Cognitive; week 5; culture and attention
What is culture?
Way of life of a group of a large group of people grouped in the same geographical location.
Behaviors, beliefs, expectations, values, and interpretations of symbols (language, emojis) that they agree on (often implicitly), passed along by communication and imitation from one generation to the next.
Cultures are dynamic. They change subtly from one area to the next, from one period of time to the next.
Does culture affect cognition?
Most of psychological sciences are conducted on WEIRD populations:
Western, educated, industrialized, rich and democratic societies. Is that a problem?
How do people from different cultures differ in their cognition?
Caution: we need to be careful not to overgeneralize and stereotype. What we’ll talk about are average differences.
Caution 2: Cognition versus performance: experience affects performance in most tasks, but performance is only a marker of cognition (e.g., language production)
Low-level Vs High-level
Low-level:
perception
attention
encoding
unconscious
inflexible
early evolution
mostly hard-wired
High-level
systematic decision making
brainstorming/ creativity
rule usage
conscious (mostly)
flexible
late evolution
can change
Can culture affect perception?
some believe that culture affects cognition at its most basic level

Reminder: social attention = the priority we automatically give to social stimuli, generally considered to be bottom-up
However, top-down influences and experiences can shape even these processes.
Eye-contact - Western Vs East Asian cultures
Direct eye-contact:
encouraged in western societies
may be considered rude in Eastern cultures (especially with elders)
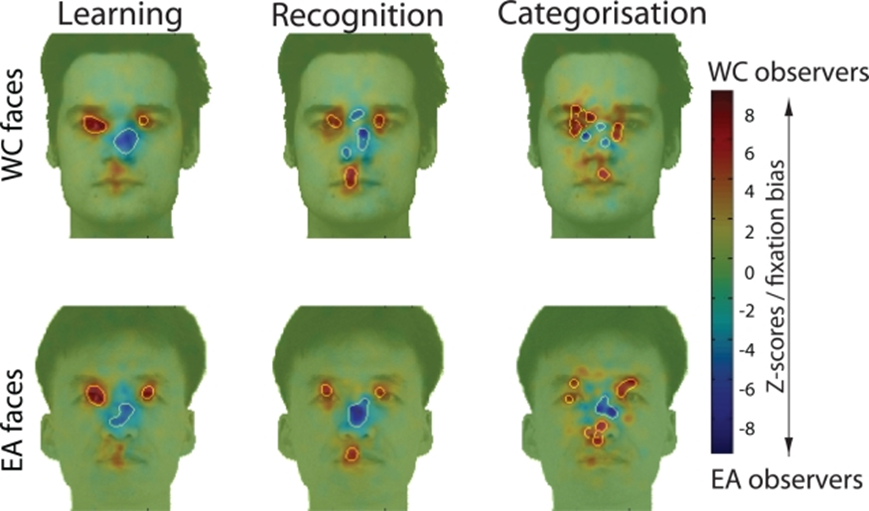
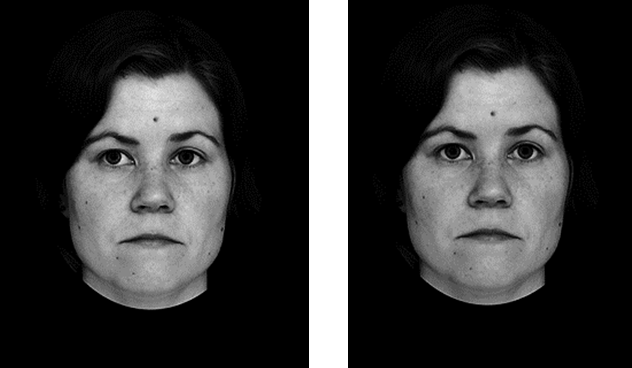
Uono & Hietenan, 2015:
Research question: Does eye contact perception differ in people with different cultural backgrounds?
Finnish (European) vs. Japanese (East Asian)
Task: Is this face looking at you?
results:
Finish participants were more accurate in discerning gaze of Finish faces
Finish participants showed an ‘own-race’ effect – better perception for White European faces
Japanese participants did not show an ‘own race’ effect
Conclusions
Visual experience with Finnish faces throughout development likely led to more effective processing of these faces
Eye contact is quite minimal in Japanese culture so perhaps participants just didn’t have as much experience
Can culture affect attention more generally?
