Chapter 25: Blood
Composition of Blood
Plasma
55% of blood
90% is water
7% is protein
3% is dissolved materials
Golden straw colour
Function
Transport of dissolved substances e.g:
Digested foods - glucose, water, vitamins, minerals
Wastes- urea, salt, carbon dioxide
Hormones - insulin
Antibodies
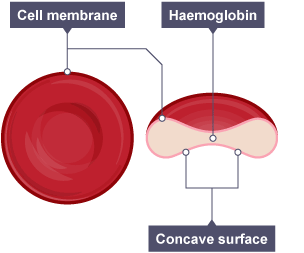
Red Blood Cells (red blood corpuscles/erythrocytes)
Made in bone marrow of large bones e.g. long bones in arms and legs - sternum, ribs.
No nucleus
No mitochondria
Biconcave shape - larger surface area
Flexible cell membranes
Contain haemoglobin - high affinity for oxygen
5 million per cubic millimetre
3 million replaced every second
Life of 4 months
Function: Transport oxygen
White Blood Cells
Have a nucelus
No definite shape
Formed in bone marrow - mature in spleen and lymphatic system.
Life of a few days to a few years
Less numerous than RBCs
Function
Protect against disease in two ways:
Lymphocytes - produce antibodies (25% of WBCs, 10 year lifespan, large round nucleus)
Phagocytes - engluf bacteria by phagocytosis, also known as macrophages (survive 6-9 days, nucleus kidney shaped)

Platelets (thrombocytes)
Made in bone marrow
Cell fragments
Function: Clot blood (damaged cells produce chemical that causes platelets to clot)
Functions of Blood
Transport heat
Transport of food, hormones etc.
Fight infection through phagocytosis, lymphocytes producing antibodies, and platelets clotting to prevent microorganism entry.
Blood Groups
A
B
AB
O
400 other blood groups, most common is Rhesus factor, which is a chemical on the surface of red blood cells.
85% Rh+ 15% Rh- (irish population)
Rhesus negative mother with rhesus positive baby can result in problems.