Heart Lab
Overview of the Heart and Circulatory System
Basic Structure
Lungs
Diaphragm
Base
Apex
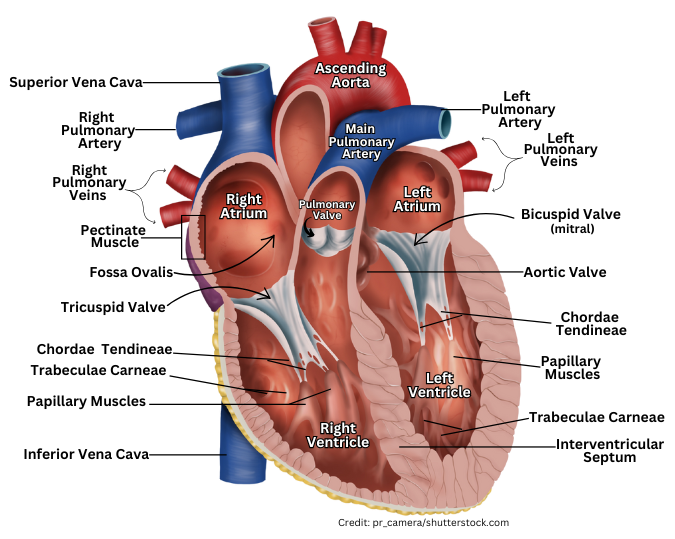
Heart Anatomy
Chambers of the Heart
Right Side
Right Atrium: Receives deoxygenated blood from the body via the superior and inferior vena cavae.
Right Ventricle: Pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs through the pulmonary trunk.
Left Side
Left Atrium: Receives oxygenated blood from the lungs through the pulmonary veins.
Left Ventricle: Pumps oxygenated blood to the rest of the body via the aorta.
Anatomy Details
Auricles: Extensions of the atria that increase capacity.
Ventricles: Larger chambers that pump blood out of the heart.
Anterior Ventricle: Refers to the left ventricle.
Posterior Ventricle: Refers to the right ventricle.
Major Blood Vessels
Blood Flow Pathways
Aorta: Major artery supplying oxygenated blood to the body.
Superior Vena Cava: Brings deoxygenated blood from the upper body to the right atrium.
Inferior Vena Cava: Carries deoxygenated blood from the lower body to the right atrium.
Pulmonary Trunk: Divides into the right and left pulmonary arteries; carries deoxygenated blood to lungs.
Pulmonary Veins: Bring oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium.
Coronary Arteries: Supply blood to the heart muscle itself.
Coronary Circulation
Right Coronary Artery: Supplies blood to the right side of the heart.
Left Coronary Artery: Supplies blood to the left side of the heart.
Cardiac Veins: Drain into the coronary sinus and then into the right atrium.
Heart Valves
Function and Types
Tricuspid Valve: Between right atrium and right ventricle.
Pulmonary Semilunar Valve: Between right ventricle and pulmonary trunk.
Bicuspid (Mitral) Valve: Between left atrium and left ventricle.
Aortic Semilunar Valve: Between left ventricle and aorta.
Intrinsic Conduction System
Sinoatrial (SA) Node: Natural pacemaker of the heart.
Atrioventricular (AV) Node: Receives impulses from SA node and transmits them to ventricles.
AV Bundle (Bundle of His): Pathway from AV node to bundle branches.
Right & Left Bundle Branches: Conduct impulses through the ventricles.
Purkinje Fibers: Spread electrical impulses throughout the ventricles causing contraction.
Blood Flow Pathway
Pulmonary Circuit
Right atrium → Tricuspid valve → Right ventricle → Pulmonary semilunar valve → Pulmonary trunk → Lungs → Left atrium.
Systemic Circuit
Left atrium → Bicuspid valve → Left ventricle → Aortic semilunar valve → Aorta → Body → Returns via SVC and IVC to Right atrium.
Fetal Circulation vs. Newborn Circulation
Fetal Circulation: Oxygen and nutrients from the placenta; lungs nonfunctional; shunts like foramen ovale and ductus arteriosus bypassed.
Newborn Circulation: Independent cardiovascular system; fetal shunts close to reroute blood.
Postnatal Changes in Circulation
Ligamentum Arteriosum: Remnant of ductus arteriosus.
Fossa Ovalis: Remnant of foramen ovale.
Medial Umbilical Ligaments: Remnants of umbilical arteries.
Ligamentum Teres: Remnant of umbilical vein (round ligament of the liver).