Module 15: Evolutionary Psychology
How do evolutionary psychologists use natural selection to explain behavior tendencies?
- Behavior geneticists explore the genetic and environment roots of human differences.
- ^^Evolutionary psychology^^: Study of the evolution of behavior and the mind, using natural selection
- Uses Charles Darwin’s principle of natural selection to understand the roots of behavior and mental processes
- Charles Darwin’s Idea of ^^Natural Selection^^: Principle that, among the range of inherited trait variations, those contributing to reproduction and survival will most likely be passed on;
- Organisms’ varied offspring compete for survival
- Certain biological and behavioral variations increase organisms’ reproductive and survival chances in their particular environment
- Offspring survive → more chance of their genes passing to next generation
==Natural Selection and Adaptation==
- Some genetic variations arise from mutations, others from new gene combinations at conception
- ^^Mutation:^^ random error in gene replication that leads to a change
==Evolutionary Success Helps Explains Similarities==
- Our shared human traits “were shaped by natural selection acting over the course of human evolution”
Our Genetic Legacy
- Our behavioral and biological similarities arise from our shared human genome, our common genetic profile
- Humans share a genetic legacy and are predisposed to behave in ways that promoted our ancestors’ surviving and reproducing
==An Evolutionary Explanation of Human Sexuality==
How might an evolutionary psychologist explain gender differences in sexuality and mating preferences?
Gender Differences in Sexuality
- Males are more likely than females to initiate sexual activity
- Men also have a lower threshold for perceiving warm responses as sexual come-on
- Men more often than women perceive a woman’s friendliness to sexual interest
- This helps explain, but not excuse, men’s greater sexual assertiveness
- Unfortunate consequences can range from sexual harassment to rape
Natural Selection and Mating Preferences
- Evolutionary psychologists use natural selection to explain why women’s approach to sex is usually more relational, and men’s more recreational
- While a woman incubates and nurses one infant at a time, a male can spread his genes through other females
- Our natural yearnings are our genes’ way of reproducing themselves: Woman pairing wisely, men by pairing widely
- What do heterosexual men and women find attractive in a mate?
- Evolutionary psychologists say that men who were drawn to health, fertile-appearing women, suggest many childbearing years, which stood a better chance of sending their genes in the future
- Teen boys → women several years older than them
- Mid-twenties men → women around the same age
- Older men → women younger than them
- Women, in turn, are attracted to men who seem mature, dominant, bold, and affluent (wealthy), with a potential for long-term mating and investment in their joint offspring
- Because women incubate and nurse babies, they increase their own and their children’s chances of survival by searching for mates with the potential for long-term investment in their joint offspring
- Nature selects behaviors that increase the likelihood of sending one’s genes into the future
The Evolutionary Perspective on Human Sexuality
What are the key criticisms of evolutionary psychology, and how do evolutionary psychologists respond?
- Critics argue the evolutionary psychologists (1) starts with an effect and work backward to an explanation, (2) do not recognize and cultural influences, and (3) absolve people from take responsibility for their sexual behavior
- Evolutionary psychologists respond that understanding our predispositions can help us overcome them. They also cite the value of testable predictions based on evolutionary principles, as well as the coherence and explanatory power of those principles.
==Reflection on Nature and Nurture==
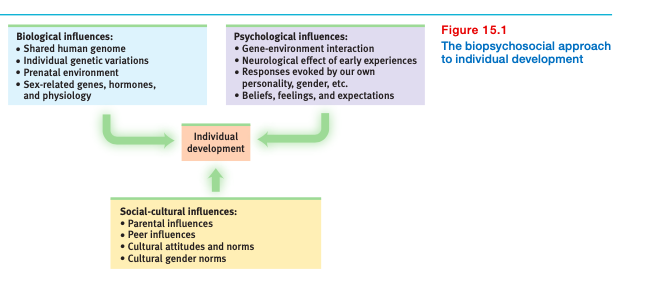
What is included in the biopsychosocial approach to individual development?
Where there is variation, natural selection, and heredity, there will be evolution
If genes and hormones predispose males to be more physically aggressive than females, culture may magnify this gender difference through norms that encourage males to be macho and females to be the kinder, gentler sex
- If men are encouraged toward roles that demand physical power, and women toward more nurturing roles, each may then exhibit the actions expected of them and find themselves shaped accordingly. Roles remake their players
- Presidents in time become more presidential, servants more servile. Gender roles are similarly shape us
- As the roles we play change over time, we change with them
We are the product of nature and nurture, but also an open system (biopsychosocial approach)
Individual development results from the interaction of biological, psychological, and social-cultural influences
Everything psychological is simultaneously biological