MODULE 4.2: ATTENTION
controlled attention
topics
practice and automaticity
automatic vs. controlled processing
selective attention
divided attention
how does control of processing actually work?
practice, automaticity, automatic vs. controlled processing
color stroop
classic stroop task
try to name the ink color and do not read the word
attention and practice
with practice, (many) activities require less attention
ex- practiced drivers
reading is so automatic that we can’t “turn it off”
controlled vs. automatic processing
CONTROLLED PROCESSING: in tasks that require effortful attention
AUTOMATIC PROCESSING: in tasks well practiced, not much effort or attention needed
it can occur even without intention/conscious decision
its steps occur without conscious awareness
it does not interfere with other mental activity
caveat
an activity thought of as “automatic” may not actually be automatic in all its aspects
many aspects of “automatic” activities are not so
reading comprehension
typing an essay
riding a bike
careful about considering that seemingly automatic activity “does not require much effort/attention”
implications
practice leads to transition from controlled to automatic processing
however, for any given seemingly “automatic” behavior
only some components may have become automatic
some components may not have become automatic
aspects of task may still require controlled, effortful processing
selective attention
SELECTIVE ATTENTION: focusing on one input or one task while ignoring other stimuli
AUDITION: paying attention to one stream of sound over others
cocktail party problem
following one person’s conversation at party
daily life
VISION: paying attention to one object over others
controlled visual search- focusing on each object
AUDITORY-VISUAL: paying attention to reading vs. music
dichotic listening task
DICHOTIC LISTENING: two different speech streams to left, right ears; headphones
pay attention to speech in one ear (the attended channel) while ignoring information in other (the unattended channel)
SHADOWING: repeat back attended channel speech
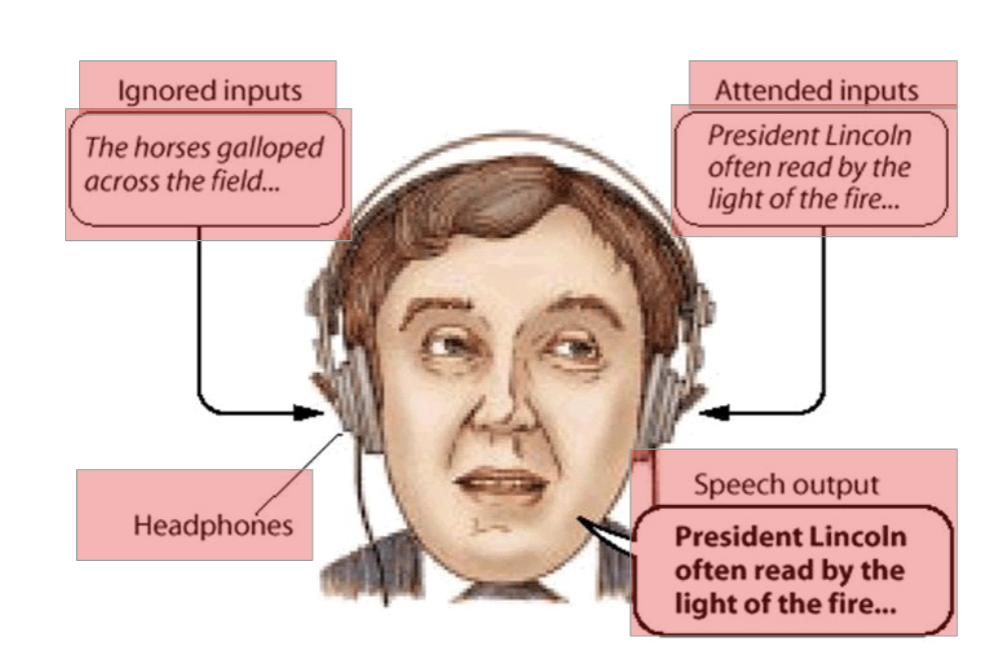
findings
very little reported about unattended message content
auditory selective attention
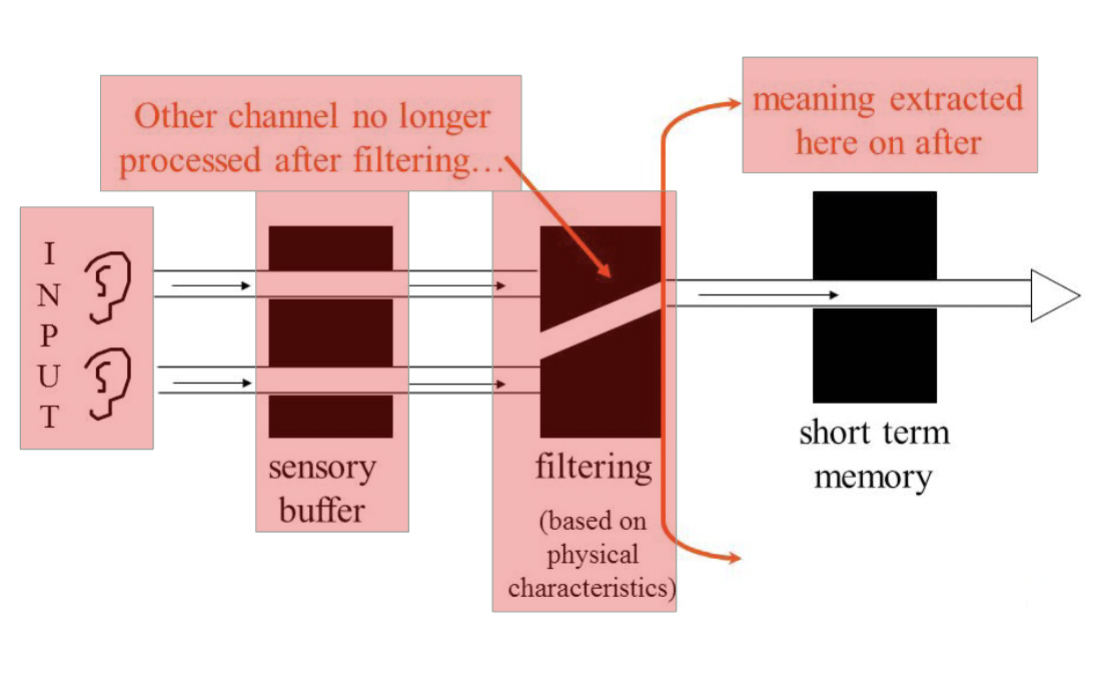
filter theory
Donald Broadbent
filter selects one message to process
early selection
cocktail party effect
certain pieces of information noticed even in unattended channel
participants own name
real life also
attenuation theory
Anne Treisman
unattended channel attenuated, not blocked
lowered volume
types of processing
lower volume channel processed less
thresholds for processing
certain stimuli- very low threshold
get processed

neural bases
fMRI
rest
clear speech
masked speech
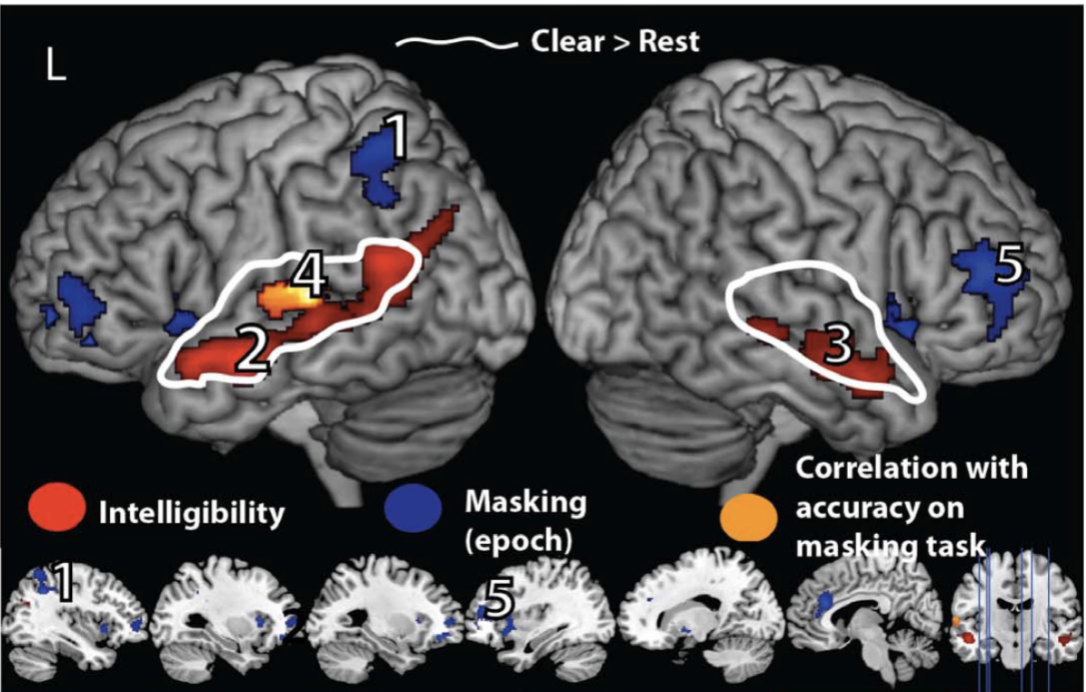
implication of regions more active for
clear than rest
non-noisy auditory speech processing
clear than masked
typical auditory processing areas less active in noise
masked than clear
cognitive control areas to deal with noise

