Orientation Day: MS and Psych
MEDICAL SURGICAL NURSING
CHF or Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive heart failure - a chronic condition where the heart is unable to pump sufficiently to maintain blood flow to meet the body's needs.
Right to Left is Rare
Left to Right is Possible
Point of Maximum Impulse (PMI) - Apical Pulse or 4th to 5th ICS LMCL
LEFT SIDED HEART FAILURE (r/t LUNGS)
2 pillows/ high fowlers/ tripod
s/sx. Frothy saliva, Dyspnea, Coughing, Wheezing, Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
RIGHT SIDED HEART FAILURE (r/t REST)
Backflow to the rest of the body
s/sx. Jugular vein distention, Ascites, Edema, Hepatomegaly, Loss of appetite
DLADA toxicity level
Digoxin x 2
Lithium x 2
Aminophylline x 20
Dilantin x 20
Acetaminophen x 200
COPD
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease - a common lung condition characterized by restricted airflow, inflammation, and tissue destruction, leading to difficulty breathing, chronic cough, and mucus production.
2L - Maximum O2 for COPD driven by hypoxic drive
Hypoxic Drive - the body's respiratory system being primarily stimulated by low blood oxygen levels (hypoxia) rather than the typical high carbon dioxide (CO2) levels that usually trigger breathing
Arthritis
Rheumatoid, Osteo, Gouty Arthritis
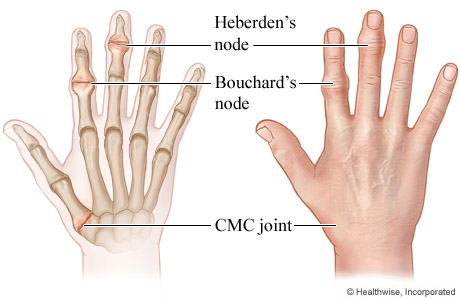
OA - Localized, Bouchard’s and heberden’s