Analytic thinking versus holistic thinking
Analytic: emphasize a linear object-oriented focus
(dominant in Western Europe and North America)
Holistic: emphasize a non-linear context-oriented focus
(dominant in East Asian cultures such as China, Korea, and Japan)
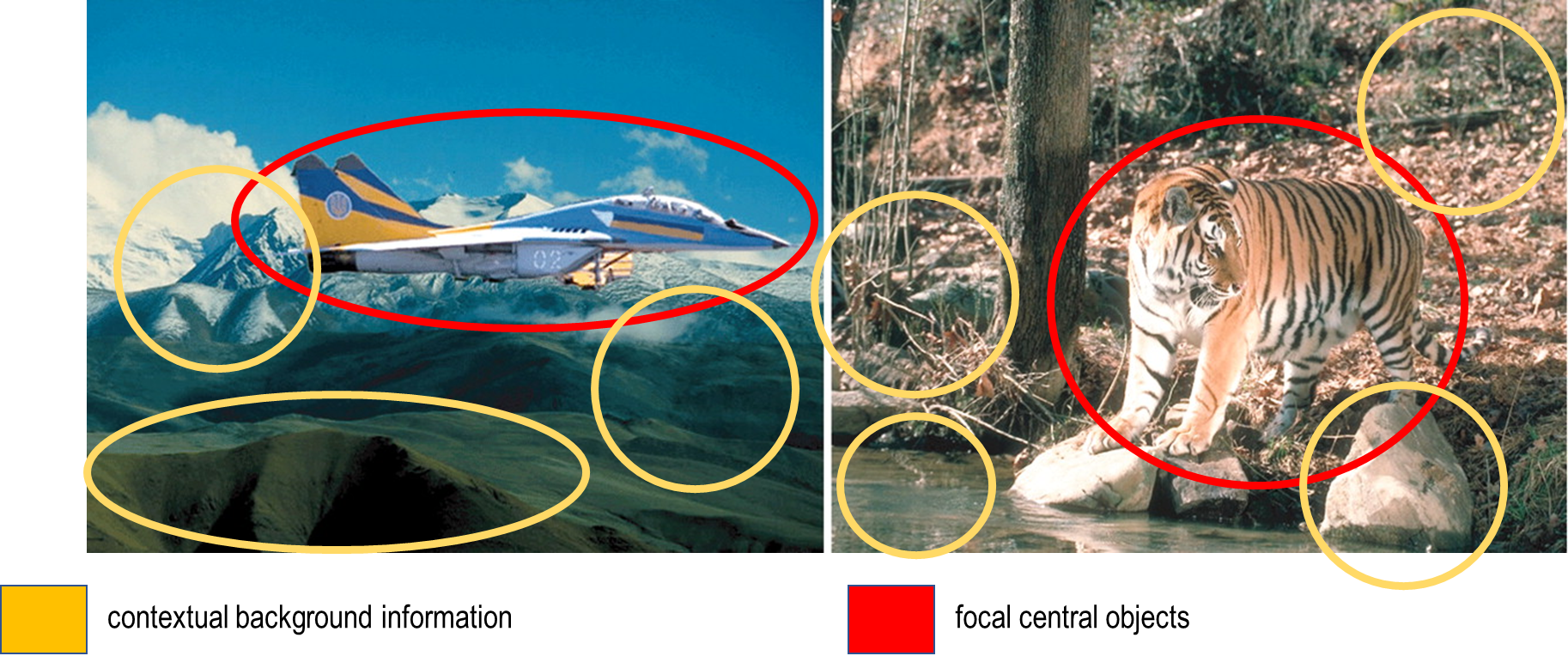
Masuda and Nisbett, 2001:

finding: Japanese participants were more likely than American participants to make statements regarding contextual information and relationships then
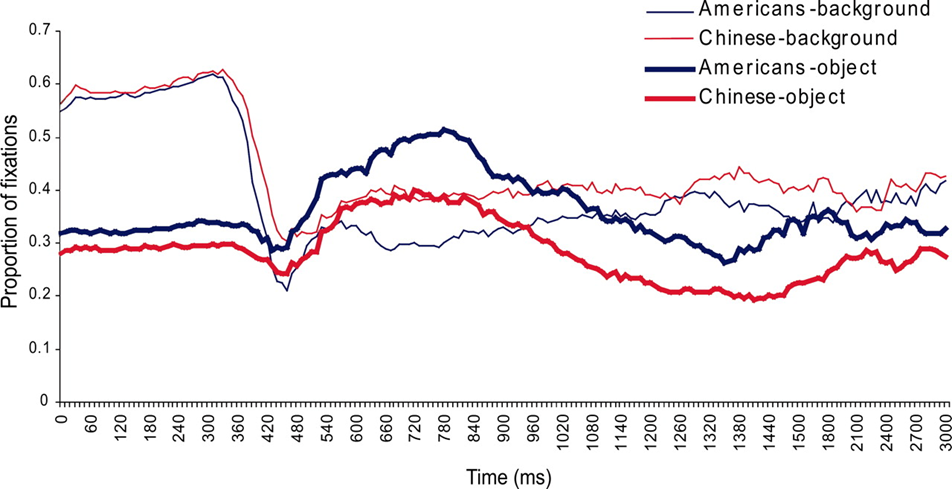
Cultural variation in eye-movements during scene perception
Chua et al. 2005

results:
“Differences in judgment and memory may have their origins in differences in what is actually attended as people view a scene”
However, Senzaki et al. (2014): Japanese participants’ attention was the same, until they were asked to report what is going on.
What implications does this have for gaze cueing?
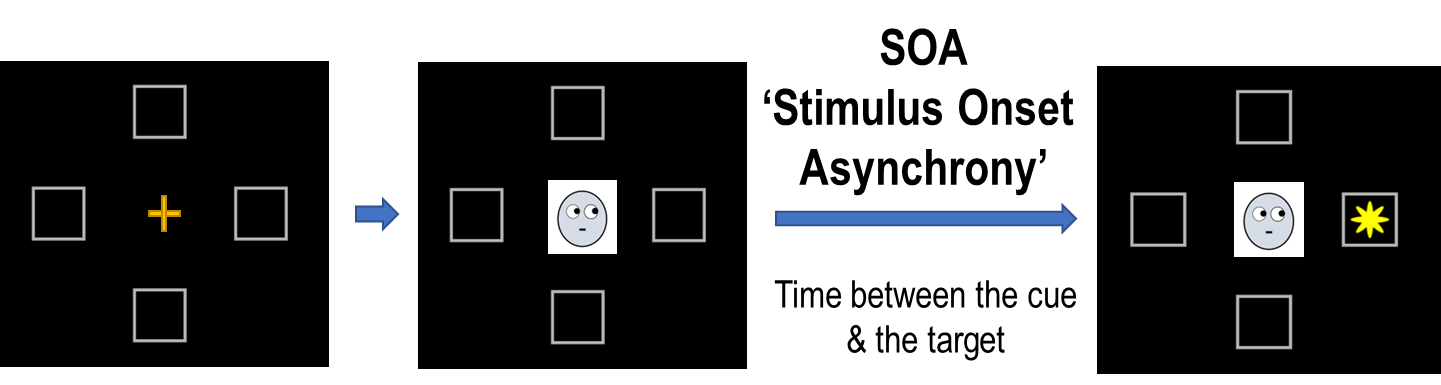
Gaze cueing paradigms typically use short SOAs
Participants show the gaze cueing effect regardless of if the cue is predictive
BUT what if we used a longer SOA that let the participant have time to process the contextual information (i.e. that the cue is non-predictive)?
