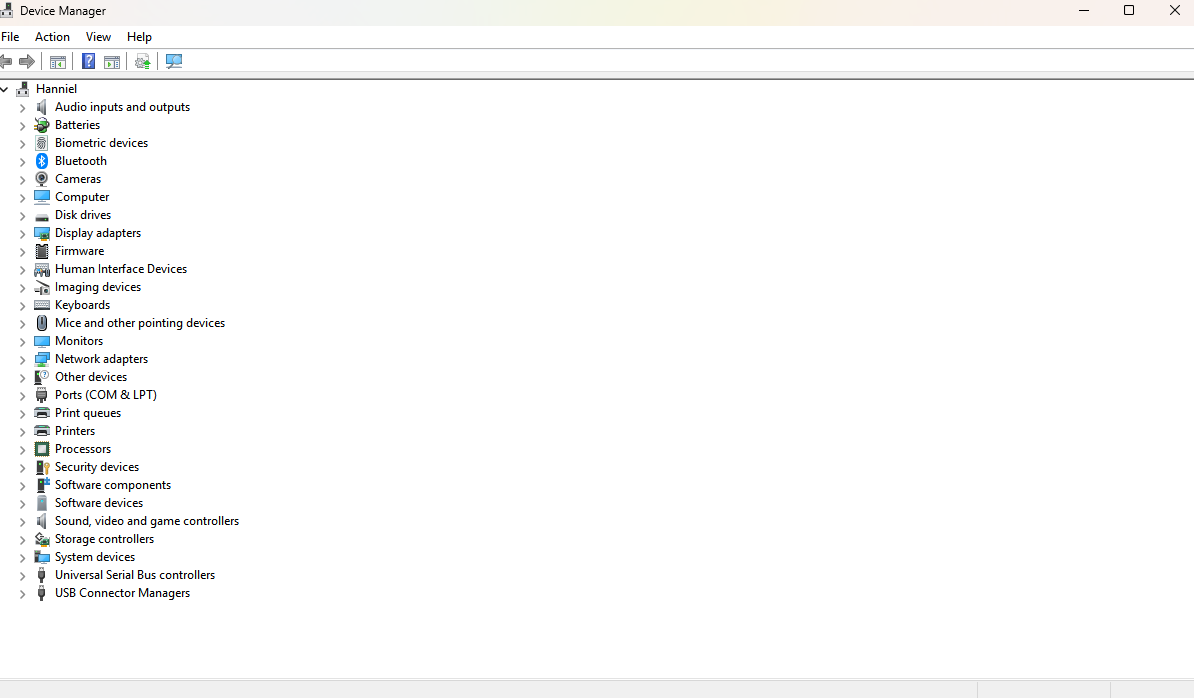
Device Manager (
devmgmt.msc): Allows centralized management of peripheral devices (e.g., keyboards, mice, speakers), and their associated device drivers. Also provides the ability to update, disable, or uninstall system drivers.Device drivers are hardware and operating system-specific. Some drivers are written to function across multiple operating systems, however.
Certificate Manager (certmgr.msc)
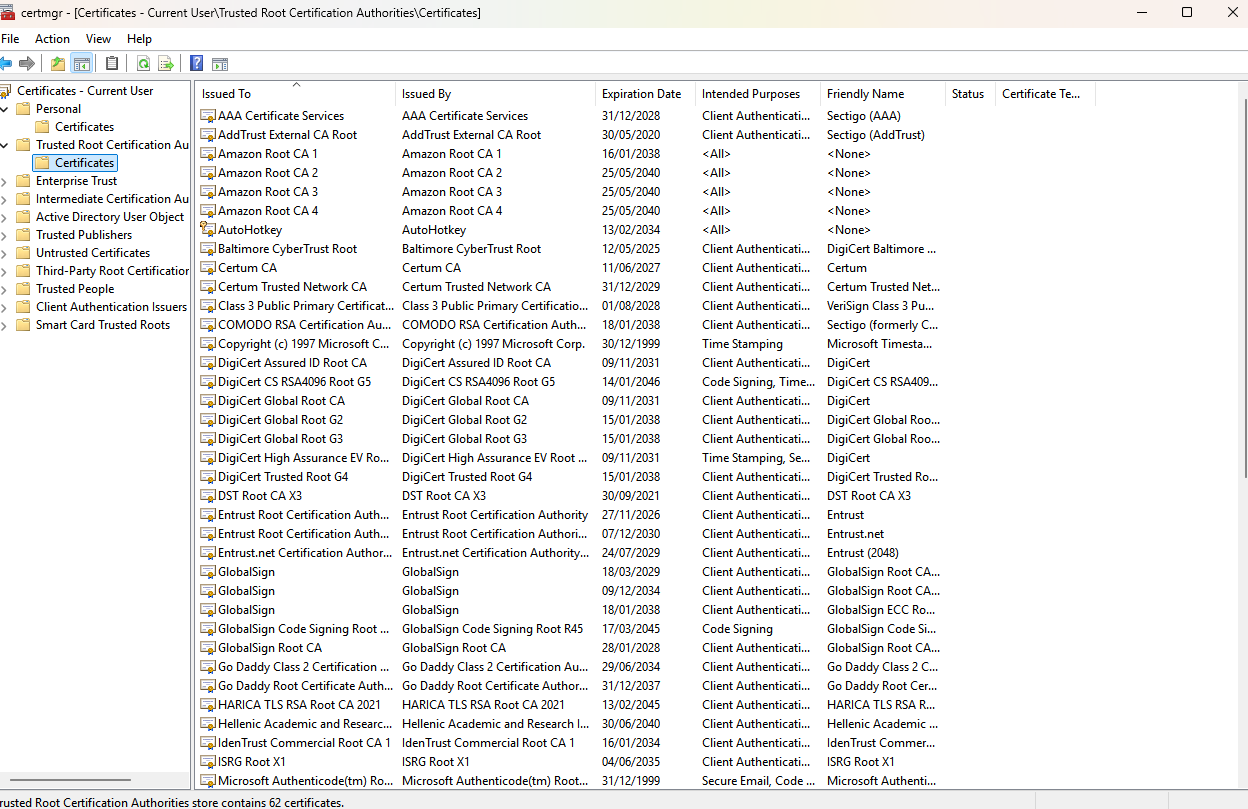
Certificate Manager (
certmgr.msc): Allows users to manage digital certificates on the system, including viewing, installing, or deleting certificates used for security purposes in various applications.
Local User and Groups (lusmgr.msc)
Local User and Groups (