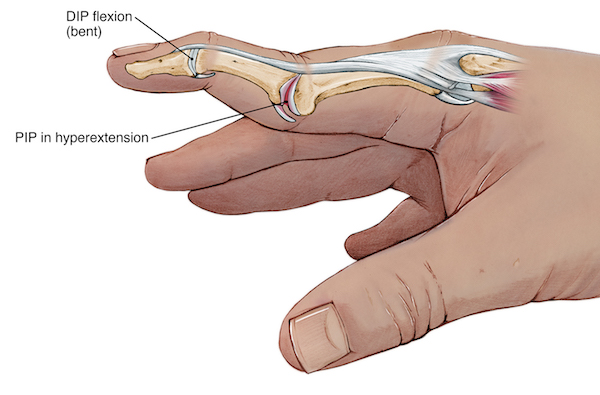
RA - Systemic, Swan Neck Deformity
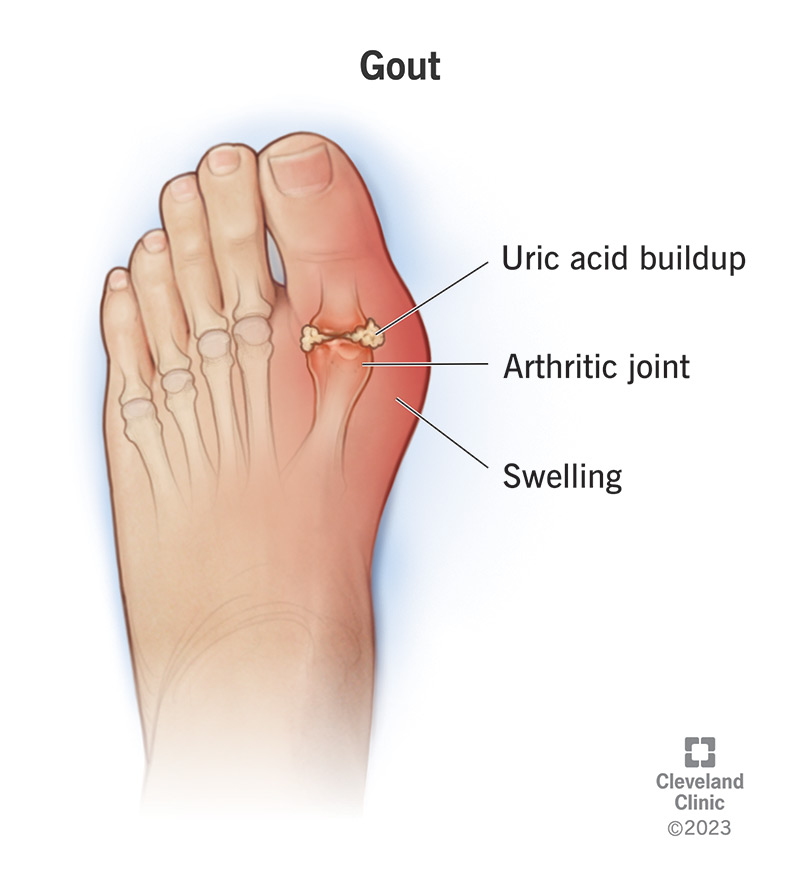
GA - Nocturnal, Uric acid
Burns
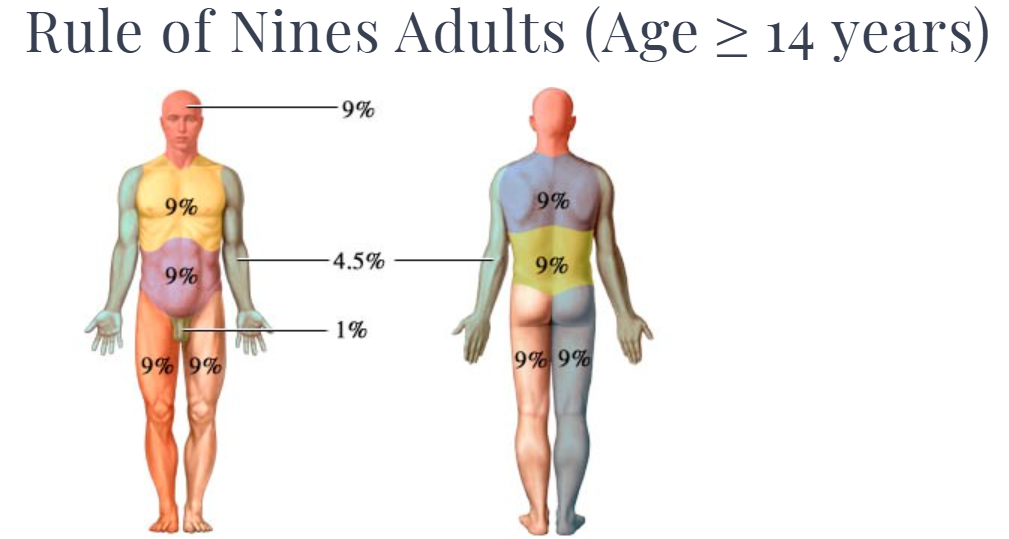
Rule of Nines (DARNA)
Head (3), face (3), and neck (3) = (9)
Left arm (9) and Right Arm (9)
Chest Anterior (18) and Posterior (18)
Left leg (18) and Right leg (18)
Perineum (1)
Paralysis (-plegia)
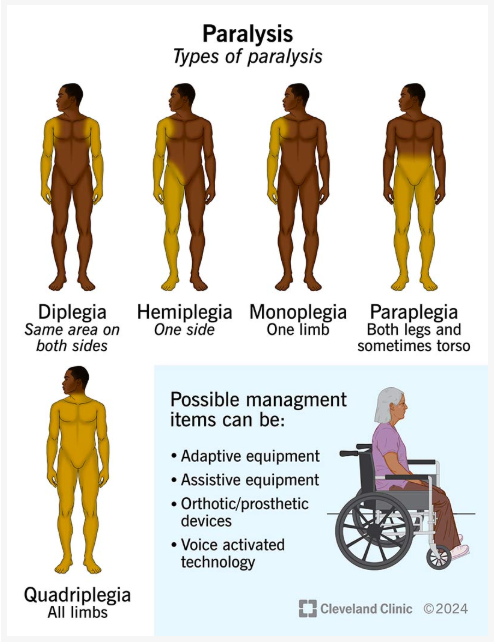
Key terms
Theophylline - known as bronchodilator
Digoxin (Lanoxin) - digitalis glycosides. manages heart rhythm. HR <60 DO NOT ADMINISTER
Phenytoin - anticonvulsant
GABSH - Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus (GABHS), a type of bacterium that causes "strep throat," scarlet fever, and skin infections
Stenosis - abnormal narrowing of a passageway
PSYCHIATRIC NURSING
Anxiety
Anxiety - vague sense of impending doom (SNS response)
High HR, BP, RR
+1 Mild - “you seem restless“ - Alert - Wide
+2 Moderate - Pacing - PRN meds - Selective inattention - Narrow
+3 Severe - “Don’t know what to do, what to say” - Directive
+4 Panic - “Don’t touch client“ - Suicide/Safety - Respiratory Alkalosis - Bag
ABG Analysis
Normal Values
pH - 7.35 to 7.45
CO2 - 35 to 45
HCO2 - 22 to 26
Principle #1 (opposite)
Down - Acidosis
Up - Alkalosis
If opposite pH and CO2, decide respiratory
Principle #2 (same)
If same pH and CO2, decide metabolic
Principle #3