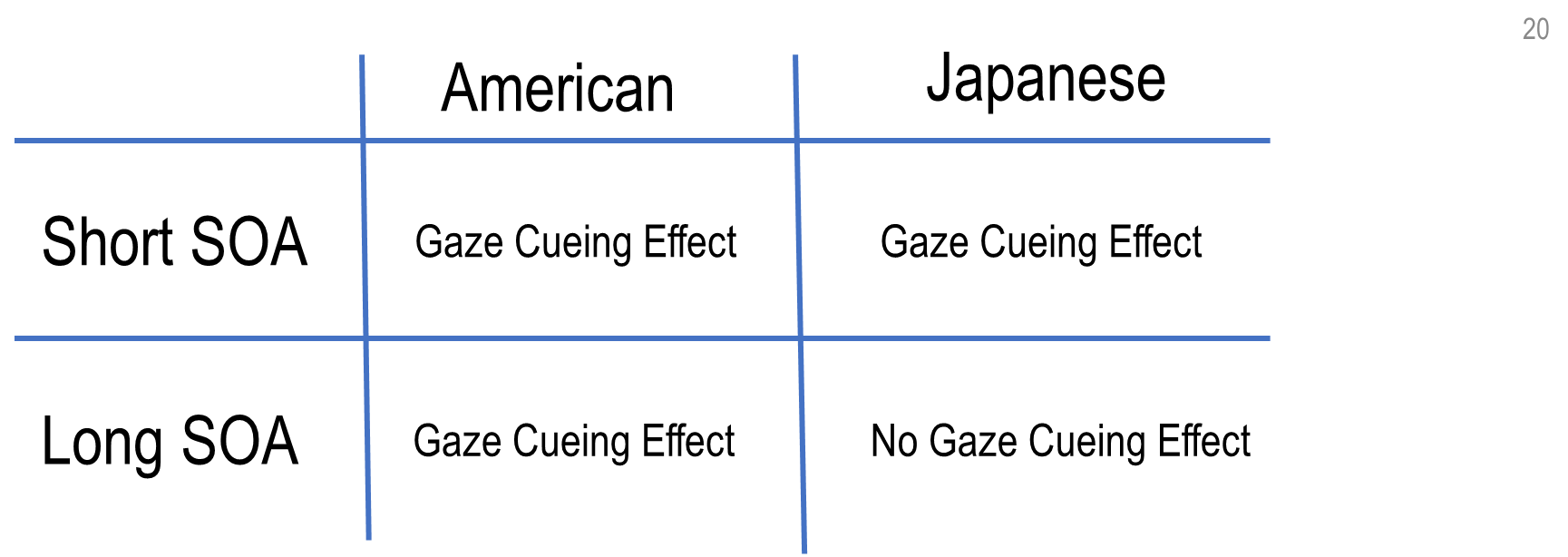
conclusion: At longer SOAs Japanese participants are better at using contextual information and disengage from the irrelevant gaze
Frame and Line Test (Kitayama et al. 2003)
exposure to society around us plays a role
individuals tended ot show the cognitive chracteristic common in the host culture
When do cultural attention-differences develop?
Imada et al., 2013
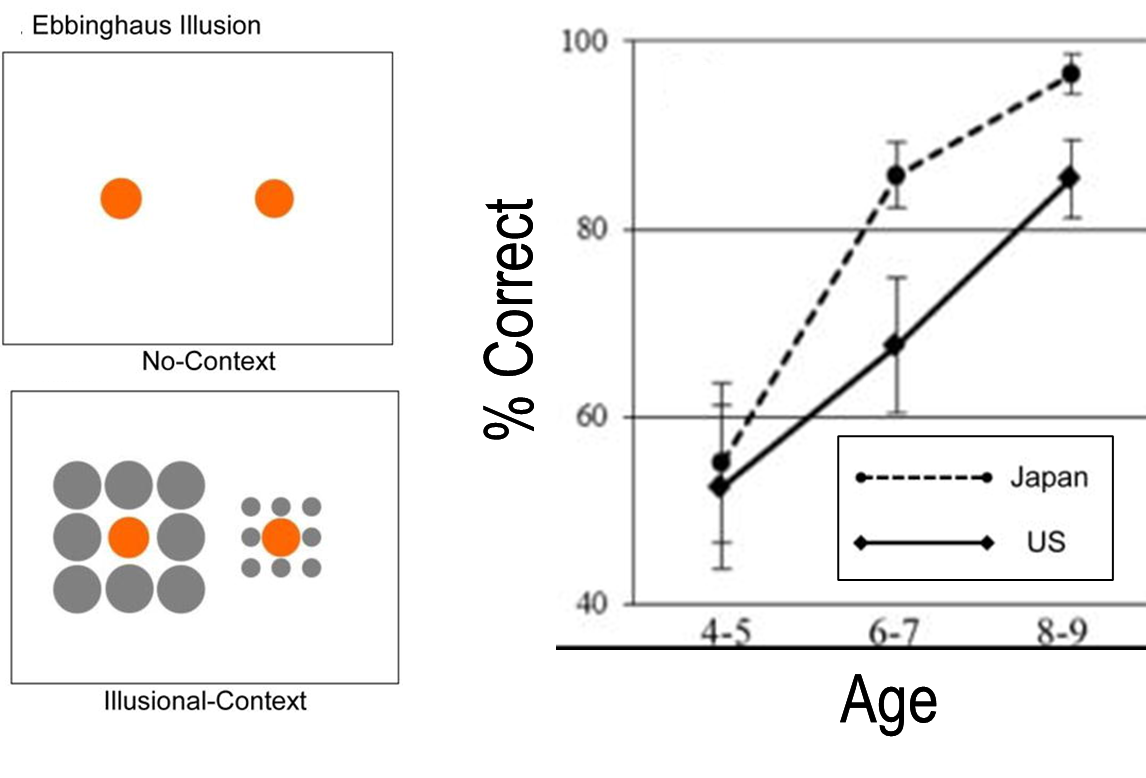
at age 4-5 children did not show any difference in accuracy
by age 6-7 Japanese children showed better performance, indicating higher context sensitivity
Culture and the physical environment: holistic vs analytic perceptual affordances
Affordance: property of an object that defines its possible uses
Are culturally specific patterns of attention afforded by the perceptual environment of each culture?
