
In Class Notes 10/8: Understanding Sex and Gender Differences
Sex and Gender 🤝
Sex and gender are two distinct concepts that are often confused with each other.
Sex is defined as biological differences in ordnance, hormones, and body shape between males and females.
Gender, however, is defined as differences in male and female roles, behaviors, clothes, and activities that are socially defined.
Gender Roles Across Cultures 🌎
Gender roles can vary significantly across cultures. In some parts of the world, there are restrictions on education and job opportunities for females. In other cultures, women may not be allowed to drive or must have a male escort in public.
Parental Attitudes Towards Gender Roles 👪
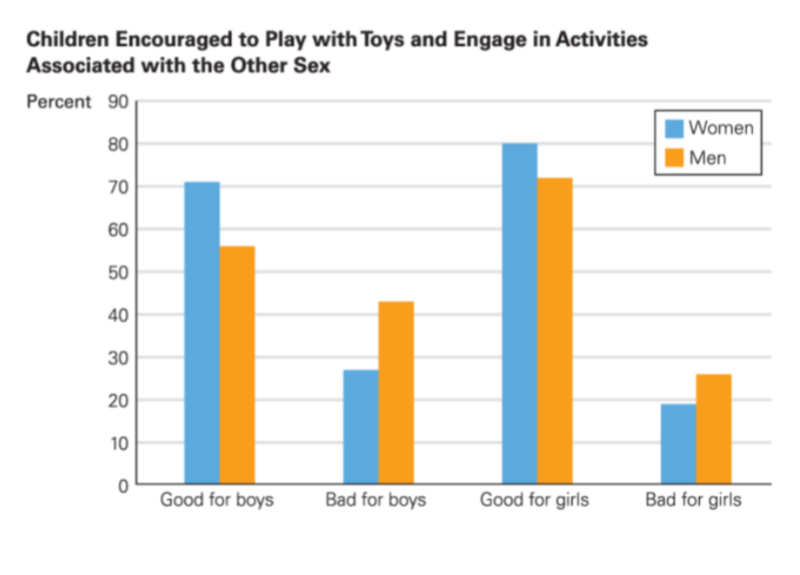
Parents often have strong feelings about children playing with toys associated with the opposite sex. However, attitudes towards this have relaxed over time, especially for girls. Boys are still expected to conform to traditional male roles.
Women | Men | |
Think it's good for boys to play with traditional girls' toys | 70% | 55% |
Think it's bad for boys to play with traditional girls' toys | 25% | 45% |
Think it's good for girls to play sports and engage in traditionally male activities | 80% | 72% |
Think it's bad for girls to play sports and engage in traditionally male activities | 18% | 25% |
Noticing Gender Differences in Children 👧🏻👦🏻
Children as young as preschoolers can adopt rigid male and female roles based on the messages they receive from their parents, siblings, and peers. Children with opposite-sex siblings are less likely to have rigid gender roles.
Theories of Gender Development 📚
Freud's Psychosexual Stages
Freud's third psychosexual stage is the phallic stage, which occurs during the preschool years. During this stage, the penis becomes the focus of concern and pleasure for boys, while girls experience penis envy.
Stage | Description |
Oral | Focus on the mouth and feeding |
Anal | Focus on the anus and bowel movements |
Phallic | Focus on the penis and pleasure |
Freud also proposed the Oedipus complex, which suggests that preschool-age boys secretly want to murder their fathers to access their mothers. He also proposed the Electra complex, which suggests that preschool-age girls secretly want to murder their mothers to sleep with their fathers. However, these theories are not widely accepted and are considered to be a stretch.
Identifying with Same-Sex Parents 👩👧🏻👨👦🏻
Around the age of 4, children start to identify with their same-sex parents and try to model themselves after them. Girls try to be like their mothers, while boys try to be like their fathers.## 🤝 Theories of Gender Development
Psychoanalytic Theory
According to psychoanalytic theory, children develop gender roles as a way to resolve the Oedipus complex. This theory suggests that children want to be like their parents, but also want to eliminate them in order to fulfill their desires.
"The Oedipus complex is a psychological concept that describes the desire of children to possess the opposite-sex parent and eliminate the same-sex parent."
Behaviorism
Behaviorism suggests that gender differences and roles are products of our environment and are shaped by rewards and punishments.
Concept | Definition |
Social Norms | Unwritten rules that govern behavior in a society |
Gender Roles | Expectations of how men and women should behave in a society |
Rewards and Punishments | Consequences that shape behavior and reinforce social norms |
Social Learning Theory
Social learning theory suggests that children learn gender-related behaviors by observing others and internalizing these standards.
