Valvular Heart Disease
mitral valve 2 leaflets only
all other valves tricuspid
stenosis- narrowing of valve leaflet
regurgitation - incompetence, not keeping seal it should
rheumatic hear disease - streptococcal infection, most common cause of mitral stenosis
congenital too
mitral stenosis also seen in Lupus…
Mitral valve orifice <2 cm squared
left ventricle function normal in mitral stenosis until very late stages
flow rate depends on HR, pumping blood faster, trans valvular gradient will increase too
breathless, haemoptysis, systemic embolisation, chest pain or hoarseness in mitral stenosis
any valve that’s abnormal can get infected
clinical examination in mitral stenosis: -RV heave -JVP prominent a wave -mitral facies
can be longer p wave on ECG in mitral stenosis
prominent R waves in V1 and V2
bulging of left heart border or left atrium enlargement on xray of mitral stenosis
thickening and scarring of the leaflets
fusion of the commissures
treatment for mitral stenosis:
-diuretics -restriction of Na intake
when severe valvotomy (balloon or surgical), the balloon is very temporary measure
replacement of mitral valve
mitral regurgitation
mitral valve prolapse more likely in the UK and also degenerative
effective regurgive .. not fixed
preload, afterload, LV contractility affect whether mitral regurgitation is acute or chronic
•Acute MR (valve perforation, chordal/papillary muscle)