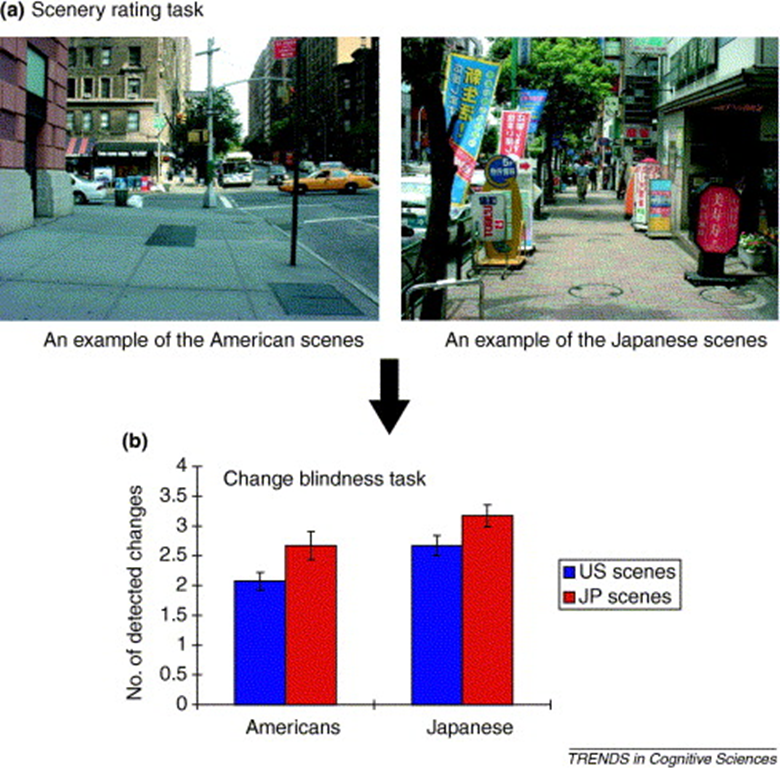
Study 1: Scene perception study
Conclusion: Japanese city scenes are more complex and ambiguous than American city scenes, suggesting that objects look more embedded in the field in the Japanese perceptual environment.
Study 2 change blindness task
Miyamoto et al. 2006
Japanese participants were more likely to detect the change (as they attend more to contextual information)
Both Japanese and American participants who viewed scenes from Japanese cities were more able to detect changes
Japanese cities helped participants attend to more contextual information.
“Culturally characteristic environments may afford distinctive patterns of perception”
Summary
Initial response to stimuli is the same (bottom-up) but modulated later, based on the task
Culture shapes how we attend to information
Westerners and East Asians attend more likely to attend analytically and holistically:
Differences are both social and non-social
Easterners tend to take more consideration of contextual information than Westerners
Default patterns of attention can be modified
Cognitive psychology paradigms can help to both reveal and improve understanding of cultural differences
Reading-
PERCEIVING AN OBJECT AND ITS CONTEXT IN DIFFERENT CULTURES: A Cultural Look at New Look
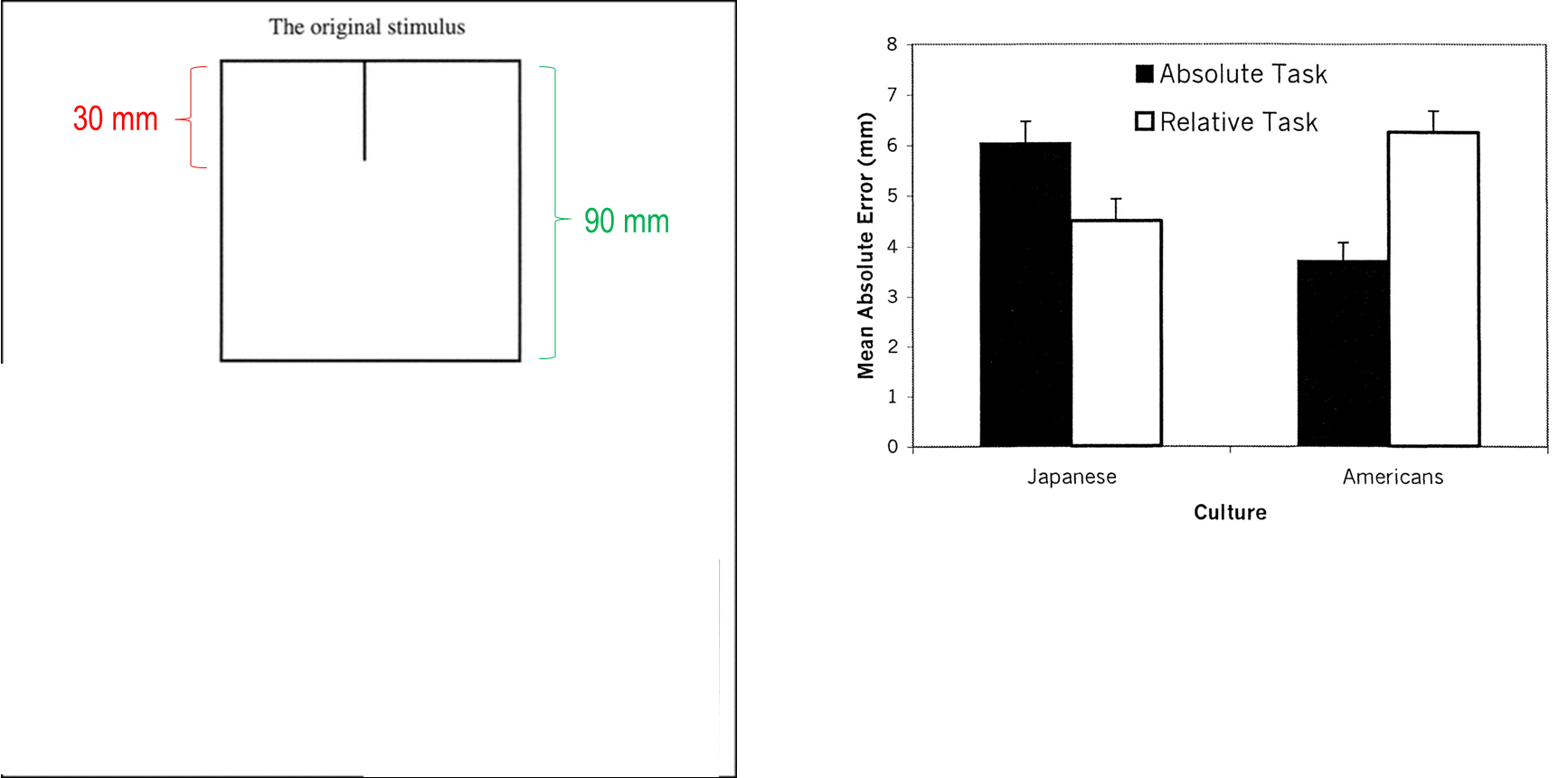
Abstract: —In two studies, a newly devised test (framed-line test) was used to examine the hypothesis that individuals engaging in Asian cultures are more capable of incorporating contextual information and those engaging in North American cultures are more capable of ignoring contextual information. On each trial, participants were presented with a square frame, within which was printed a vertical line. Participants were then shown another square frame of the same or different size and asked to draw a line that was identical to the first line in either absolute length (absolute task) or proportion to the height of the surrounding frame (relative task). The results supported the hypothesis: Whereas Japanese were more accurate in the relative task, Ameri cans were more accurate in the absolute task. Moreover, when engaging in another culture, individuals tended to show the cognitive characteristic common in the host culture.
