Ch. 3: Federalism
Reading Questions (72-84)
What is Federalism?
A way of organizing a nation where two (or more) levels of government have authority over the same area/people.
National (Federal) government can pass laws that effect states.
Ex: State of California & National/Federal Government both have power over California residents.
What are the 3 types of power distribution mentioned in the reading? Explain each
Federalism: Two or more levels of government have authority over the same area/people.
Unitary Gov.: All power remains only in the Federal Government
Confederation: National Government is weak, most power is given to states
The U.S originally began as a Confederation
Changed to Federalism since America was too spread out and large to have a central government
According to Gonzales v. Raich, what power gives the Federal government the authority to criminalize and regulate marijuana sales and consumption in California? (Pg. 72)
The Constitution’s commerce clause allows the federal government to regulate commerce within foreign nations and states.
Marijuana users argued this, since it was grown, transported, and consumed in the state, with no federal involvement.
Commerce is the exchange of goods or services between two or more entities (usually involving currency).
How many levels of government exist in the United States Federal system?
Two: Federal and State
There is also local but that isn’t written in the constitution.
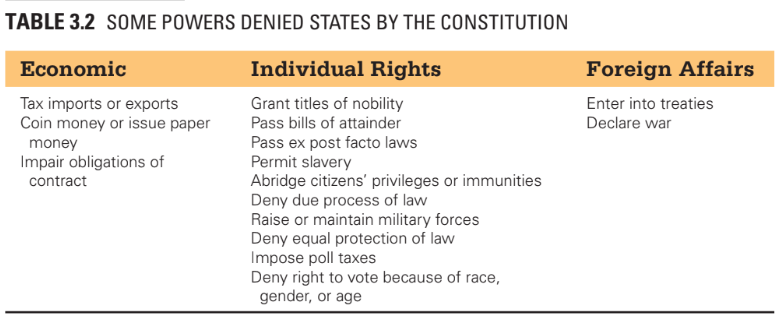
Identify several powers that belong exclusively to the Federal government, and several that belong exclusively to the states (Pg. 78/79)
Federal Government Powers: Declare war, manage treaties, establish military, collect (federal) taxes, & regulate inter-state commerce.
States: Managing elections, ratifying constitutional amendments, establishing governments, state militias, & manage.
Both: Establishing courts, maintaining law/order, protecting citizens’ health/safety, and regulating financial institutions.
What is the supremacy clause and why’s it so important?
Federal Government is boss. State laws can’t override a Federal law.
Marijuana law is legal in CA, but Federal law says no. Federal law overrides the state law.
Establishes power over states. If there’s a conflict, Federal government usually prevails.
Why is the Commerce Clause so important in expanding Federal power beyond the literal scope of the Constitution?
Construction says: National gov. can manage outer-state commerce.
Commerce can go though any form, so the clause gives the Federal government the power to manage all that.
Allows Congress to build infrastructure, manage trade, & protect consumers.
Why is the 10th Amendment vital in maintaining balance in a federal system?
The 10th amendment ensures both Federal and State governments don’t overstep on each other.
Aka: Federal/National government only has powers that the Constitution gives it.
What are implied powers, Reserved Powers, and Concurrent powers. Give an example of each.
Implied Powers: Are powers of the federal government that aren’t specifically stated in the Constitution, but align with the goal of the Constitution.
Ex: Congress creating the National Bank was “necessary & proper for the government to function”
Reserved Powers: Powers reserved for the state since they aren’t stated in the Constitution (comes from the 10th amendment).
Concurrent Powers: Powers that are shared with Federal & State
Ex: Capitol is a State Road, 101 is a Federal Road
What function does the elastic clause serve for the federal government
Authorizes Congress to pass all laws “necessary and proper” to carry out the enumerated powers. (Pg. 81)
Why is McCulloch vs Maryland in this chapter rather than in the chapter with all the other cases?
State said no National Bank, but Supreme Court ruled Yes National Bank in McCulloch vs Maryland
Implied Powers are super important, since without it, the Federal Government would be locked to duties only in the Constitution.
Extra Notes (From Reading):
Intergovernmental Relations: How national, state, and local governments interatc
Interactions include regulations, transfer of funds, & sharing information
Interstate Commerce Power: Allows Congress to protect environment, civil rights, providing health care for elderly/less fortunate, etc.
Full faith and Credit: Every state has to honor every other state’s rights/records.
US v Lopez: Congress passed a law saying “No Guns in School”. Texas argued that congress couldn’t rule over state schools. Fed. said “Commerce Clause” but supreme court shot that down and ruled in Texas’s favor.
Good argument for “The Government needs to stay back (conservative)”
Rest of Ch.3 Questions
What are enumerated, implied, and reserved powers
What is Full Faith and Credit? Give an example
States need to give other states respect for their documents
Examples: Marriage license & Drivers licenses
Explain what extradition is and how it might be applied
All states must extradite to other nations
Example: WikiLeaks CEO ran to Equador’s Embasy in England
What are Privileges and Immunities? Give an example. How is it different from Full Faith and Credit?
Out of state visitors can’t be treated differently from in-state residents.
Exceptions: College tuition
What is the difference between Dual Federalism and Cooperative Federalism? Which one do we employ?
Dual Federalism is when there are teirs of government (Federal & State like the US)
Cooperative Federalism is when local governments must cooperate with each other and share power.
What is Devolution?
When the responsibilities of the Federal Government fall to the state gov.
Define Grants-in Aid. What are they typically used for?
Grants are the federal government giving money for someone/something to do a task.
Ex: If the federal government wanted the state to do … give them money.
What is the distinction between a categorical grant and a block grant? Which party prefers each? Why
Extra Notes:
Far Right/Left is a spectrum. Far Rights are conservatives (Republicans), Far Lefts are Liberals (Democratic & Green Parties).
Federalists 10 Questions:
According to Madison, what is a “faction” in today’s terms?
Political Parties
What are the dangers of faction according to Madison
Causes the nation to rip apart since different “Factions” would fight with each other, opposing each other instead of acting for the common good.
If factions “control” a state, they could terrorize the minority. A strong central government could be able to control factions.
What are the ways in which Madison proposes a nation can control faction? (Yes, all of them, even the ones he discounts eventually)
Abolish liberty (remove the right for people to faction in the first place).
Allow everyone to have beliefs, but use manipulation to standardize those beliefs.
Have the federal government have more power to control these factions.
Identify the reasons why all but one of his solutions are ultimately dismissed.
The 1st solution was to abolish liberty, which goes against everything American.
What is Madison’s ultimate suggestion for the best way to control faction?
Have the federal government have more power to control these factions.
How does Madison’s solution solve the problem of faction?
Madison believes a strong central government will help control regional factions.
Brutis 1 says the opposite, there shouldn’t be a strong central government because it would control everything (would eventually swallow up states’ power).
Summary: Fed 10 says there should be a strong government
→ States wouldn’t even need to exist bc of how strong the central government is.