If same CO2 and HCO2, decide partially compensated
fully compensated if pH level becomes normal
Nursing Process
Diagnosis - Ineffective individual coping
Planning/Implementation - to lower anxiety, environmental stimuli, and relaxation techniques
Evaluation - Effective individual coping
Antianxiety Agents (Pharma moment)
Valium - short term - withdrawal causes rebound phenomenon within 1 week (seizures) - so choose gradual taper dose or 10% to 25% every 1 to 2 weeks
Librium
Ativan
Serax
Tranxene
Zepam, zolam, zepine
ANTIANXIETY INCREASES GABA
GABA - Gamma Aminobutyric Acid
Inhibitory
Remember EVERYTHING lowers down
NO ALCOHOL AND COFFEE
Develops orthostatic hypotension
Sit
Dangle feet
Stand
ECG components
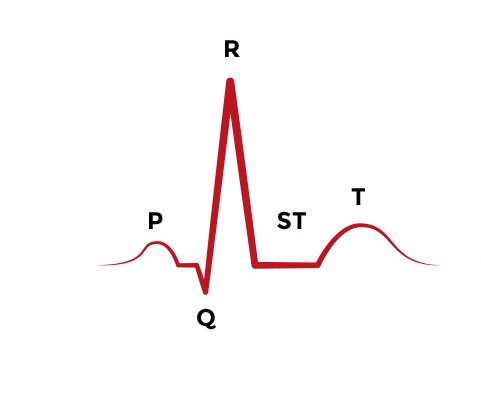
Contraction - Depolarization
Relaxation - Repolarization
AD - Atrial Depolarization
VD - Ventricular Depolarization
VR - Ventricular Repolarization

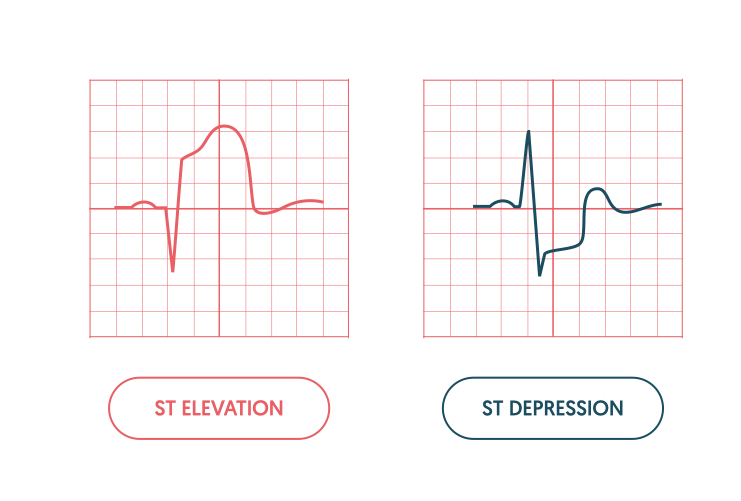
PR interval: 0.12-0.20
QRS complex: 0.6-0.10 (half pr)
Prolonged PR interval: 0.30 (1st degree heart block)
Widened QRS: 0.20
REMEMBER:
AsystolE - Epinephrine
VentricLe - Lidocaine
Hypo and Hyperkalemia
Potassium (K+) normal value is 3.5-5
prolonged, wide, or tall is hyper
short or narrow is hypo
U wave is hypo
Hyperkalemia - Kayexalate or Insulin + Glucose
Hypokalemia - Banana, Orange, and Potatoes
REMEMBER:
NEVER IV PUSH POTASSIUM