Although perception depends on sensory input, it also involves a variety of top-down processes that are automatically recruited to ac tively construct a conscious percept from the input. According to this thesis, called New Look in the 1950s, the percept is significantly mod ified by expectations, values, emotions, needs, and other factors that are endogenous to the perceiver. Exogenous factors, such as physical properties of the imping ing stimulus, cannot account, in full, for the emerging percept. Al though initial demonstrations evoked considerable controversy and skepticism, the basic idea has proved quite viable, and has since taken a strong hold in the mainstream of cognitive and social psychology. In large part, however, this literature has so far ignored culture. This omission is both surprising and unfortunate. As a pool of ideational re sources (e.g., lay theories, images, scripts, and worldviews) that are embodied in public narratives, practices, and institutions of given geographic regions, historical periods, and groups, whether ethnic, religious, or otherwise, culture may be expected to be one source, and perhaps the most fundamental source, of each person’s values, expectations, and needs. The purpose of the current work, then, was to take a renewed look at the New Look from a cultural point of view
Culture and cognition
A number of recent studies focusing on cultural variation in cogni tive processes have already shed some light on this issue. As a whole, these studies suggest that different cultures foster quite different modes of cognitive processing. In particular, people engag ing in North American cultures (North Americans, in short) are assumed to be relatively more attuned to a focal object and less sensitive to con text. North Americans are thus described as analytic or field independent in cognitive style. Conversely, persons engaging in Asian cultures (Asians, in short) are hypothesized to be attuned more to contextual information—namely, in formation that surrounds the focal object. Asians are thus described as holistic or field dependent in cognitive style. These culturally divergent cognitive characteristics have been examined with several different measures, such as attitude attribution, performance in a rod-and-frame task (RFT), a Stroop interference effect, and context-dependent memory. A reasonable conjecture from this emerging literature is that the cross-cul turally divergent modes of cognitive processing must be differentially advantageous, depending on the demands of a particular task. Specifically, some tasks require ignoring contextual information when making a judgment about a focal object. For example, a judgment about another person may often be tainted by wrong stereotypes associ ated with a group of which that person is a member. In these circum stances, it is necessary to discount any such stereotypes. Such tasks may be called absolute tasks in that the focal judgment must be uninfluenced or unchanged by any contextual information. In these tasks, performance should be better for North Americans than for Asians. Using the RFT, Ji et al. (2000) recently provided evidence supporting this prediction. Participants viewed a tilted frame with a ro tating line placed at the center. The participants’ task was to rotate the line so that it was orthogonal to the earth’s surface (or it was aligned to the direction of gravity) while ignoring the frame. Ji et al. found that Americans were more accurate than Chinese in aligning the line (hence indicating their superior ability to ignore contextual information). This evidence is noteworthy because the RFT has no obvious so cial elements. In contrast, other tasks require incorporating contextual informa tion. For example, a judgment about another person often benefits from attention duly given to the specific social situation in which that person behaves. These tasks may be called relative tasks in that the fo cal judgment must change in accordance with the nature of the rele vant context. One might expect that Asians with contextual sensitivity would have an advantage over North Americans in performing such tasks. The evidence supporting this prediction comes exclusively from social domains. Thus, it is well known that North Americans often fail to give proper weight to significant contextual information in drawing a judgment about a focal person. This bias, called the fundamental at tribution error, is typically substantially weaker in Asian cultures
The present research
The available evidence indicates that there is substantial cognitive difference across cultures. Furthermore, this difference can be demonstrated with both tasks that are obviously social and those that are minimally social. Nevertheless, there are some significant limitations that have hampered the further development of theory on cultural variation in cognitive competences. First, with the important exception of the work by Ji et al. (2000), virtually no studies have evaluated performance against any objective criterion. This makes it difficult to draw any conclusions on the nor mative status of the cognitive biases that are suggested in the litera ture. Second, in all the existent studies examining relative tasks (e.g., attitude attribution), participants were not instructed to use contextual information, and therefore it is uncertain whether the cross-cultural differences were due to Asians’ greater propensity to attend to the con text, their greater competence to incorporate information in the con text, or both. Third, though the RFT findings of Ji et al. suggest that North Americans’ greater ability to ignore context extends from social to nonsocial tasks, it is not clear whether Asians’ greater ability to in corporate context extends to nonsocial tasks. Fourth, and perhaps most important, in all the existent studies, very different domains, such as line alignment and social perception, were used in defining the two theoretical types of tasks. This makes it impossible to draw any mean ingful comparison between performance in an absolute task and per formance in a relative task. In an effort to address these limitations inherent in the current evi dence, we developed a new test called the framed-line test (FLT). The FLT is specifically designed to assess both the ability to incorporate and the ability to ignore contextual information within a single domain that is arguably nonsocial. Further, this assessment can be made in reference to an objective standard of performance. Specifically, on each trial, par ticipants are presented with a square frame, within which is printed a vertical line. The participants are then shown another square frame of the same or different size and asked to draw a line that is identical to the f irst line in either absolute length (absolute task) or proportion to the height of the surrounding frame (relative task). In the absolute task, the participants have to ignore both the first frame (when assessing the length of the line) and the second frame (when reproducing the line). Hence, North Americans should perform this task better than Asians. In the relative task, the participants have to incorporate the height information of the surrounding frame in both encoding and reproducing the line. Hence, Asians should perform this task better than North Americans. Moreover, one major advantage of the FLT is that it allows an assessment of the relative ease or difficulty of the two tasks. We predicted that whereas Asians would be more ac curate on the relative task than the absolute task, the reverse would be the case for North Americans
Study 1: the FLT in Japan and the US
Method:
participants:
Twenty undergraduates at Kyoto University, in Kyoto, Japan (8 males and 12 females), and 20 undergraduates at the University of Chicago (9 males and 11 females) volunteered to participate in the study. All the Japanese undergraduates were native Japanese, and all the Ameri can undergraduates were of European descent.