lusrmgr.msc): This management console enables administrators to manage user accounts and groups on the local computer, including creating new accounts, modifying existing accounts, and assigning group memberships to control user permissions.
Performance Monitor (perfmon.msc)
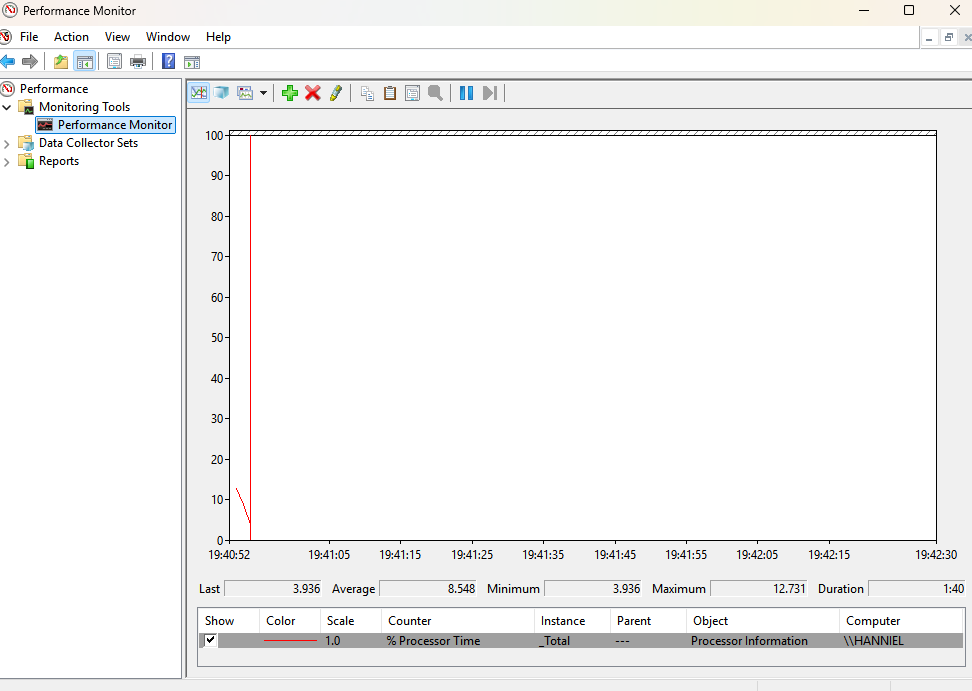
Performance Monitor (
perfmon.msc): This tool provides long-term/historical monitoring of system performance, allowing administrators to analyze OS metrics such as CPU usage, memory consumption, and disk activity. Users can also set alerts and automated actions, and generate reports to view data.Good to check for intermittent but unpredictable issues (e.g., intermittent network connectivity).
Group Policy Editor (gpedit.msc)
Group Policy Editor (
gpedit.msc): Windows utility that provides centralized, granular control over what features Windows users have available. Used for local device management.
