Unit E: Science Exploration
Things in space
Nebula
Nebulae are accumulations of gas and dust in space
the attraction of particles causes the nebula to start collapsing into a small, rotating cloud
If the core gets hot enough, it will start to glow. This is called a protostar, the first stage in a star’s formation
soon it becomes hot enough to achieve fusion, creating a star
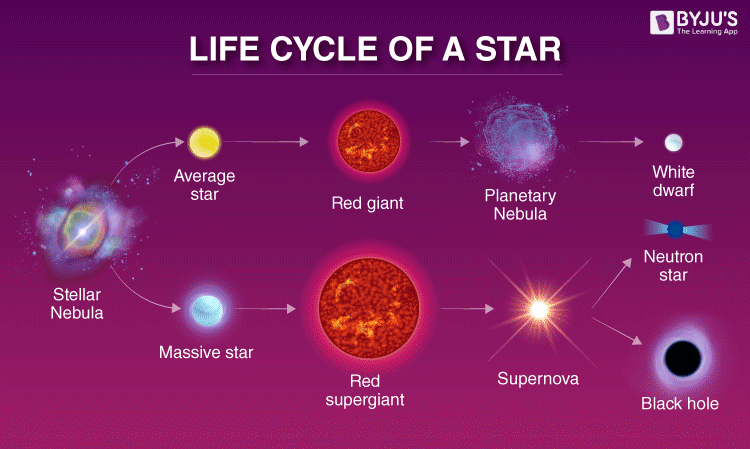
Star
A star is a hot, glowing ball of gas (mainly hydrogen) that gives off a ton of light energy
The colour of a star depends on its surface temperature. Very hot stars look blue. Cooler stars look red.
Constellation
Constellations are grouping of stars we see as patterns in the night sky There are 88 rexognized constellations
Ex. Big dipper, Orion, and Virgo
Planet
Ancient people knew about 5 planets: Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn (that’s all they could see and Earth wasn’t included becasue they believed it was the centre of the universe)
Planet- means “wanderer” in Greek
Over time, each planet moves in a weird way. This is called retrograde (the path a planet takes), but it’s just an optical illusion.
In contrast, the stars move in a perfect circle
Moon
The moon is a natural satellite that obrits a planet
Our moon moves from east to wast across the skiy. This movement is called the ecliptic
The moon had phases. It takes 28 days ti complete a cycle
Black hole
Solar wind and the Sun
solar wind is charged particles released by the sun in every direction
Earth is protected by solar wind with its magnetic field
solar wind is known as the aurora borealis
sunspots are spots on the sun that are darker. This is a result of the sun’s magnetic field that prevents heat from flowing to the surface
The Planets
Mercury- closest to the sun
Venus- the hottest planet
Earth -the only planet that can sustain life
Mars- - the red planet( from rust- iron III oxide)
Jupiter- the largest planet
Saturn- rings
Uranus- tilted axis
Neptune'
(not really) Pluto- classified as a planetoid
Inner planets
The first 4 planets
smaller, rockier in composition, and closer to the sun that the Jovian planets
Outer planets (Jovian-Jupiter)
large, gaseous, and located great distance from the sun
The Protoplanet Hypothesis
The “protoplanet hypothesis” is a model for explaining the birth of solar systems. The process can be described in three steps:
1. A cloud of gas and dust in space begins swirling.
2. Most of the material (more than 90%) accumulates in the center, forming the Sun.
3. The remaining material accumulates in smaller clumps circling the center. These form the planets
Eclipses
A solar eclipse is when the moon, passing between the sun and the earth, casts a shadow on earth
A lunar eclipse occurs when Earth passes between the Sun and the Moon, casting its shadow over the Moon
Asteroids, Comets, and Meteors
Asteroids are belts of small rocky or metallic bodies travelling in space
Majority of them are found between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter
Comets are objects made of dust and ice. They are pushed by solar wind and their tails glow when they get close to the sun
Meteoroids are small or big pieces of rocks flying through space with no paticular path
A meteriod becomes a meteor when its pulled into the Earths atmoshphere and the the ifrsction causes it to give off light
A meteor becomes a meteorite when it hits Earth’s surface
Solstices and Equinoxes
Winter solstice- December 21st (shortest day)
Vernal equinox- March 21st (halfway to summer)
SUmmer equinox- June 21st (longest day)
Autumnal equinox- September 21st (halfway to winter)
Early Views of Space
The geocentric model of the universe
The arth is at the center of the universe
Every orbit is a perfect circle
This was the model of Airistotle, ptolemy, and pythagoras
it was believed that there was a dome of stars enclosing our solar system
The heliocentric model of the universe
Sun at the center
every orbit is eliptical (oval)
This was the model of Coppernicus, Galileo. Kepler, and Newton

Gailieos observations (and the conclusions he made)
Craters on the moon- celestial bodies are not perfect
Sunspots- the sun turns of its axis so maybe the earth does too.
Moon orbiting jupiter- not everything revolves around the earth
Phases of venus- venus orbits the sun so maybe the earth does too
Defending heliocentricity
Galieo used his observations to defend copernicus’ theory
The main point- celestial bodies (like earth) can orbit other celestial bdies
followed by two astronomers Tycho Brahe and Johannes Kepler
Kepler’s Laws (techically Brahe’s, his teacher)
Planets move in elliptical orbits
The closer to the sun a planet is, the faster it will move
Discoveries
The Atronomical Unit
1 A.U = the distance between teh Earth and the Sun = 150,000,000 km
The Light Year
1 light year = the distance that light travels in a year = 9,460,728,000km= 63,240 A.U
Speed of Light = 299,792 km/sec
It takes 8 minutes fro light to travel from the Sun to the Earth
Astronomer tools
Astrolabe- measured altitude
cross-staff- measure the angle bewtween the moon nand any given star
Positions of Objects in Space
Azimuth
Azimuth is direction(degrees)
North = 0 degrees
East = 90 degrees
South = 180 degrees
West = 270 degrees
measured with a compass
Finding a celestial body in the sky
Altitude is height- horizon = 0 degrees.
Zenith (directly overhead) = 90 degrees
Rockets
Compiled of three components
structural components- the rockets itself, engines storage tanks, fins
fuel- liquid oxygen, liquid hydrogen, gasoline
payload- what its carrying- people water, air, food
Soviet Satellites
October 4th 1957- first launched satellite, the Sputnik
A month later a second space capsule was launched , carrying a small dog named Laika
IMPORTANT DATES TO REMEMBER
First satellite- 1957
Went to the moon and back-1969
Cool stuff
Microgravity- the condition which the gravitational forces are greatly reduced
Space shuttles- rockets used by space until 2011. They were re-usable
Ion drives- engines that use xenon fas instead of chemical fuel, The gas is electrically charged. Pros: lasts a long time and only rewuires a small amount of xenon gas. Cons: weak as hell
Solar sails- used to power spacecrafts. Pros- fast and saves on fuel. Cons- no power outside the solar system
Producing Water and Oxygen
Water- waste water is distlled and the steam is condensed into potable water
Oxygen- electrically electrocute water to seperate the elements. Hyfrogen is thrown overboard and oxygen is kept.
Dangers of Space
Environmental
cosmic and solar radiation
Extreme hot and cold
meteors
Body changes
Bones expand
visual depth is affected
SATELLITES
Observation
What satellites were mostly used for
geosynchronous orbit (high orbit)
Remote sensing
Low orbit
take high resoloution of the earths surface
Communication
low to medium orbit
Ex. Satellite radio
GPS
Global postitioning system
geosynchronous (high) orbit
requirea t least 4 satellietes to recieve an accurate calculation
Technology made for space used on earth
Space food- baby and freeze-dried foods
computer robotics- emergency response robots for use in dangerous situations (bombs)
Simulation of space environment for space training- VR
Refracting optical telescopes
Optical telescopes uses visible light
a refracting telescope had a objective lens that refracts light from the outside
as well as an ocular lens that refracts light to the eye
When multiple telescopes are used to view n object, it is called inferometry (we do this with our eyes)
Reflecting telescope
Has a primary and secondary mirror that capture light from outside
and an eye eyes that refracts light to the eye