"Children learn by observing and imitating the behavior of others, and they strive to internalize the standards of their culture."
Cognitive Theory
Cognitive theory suggests that children develop a gender schema, or a mental framework, for understanding sex differences.
Age | Cognitive Development |
5 years old | Children start to categorize themselves and others as male or female |
5 years old | Children start to think and behave accordingly to their gender schema |
Evolutionary Theory
Evolutionary theory suggests that males and females try to become attractive to the opposite sex according to cultural gender rules.
"Sexual attraction is crucial for reproduction, which is crucial for the survival of the species."
🤝 Moral Development
Empathy and Prosocial Behavior
Empathy and prosocial behavior are essential components of moral development.
Concept | Definition |
Empathy | The ability to understand and share the feelings of others |
Prosocial Behavior | Behavior that is intended to benefit others, without expecting anything in return |
Aggression
Aggression is a common behavior in preschoolers, but it should decrease as they develop empathy and self-control.
Type of Aggression | Definition |
Instrumental Aggression | Aggression designed to get something from someone else |
Retaliation Aggression | Aggression in response to a perceived threat or attack |
Relational Aggression | Aggression designed to cause social harm to others |
Bullying | Unprovoked physical or verbal attacks on someone who is unlikely to defend themselves |

🚨 Accidental Injury and Prevention
Lead Exposure
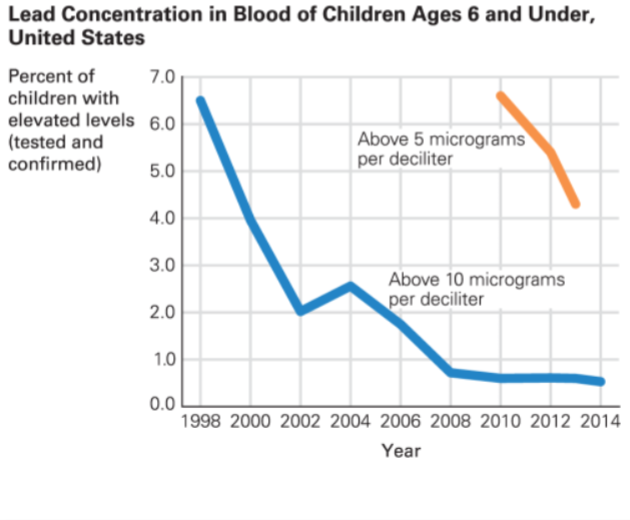
Lead exposure is a significant risk for preschoolers, as it can cause learning disabilities and affect brain development.
Year | Number of Children with Elevated Blood Lead Levels |
1998 | 434,000 |
2014 | 50,000 |
"Lead exposure is more dangerous for children than adults because their brains are still developing."
Prevention
Prevention is key to reducing the risk of accidental injury and lead exposure.
Keep children away from lead-based products
Teach children not to put objects in their mouths
Ensure children are vaccinated against diseases
Create a safe environment for children to play and explore## Lead Poisoning 🚨
Lead poisoning is a serious health concern, especially for children. Prior to 1998, lead was commonly found in various household items, including:
Paint: Lead paint was widely used in homes until it was banned in the early 1980s. As the paint breaks down, it releases fine dust that can be ingested by children.
Bullets: Lead bullets can also be a source of lead poisoning if ingested.
Water pipes: Lead pipes were commonly used in older homes and can leach lead into the water supply.
Effects of Lead Poisoning
Lead poisoning can have serious health consequences, including:
Developmental delays
Learning disabilities
Organ damage
Reducing Lead Exposure
To reduce the risk of lead poisoning, it's essential to:
Ensure that children do not ingest lead-based products
Keep homes clean and dust-free
Use lead-free paint and materials
Test water for lead contamination
Child Maltreatment 🚨
Child maltreatment refers to intentional harm or avoidable endangerment of a child under the age of 18.
Types of Child Maltreatment
Child Abuse: Any deliberate action that harms a child's physical, emotional, or sexual well-being.
Child Neglect: Failure to meet a child's basic physical, emotional, or educational needs.
Definitions
"Child abuse is any non-accidental physical injury, sexual abuse, or emotional abuse inflicted on a child."
"Child neglect is the failure to provide for a child's basic needs, including physical, emotional, and educational needs."