Group Policy Management Console (gpmc.msc)
Group Policy Management Console (
gpmc.msc): Provides centralized control over the features Windows users have available. Administration is provided via Active Directory.
1.4c - Additional Windows Tools: Professor Messer
Additional tools
System Information (msinfo32.exe)
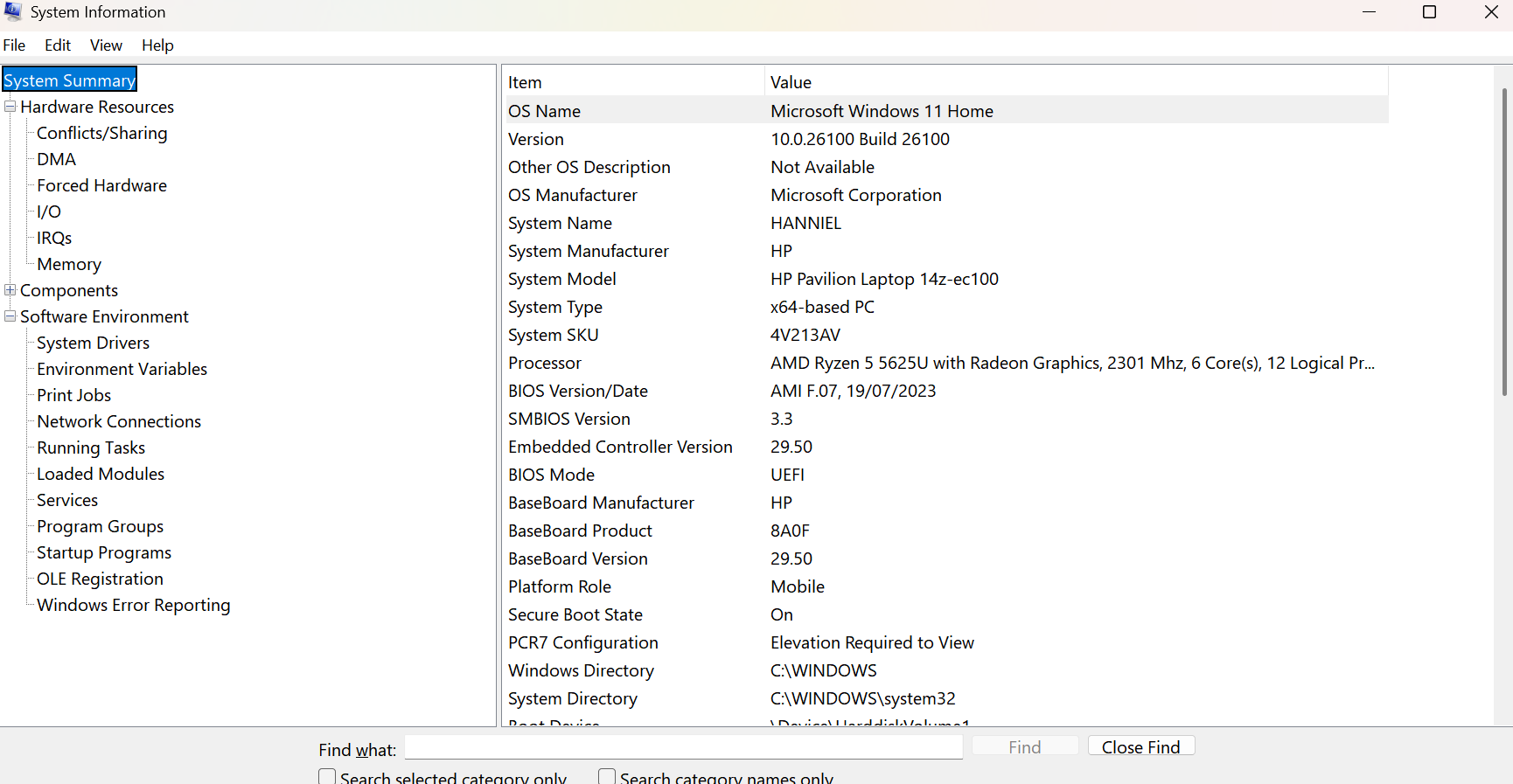
System information (
msinfo32.exe): Provides a quick overview of a machine and it’s configurations. Includes Hardware Resources (Memory, DMA, conflicts), Components (Multimedia, display, network), and Software Environment (System Drivers, Print Jobs, Services).