•Breathlessness: pulm oedema, cardiogenick shock
•Chronic MR:
•Fatigue, exhaustion (low CO), Right heart failure
•Dyspnoea or palpitations due to AFib
•Pulse – normal or reduced in heart failure
•JVP – prominent if RH failure present
•Brisk and hyperdynamic apex beat
•RV heave
holosystolic/pansystolic, loud at apex radiating to axilla
aortic valve 3-4 cm squared
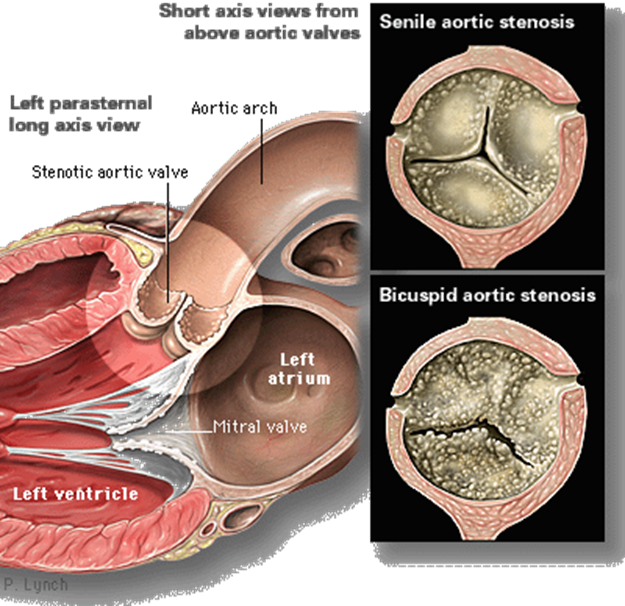
degenerative, rheumatic and some born with bicuspid aortic valve through fusion of cusps or just made out of two leaflets not necessarily equal - most common
aortic stenosis most common valve disease in adult life
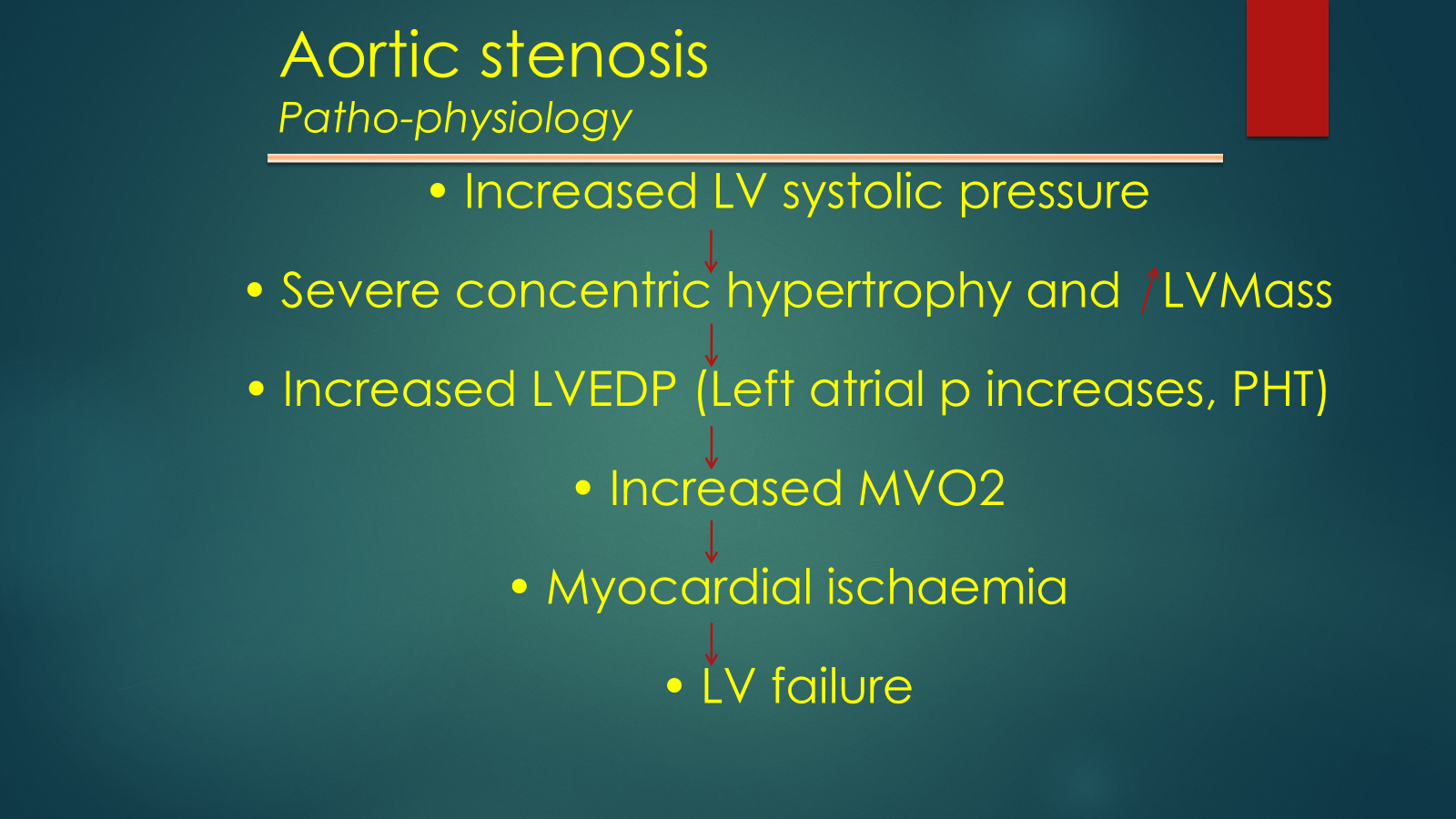
long asymptomatic phase
when symptomatic survival drops
4L per second speed of blood circulation, causes more degeneration as more damage and scarring and calcification will occur on endothelium
aortic regurgitation either pulmonary oedema and cardiogenic shock or left ventricular failure
early diastolic, decrescendo, soft murmur
displaced apex beat, large pulse that collapses very quickly
high systolic blood pressure
wide pulse pressure
pulse into carotids coming up and down if lying flat
after second heart sound decrescendo soft murmur
cardiomegaly/bovine heart
ECG ST/T changes (LV strain)
failure of three leaflets centrally allows regurgitation to occur
vasodilator therapy, delays surgery for 3-4 years
or aortic valve replacement or repair
 Knowt
Knowt