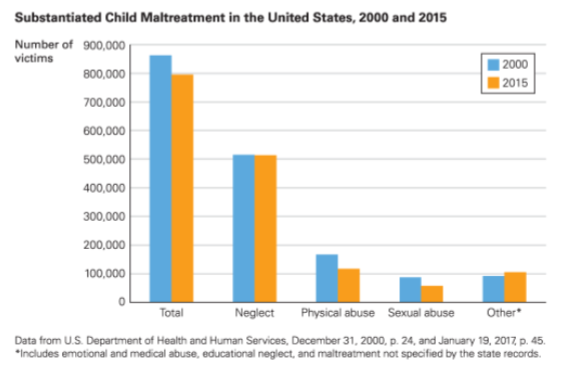
Statistics
Year | Total Substantiated Cases | Neglect Cases | Physical Abuse Cases | Sexual Abuse Cases |
2000 | 850,000 | |||
2015 | 800,000 |
Mandated Reporters
Mandated reporters are individuals who are required by law to report suspected child maltreatment. These include:
Teachers
Guidance counselors
Therapists
Social workers
Healthcare professionals
First responders (police officers, firefighters, EMS)
Reporting Child Maltreatment
Mandated reporters must report any suspected child maltreatment, even if another explanation is likely. Reports can be made to Child Protective Services (CPS).
Investigation and Substantiation
CPS investigates reports of child maltreatment and determines whether the allegations are substantiated. The ratio of reported cases to substantiated cases is approximately 5:1.
Challenges in Investigating Child Maltreatment
Each child is counted only once, even if there are multiple reports or incidents.
Substantiation requires proof, which can be difficult to obtain, especially in cases involving young children.
Mandated reporters may report suspected maltreatment even if another explanation is likely.
Some reports may be screened out due to inadequate information.## 🚨 Consequences of Child Maltreatment 🚨
Child maltreatment can have severe and long-lasting consequences on a child's physical, emotional, and psychological well-being.
Physical Consequences
Brain damage from injuries sustained during abuse
Neurological damage due to excessive stress hormones affecting brain development
Emotional and Behavioral Consequences
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): a mental health condition triggered by a traumatic event, leading to symptoms such as anxiety, depression, and flashbacks.
Difficulty forming attachments and relationships due to inconsistent or abusive caregiving
Increased aggression and isolation
Social issues and economic consequences in adulthood
🚫 Prevention of Child Maltreatment 🚫
There are three main levels of prevention:
Level | Description |
Primary Prevention | Creating conditions to minimize harm, such as laws and customs regulating child discipline and care |
Secondary Prevention | Targeted interventions for high-risk situations or vulnerable populations, such as rules for daycare centers and after-school programs |
Tertiary Prevention | Limiting damage after maltreatment has occurred, through therapy and changing the child's home situation |
🏠 Foster Care and Adoption 🏠
If a child is removed from their home due to maltreatment, the goal is to reunite them with their birth family. However, if this is not possible, alternative options include:
Kinship care: temporary legal guardianship by a relative, such as a grandparent or older sibling
Foster care: temporary care by a non-relative, preferred over institutional care
Adoption: permanent placement with a new family, although this can be challenging due to various factors, including:
Judges' reluctance to terminate parental rights
Adoptive parents' preferences for younger children or specific characteristics
Agency rules and biases
🎓 The Marshmallow Experiment 🎓
A famous study by Stanford professor Walter Mischel tested the ability of 4-year-olds to delay gratification. The experiment involved offering a child a marshmallow and promising a second one if they waited 15 minutes without eating the first.
1 out of 3 children were able to delay gratification and received the second marshmallow
15 years later, the children who delayed gratification were found to be more successful, with better grades and relationships
A follow-up study in Colombia replicated the results, with 1 out of 3 Hispanic children able to delay gratification
The ability to delay gratification is seen as a key factor in success, as it demonstrates self-discipline and the ability to prioritize long-term goals over short-term desires.
In Class Notes 10/8: Understanding Sex and Gender Differences
Sex and Gender 🤝
Sex and gender are two distinct concepts that are often confused with each other.
Sex is defined as biological differences in ordnance, hormones, and body shape between males and females.
Gender, however, is defined as differences in male and female roles, behaviors, clothes, and activities that are socially defined.
Gender Roles Across Cultures 🌎
Gender roles can vary significantly across cultures. In some parts of the world, there are restrictions on education and job opportunities for females. In other cultures, women may not be allowed to drive or must have a male escort in public.