Resource Monitor (resmon.exe)
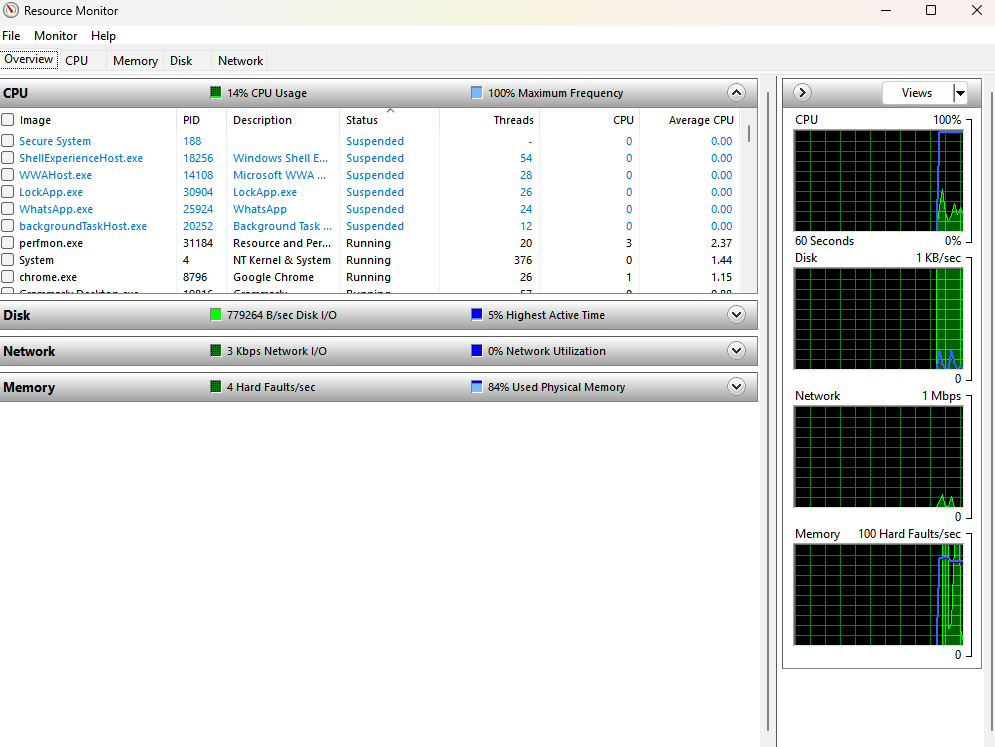
Resource Monitor (
resmon.exe): Provides historical and real-time information about the utilization of hardware resources, such as CPU, memory, disk, and network, allowing users to diagnose performance issues and monitor system resource usage.
System Configuration (msconfig.exe)
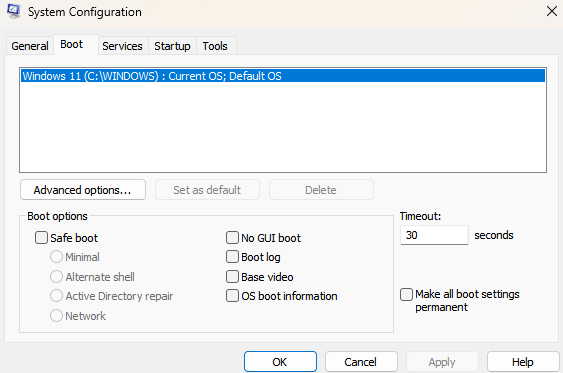
System Configuration (
msconfig.exe): Windows utility that allows users to manage boot processes, and services at startup, modify boot options, and troubleshoot system performance issues.
Disk Cleanup (cleanmgr.exe)
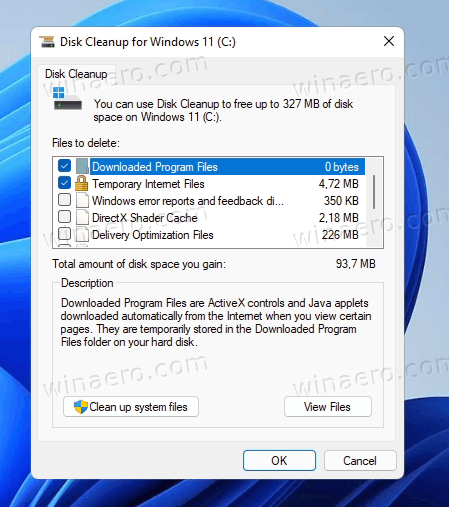
Disk Cleanup (
cleanmgr.exe): Windows utility that finds unused/unnecessary files and deletes them to free up space.
Disk Defragment (dfrgui.exe)
Disk Defragment (
dfrgui.exe): Windows utility that moves file fragments so they are contiguous (similar files in similar sections) - improves the read and write times for hard disk drives (HDDs). Windows won’t defrag an SSD.
Registry Editor (regedit.exe)
Registry Editor (
regedit.exe): A tool that allows users to view and modify the Windows registry, which contains saved settings and options for the operating system and installed applications. Do not make any changes without backing up your registry (feature built into regedit), and knowing what you’re doing.