materials and procedure:
Upon arrival in a lab, participants were told that they would per form simple cognitive tasks. They were given both the absolute task and the relative task in a counterbalanced order, receiving specific in structions for each task right before they performed it. In both tasks, on each trial they were shown a square frame, within which a vertical line was printed. The line was extended downward from the center of the upper edge of the square (see Fig. 1). The participants were then moved to a different table placed in the opposite corner of the lab (so as to ensure that iconic memory played no role) and shown a second square frame that was either larger than, smaller than, or the same size as the first frame. The task was to draw a line in the second frame. In the absolute task, the participants were instructed to draw a line that was the same absolute length as the line in the first frame. In the rela tive task, the participants were instructed to draw a line whose propor tion to the size of the second frame was the same as the proportion of the first line to the size of the first frame. We took care to ensure that the participants understood the tasks by using concrete examples, such as the ones given in Figure 1. The stimuli were prepared such that there were five different combinations of the relative sizes of the two frames and the line in the first frame.
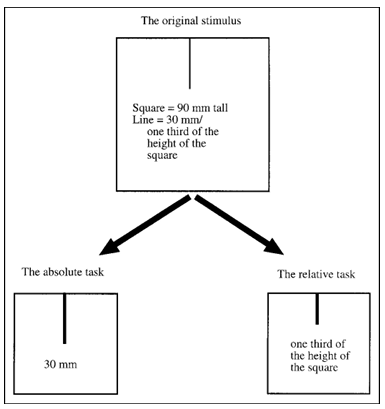
Fig. 1. Example of the framed-line test (FLT) used in these studies. Participants were shown a square frame with a vertical line, and asked to draw a line in a new square of the same or different size. The line was to be drawn so that it was identical to the first line in absolute length (absolute task) or so that the proportion between the length of the line and the height of its frame was identical to the proportion be tween the line and frame in the original stimulus (relative task).
In two combinations the first frame was smaller than the second, and in two other combinations the first frame was larger than the second. Furthermore, in half of these cases, the first line was longer than one half the height of the first square, and in the remaining half, the first line was shorter than half the height of the first square. Finally, in the fifth combination, the first and the second frames were identical in size. This last case is of interest because the correct response would be identical in the relative and the absolute tasks. The five combinations were presented in a random order. The same stimuli were used in the relative and absolute tasks.
Results and discussion
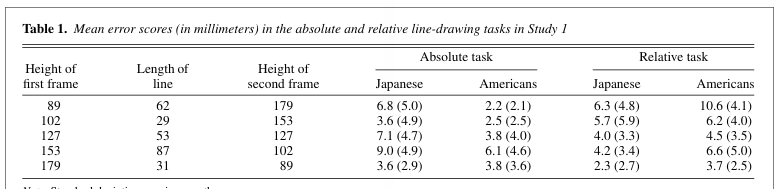
An inspection of the data showed that overestimation and underes timation occurred to a nearly equal extent for each of the five stimulus combinations. Accordingly, in order to assess performance in the two tasks, we measured the lines drawn by the participants and calculated the absolute difference between these lengths and the correct lengths. Because the absolute size of error increased somewhat as the lines be came longer, we also analyzed the percentage of the error relative to the correct line length. The results were no different whether we ana lyzed absolute error or percentage of error. We therefore discuss only the results for absolute error. The mean error scores for the two tasks are summarized in Table 1. These means were submitted to an analysis of variance (ANOVA) with one between-subjects variable (culture of participant: Japanese vs. American) and two within-subjects variables (task: absolute vs. relative; stimulus version: the five combinations of frames and line). A preliminary analysis had shown that the effects did not depend on either gender of the participants or the order in which the two tasks were given. As predicted, the interaction between culture and task proved significant, F(1, 38)= 24.41, p<.0001. The pertinent means are plotted in Figure 2. As predicted, Japanese performed the relative task significantly more accurately than the absolute task (Ms 6.05 vs. 4.52), t(38)= 2.56, p< .02. In contrast, Americans performed the absolute task more accurately than the relative task (Ms 6.35 vs. 3.71), t(38)= .01. Moreover, Americans performed the absolute task significantly better than Japanese, t(38)=4.57, p<3.92, p in the relative task, t(38) .01, and the reverse was true for performance 3.06, p<.01. The relative ease of the two tasks varied across the five stimulus combinations, as indicated by a significant main effect of version and a significant interaction between version and task, F(4, 152)= 8.95, p<.001, and F(4, 152)= 9.44, p<.001. However, the three-way interaction involving culture, task, and version was negligible (F<1). Thus, the pattern in Figure 2 emerged over all the five combinations. The same pattern emerged even when the two frames were identical in size, and the correct length was identical in the two tasks. Specifically, for this stimulus combination, Japanese performed the relative task significantly better than the absolute task, t(38) = 2.53, p<.02, although the difference in performance was considerably attenuated for Americans, t<1.