Parental Attitudes Towards Gender Roles 👪
Parents often have strong feelings about children playing with toys associated with the opposite sex. However, attitudes towards this have relaxed over time, especially for girls. Boys are still expected to conform to traditional male roles.
Women | Men | |
Think it's good for boys to play with traditional girls' toys | 70% | 55% |
Think it's bad for boys to play with traditional girls' toys | 25% | 45% |
Think it's good for girls to play sports and engage in traditionally male activities | 80% | 72% |
Think it's bad for girls to play sports and engage in traditionally male activities | 18% | 25% |

Noticing Gender Differences in Children 👧🏻👦🏻
Children as young as preschoolers can adopt rigid male and female roles based on the messages they receive from their parents, siblings, and peers. Children with opposite-sex siblings are less likely to have rigid gender roles.
Theories of Gender Development 📚
Freud's Psychosexual Stages
Freud's third psychosexual stage is the phallic stage, which occurs during the preschool years. During this stage, the penis becomes the focus of concern and pleasure for boys, while girls experience penis envy.
Stage | Description |
Oral | Focus on the mouth and feeding |
Anal | Focus on the anus and bowel movements |
Phallic | Focus on the penis and pleasure |
Freud also proposed the Oedipus complex, which suggests that preschool-age boys secretly want to murder their fathers to access their mothers. He also proposed the Electra complex, which suggests that preschool-age girls secretly want to murder their mothers to sleep with their fathers. However, these theories are not widely accepted and are considered to be a stretch.
Identifying with Same-Sex Parents 👩👧🏻👨👦🏻
Around the age of 4, children start to identify with their same-sex parents and try to model themselves after them. Girls try to be like their mothers, while boys try to be like their fathers.## 🤝 Theories of Gender Development
Psychoanalytic Theory
According to psychoanalytic theory, children develop gender roles as a way to resolve the Oedipus complex. This theory suggests that children want to be like their parents, but also want to eliminate them in order to fulfill their desires.
"The Oedipus complex is a psychological concept that describes the desire of children to possess the opposite-sex parent and eliminate the same-sex parent."
Behaviorism
Behaviorism suggests that gender differences and roles are products of our environment and are shaped by rewards and punishments.
Concept | Definition |
Social Norms | Unwritten rules that govern behavior in a society |
Gender Roles | Expectations of how men and women should behave in a society |
Rewards and Punishments | Consequences that shape behavior and reinforce social norms |
Social Learning Theory
Social learning theory suggests that children learn gender-related behaviors by observing others and internalizing these standards.
"Children learn by observing and imitating the behavior of others, and they strive to internalize the standards of their culture."
Cognitive Theory
Cognitive theory suggests that children develop a gender schema, or a mental framework, for understanding sex differences.
Age | Cognitive Development |
5 years old | Children start to categorize themselves and others as male or female |
5 years old | Children start to think and behave accordingly to their gender schema |
Evolutionary Theory
Evolutionary theory suggests that males and females try to become attractive to the opposite sex according to cultural gender rules.
"Sexual attraction is crucial for reproduction, which is crucial for the survival of the species."
🤝 Moral Development
Empathy and Prosocial Behavior
Empathy and prosocial behavior are essential components of moral development.
Concept | Definition |
Empathy | The ability to understand and share the feelings of others |
Prosocial Behavior | Behavior that is intended to benefit others, without expecting anything in return |
Aggression
Aggression is a common behavior in preschoolers, but it should decrease as they develop empathy and self-control.
Type of Aggression | Definition |
Instrumental Aggression | Aggression designed to get something from someone else |
Retaliation Aggression | Aggression in response to a perceived threat or attack |
Relational Aggression | Aggression designed to cause social harm to others |
Bullying | Unprovoked physical or verbal attacks on someone who is unlikely to defend themselves |

🚨 Accidental Injury and Prevention
Lead Exposure
Lead exposure is a significant risk for preschoolers, as it can cause learning disabilities and affect brain development.
Year | Number of Children with Elevated Blood Lead Levels |
1998 | 434,000 |
2014 | 50,000 |
"Lead exposure is more dangerous for children than adults because their brains are still developing."

Prevention
Prevention is key to reducing the risk of accidental injury and lead exposure.
Keep children away from lead-based products
Teach children not to put objects in their mouths
Ensure children are vaccinated against diseases
Create a safe environment for children to play and explore## Lead Poisoning 🚨
Lead poisoning is a serious health concern, especially for children. Prior to 1998, lead was commonly found in various household items, including:
Paint: Lead paint was widely used in homes until it was banned in the early 1980s. As the paint breaks down, it releases fine dust that can be ingested by children.
Bullets: Lead bullets can also be a source of lead poisoning if ingested.
Water pipes: Lead pipes were commonly used in older homes and can leach lead into the water supply.
Effects of Lead Poisoning
Lead poisoning can have serious health consequences, including:
Developmental delays
Learning disabilities
Organ damage
Reducing Lead Exposure
To reduce the risk of lead poisoning, it's essential to:
Ensure that children do not ingest lead-based products
Keep homes clean and dust-free
Use lead-free paint and materials
Test water for lead contamination
Child Maltreatment 🚨
Child maltreatment refers to intentional harm or avoidable endangerment of a child under the age of 18.

Types of Child Maltreatment
Child Abuse: Any deliberate action that harms a child's physical, emotional, or sexual well-being.
Child Neglect: Failure to meet a child's basic physical, emotional, or educational needs.
Definitions
"Child abuse is any non-accidental physical injury, sexual abuse, or emotional abuse inflicted on a child."
"Child neglect is the failure to provide for a child's basic needs, including physical, emotional, and educational needs."
Statistics
Year | Total Substantiated Cases | Neglect Cases | Physical Abuse Cases | Sexual Abuse Cases |
2000 | 850,000 | |||
2015 | 800,000 |

Mandated Reporters
Mandated reporters are individuals who are required by law to report suspected child maltreatment. These include:
Teachers
Guidance counselors
Therapists
Social workers
Healthcare professionals
First responders (police officers, firefighters, EMS)
Reporting Child Maltreatment
Mandated reporters must report any suspected child maltreatment, even if another explanation is likely. Reports can be made to Child Protective Services (CPS).
Investigation and Substantiation
CPS investigates reports of child maltreatment and determines whether the allegations are substantiated. The ratio of reported cases to substantiated cases is approximately 5:1.
Challenges in Investigating Child Maltreatment
Each child is counted only once, even if there are multiple reports or incidents.
Substantiation requires proof, which can be difficult to obtain, especially in cases involving young children.
Mandated reporters may report suspected maltreatment even if another explanation is likely.
Some reports may be screened out due to inadequate information.## 🚨 Consequences of Child Maltreatment 🚨
Child maltreatment can have severe and long-lasting consequences on a child's physical, emotional, and psychological well-being.
Physical Consequences
Brain damage from injuries sustained during abuse
Neurological damage due to excessive stress hormones affecting brain development
Emotional and Behavioral Consequences
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): a mental health condition triggered by a traumatic event, leading to symptoms such as anxiety, depression, and flashbacks.
Difficulty forming attachments and relationships due to inconsistent or abusive caregiving
Increased aggression and isolation
Social issues and economic consequences in adulthood
🚫 Prevention of Child Maltreatment 🚫
There are three main levels of prevention:
Level | Description |
Primary Prevention | Creating conditions to minimize harm, such as laws and customs regulating child discipline and care |
Secondary Prevention | Targeted interventions for high-risk situations or vulnerable populations, such as rules for daycare centers and after-school programs |
Tertiary Prevention | Limiting damage after maltreatment has occurred, through therapy and changing the child's home situation |
🏠 Foster Care and Adoption 🏠
If a child is removed from their home due to maltreatment, the goal is to reunite them with their birth family. However, if this is not possible, alternative options include:
Kinship care: temporary legal guardianship by a relative, such as a grandparent or older sibling
Foster care: temporary care by a non-relative, preferred over institutional care
Adoption: permanent placement with a new family, although this can be challenging due to various factors, including:
Judges' reluctance to terminate parental rights
Adoptive parents' preferences for younger children or specific characteristics
Agency rules and biases
🎓 The Marshmallow Experiment 🎓
A famous study by Stanford professor Walter Mischel tested the ability of 4-year-olds to delay gratification. The experiment involved offering a child a marshmallow and promising a second one if they waited 15 minutes without eating the first.
1 out of 3 children were able to delay gratification and received the second marshmallow
15 years later, the children who delayed gratification were found to be more successful, with better grades and relationships
A follow-up study in Colombia replicated the results, with 1 out of 3 Hispanic children able to delay gratification
The ability to delay gratification is seen as a key factor in success, as it demonstrates self-discipline and the ability to prioritize long-term goals over short-term desires.
 Knowt
Knowt