Study 2: variability and malleability of FLT performance:
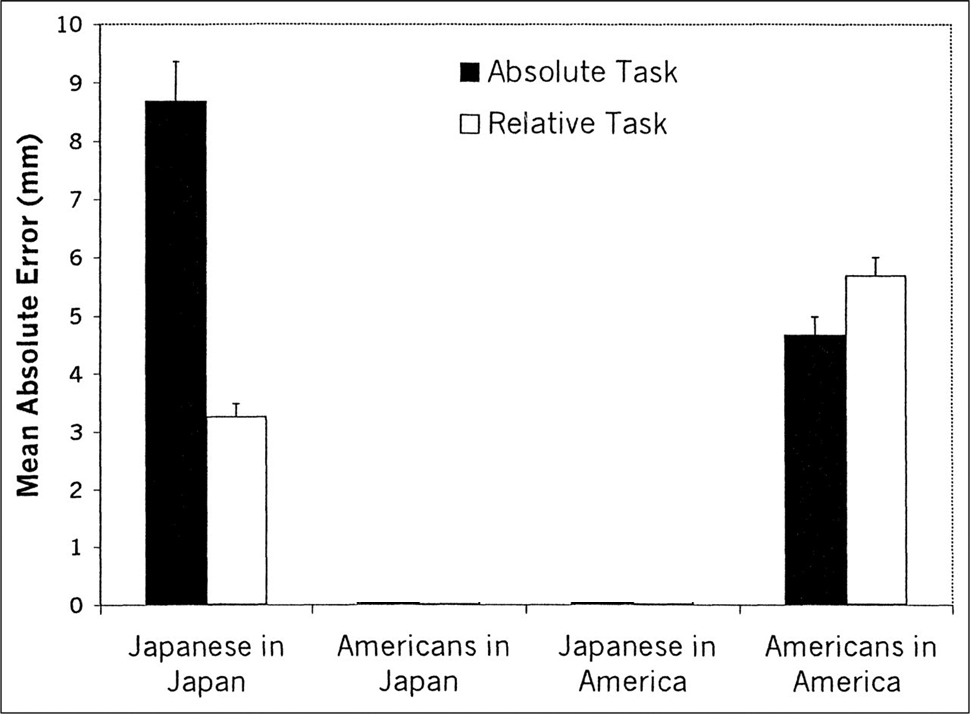
In Study 2, we sought to replicate Study 1 and to extend it by testing both Americans and Japanese in both Japan and the United States. This effort was motivated by a concern with the variability and malleability of cross-cultural variations. If, for example, the cross-cultural difference we observed is both relatively uniform within each culture and relatively stable and traitlike over time, then the cross-cultural variation should be entirely a function of the cultural origins of each participant: Americans (or Japanese) should show a prototypically American (or Japanese) pat tern more or less uniformly regardless of where they are tested. If, how ever, the cognitive abilities at issue are both variable and malleable, there ought to be considerable variation as a function of both the cultural origins of participants and the specific location in which they are tested. Specifically, participants in a foreign culture should show a pattern of cognitive biases that resembles the pattern typical in the host culture.
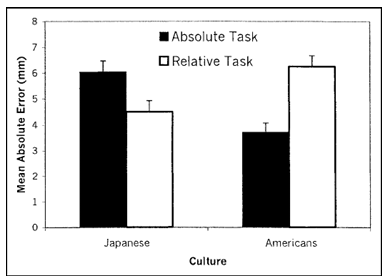
Fig. 2. Results from Study 1: Japanese and American participants’ mean error (in mms) in the two line-drawing tasks of the framed-line test. The error bars represent standard errors.
Method:
participants-
Four groups of individuals (total N 111) volunteered for the study. The Japanese in Japan were 32 undergraduates (20 males and 12 females) at Kyoto University. They were tested by a Japanese experimenter, and instructions were given in Japanese. The Americans in Japan were 18 ex change students (8 males and 10 females) who were temporarily staying at the Kansai Institute for Foreign Languages. They had stayed in Japan for 4 months at most, and their Japanese proficiency was quite limited. They were tested by a Japanese experimenter, and their instructions were given in English. The Americans in the United States were 40 undergraduates (21 males and 19 females) at the University of Chicago, and the Japanese in the US were 21 Japanese undergraduates (13 males and 8 females) who were temporarily studying at the University of Chicago. These Japanese had stayed at the university for a varying length of time, from 2 months up to 4 years. The Americans and the Japanese in the United States were both tested by an American experimenter, and instructions were given in English.
materials and procedure-
Six different combinations of the relative sizes of the two frames and the line in the first frame were prepared. They were similar to the combinations used in Study 1, except that some of the ratios of the size of the two frames were somewhat changed and the pattern with the two frames of the identical size was run in two variations. The participants were tested individually using the same procedure as in Study 1.
Results and discussion-
As in Study 1, there was no systematic tendency for over- or under estimation in any of the stimulus combinations. Also as in Study 1, the results were no different whether we analyzed absolute error or per centage of error, so we discuss only the results for absolute error. Pre liminary analysis showed no significant effects involving the gender of participants. Although past research tended to show females to be more context sensitive than males, this effect appears to be less robust than the cultural difference. Also as in Study 1, we did not find any reliable effect of the order in which the two tasks were given.
The means were submitted to a 2 6 ANOVA, with two between-subjects variables (cultural origin of participant: Japanese vs. American; testing location: Japan vs. United States) and two within subjects variables (task: absolute vs. relative; stimulus version: the six combinations of frames and line). The mean error scores are summa rized in Table 2. The size of error varied systematically across the four groups of participants, as indicated by a significant main effect for testing location and a significant interaction between testing location and cultural origin, F(1, 105) 15.97, p .0001, and F(1, 105) 8.25, p .01. Further, the size of error was larger for the absolute task than for the relative task, F(1, 105) 39.56, p .0001. However, as in Study 1, the critical interaction between task and cultural origin proved to be highly significant, F(1, 105) 10.18, p .002. More over, we also found a highly reliable interaction between task and test ing location, F(1, 105) 56.19, p .0001. The pertinent means are summarized in Figure 3. As in Study 1, Japa nese participants in Japan proved to be much more accurate in the relative task than in the absolute task, t(105) 9.90, p .01. In contrast, Ameri cans in the United States were significantly more accurate in the absolute task than in the relative task, t(105) 2.15, p .05. The remaining two groups of participants showed an effect that strongly resembled the effect of the host culture. Thus, the pattern for Americans in Japan was closer to the pattern for Japanese in Japan than to the pattern for Americans in the United States. Likewise, the pattern for Japanese in the United States was closer to the pattern for Americans in the United States than to the pattern for Japanese in Japan. Examined from a different angle, performance in the relative task was significantly better for Japanese in Japan than for Americans in the United States, t(105) 7.84, p .001, but performance in the absolute task was better for Americans in the United States than for Japanese in Japan, t(105) 4.73, p .001. In both cases, the data in the remaining two groups fell in between. It is noteworthy that essentially the same pattern was observed across the six combinations of stimuli. In particular, as in Study 1, the same cross-cultural difference in error pattern was observed even when the two frames were equal in size
General discussion:
sociocultural shaping of attention and perception-
The current work is consistent with recent theorizing on cultural variation in cognition in showing that Japanese are more capable of incorporating contextual information in making a judgment on a focal object, but North Americans are more capable of ignoring contextual information. We demonstrated this cross-cultural variation in a nonsocial task that is specifically designed to simultaneously assess the two cognitive competences of ignoring or incorporating context. The FLT may be an important source of information about a nonsocial, basic cognitive capacity that is recruited in making more complex, contextualized judgments and perceptions. Future research should clarify both the social origins of the nonsocial cognitive and attentional skills and processes involved in the FLT and the contribution of these processes to judgments and inferences about social objects and events. We repeatedly found the same cross-cultural variation in error pat tern even when the two frames were identical. This finding contradicts the notion that Asians (or Americans) are predisposed to perform the relative (or the absolute) task even when instructed to do otherwise. If our participants had such predispositions, errors should have been minimal when the two frames were identical because, under these conditions, the correct answers in the two tasks converge. In view of the current evidence, we suggest that errors were due, in part, to difficulty in accurately encoding the central line. That is, whereas Japanese may have had difficulty releasing attention from the frame and then refocusing it on the line in the absolute task, Americans may have had difficulty releasing attention from the central line and shifting it to the frame in the relative task.1 Future work should examine the role of attentional and other mechanisms in greater detail.
Limitations-
The effects of cultural origins of participants and test locations in Study 2 are quite suggestive, but should be interpreted with caution. One provocative interpretation is that the effect of test location was caused by immersion in a new culture. That is, cognitive and attentional capacities and tendencies may be modified in accordance with new demands and affordances of living in a new host culture. Such a modification might be permanent once it takes place or relatively temporary and reversible; these different possibilities have different implications for what might be expected to happen when people return to their home country. However, other interpretations of our data are also possible. Be cause of a variety of practical constraints associated with cross-cul tural experimental research, we could not exercise the degree of experimental control that we would have preferred. In particular, we depended entirely on convenience samples. We wish to acknowledge three resulting difficulties in interpretation. First, the average length of stay in the host culture turned out to be very different between the Americans in Japan and Japanese in the United States. Although this variable did not correlate with the size of error in the two tasks, a more balanced sampling would have been desirable. Second, the language used for instructions was also chosen for convenience. In particular, in the United States not only Americans but also Japanese were tested in English, but in Japan participants were tested in their native languages. This might have had an unknown degree of influence on the results because evidence indicates that language can prime the associated culture. Third, and most intriguing, both the Japanese participants in the United States and the American participants in Japan were people who voluntarily moved to the other culture. Though the obtained effects on cognitive biases may have been due to immersion in a new culture, the possibility of selection bias is equally viable. That is, only those people who have psychological affinities to another culture may find themselves living in this other culture. Although these explanations for the effect of test location are not mutually exclusive, future work should empirically address their relative significance.
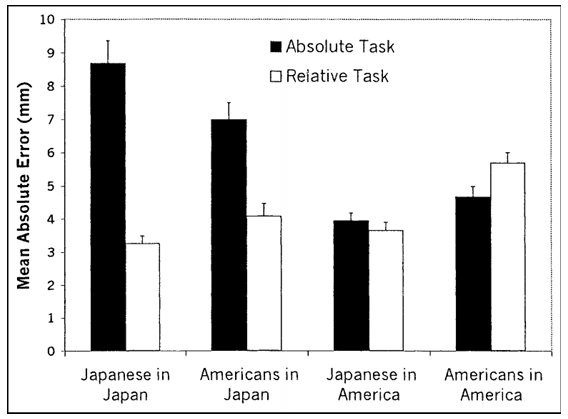
Fig. 3. Results from Study 2: Mean error scores (in mms) in the two line-drawing tasks of the framed-line test. Results are shown separately for Japanese and Americans in the two cultural locations, Japan and the United States. The error bars represent standard errors.
conclusions
Culture is a source of generic expectations; default goals, desires, and needs; and overarching values. Cultural variations in attention, per ception, and cognition, then, would enable researchers to take a renewed look at the New Look. The current work suggests that different cultures’ practices and beliefs encourage very divergent cogni tive and attentional capacities involved in either incorporating or ignor ing context while making a judgment about a focal object. Future work along the lines proposed here may reveal a degree of so ciocultural shaping of attention and perception that is substantially greater than has so far been assumed in the psychological literature. If so, this evidence would provide a solid basis for reconceptualizing human psychological processes and structures as fully embedded in and thus significantly constituted by the collectively shared practices, values, and beliefs of culture. Indeed, if properly analyzed, the the sis of the New Look will be instrumental in breaking a self-imposed shell of the traditional psychological discipline and broadening its horizon to include society, culture, and history in its territory of investigation.