chapter 3: biological bases of behavior
neuroanatomy
neuroanatomy - refers to the study of the parts and function of neurons
neurons - are individual nerve cells that make up the entire nervous system
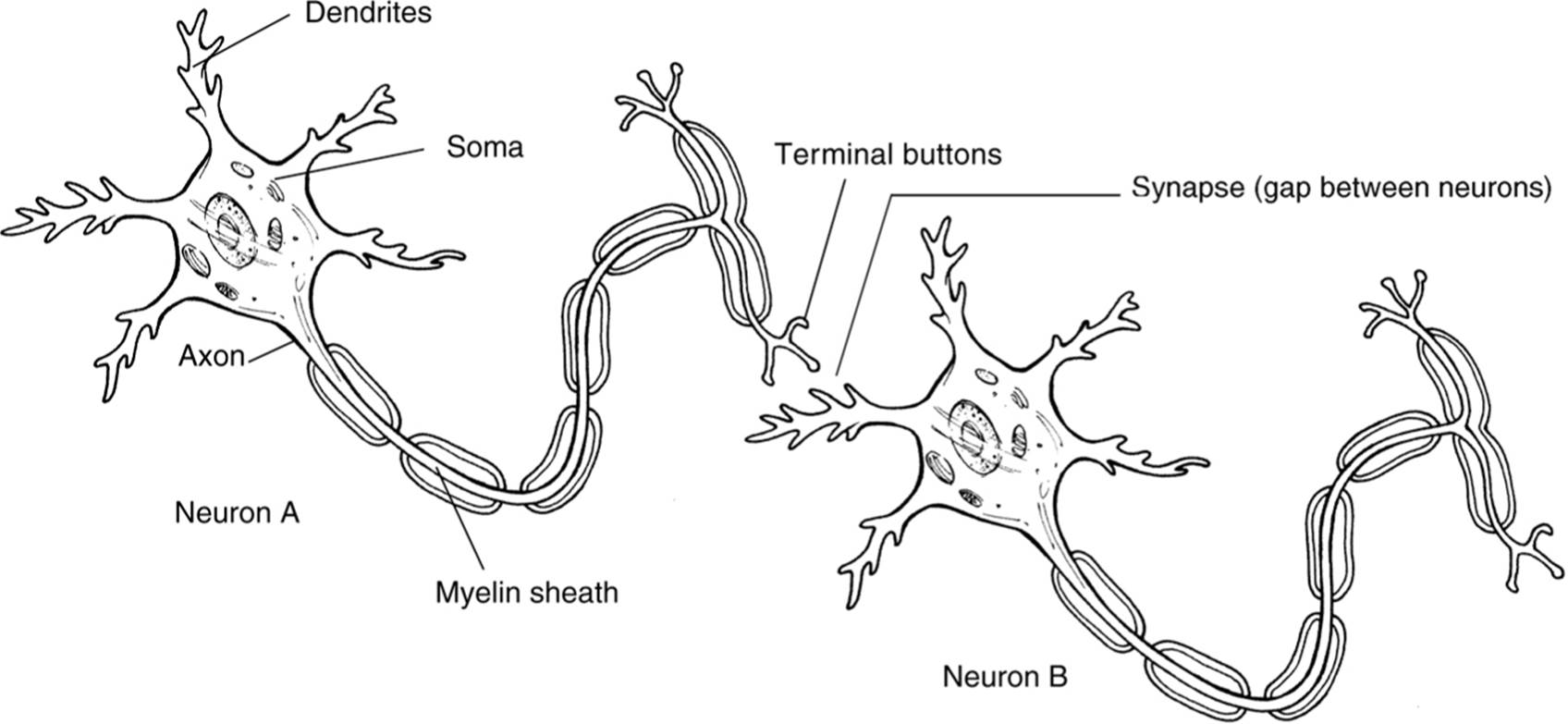
dendrites - rootlike parts of the cell that stretch out from the cell body. these grow to make synaptic connections with other neurons
cell body - also called the soma, contains the nucleus and other parts of the cell needed to sustain its life
axon - wirelike structure ending in the terminal buttons that extends from the cell body
myelin sheath - a fatty covering around the axon of some neurons that speeds neural impulses
terminal buttons - also called end button, terminal branches of the axon, and synaptic knobs, is the branched end of the axon that contains neurotransmitters
synapse - the space between the terminal buttons of one neuron and the dendrites of the next neuron
how a neuron “fires”
- when a neuron is resting, it has a slightly negative charge because there are negative ions within the cell and positive ions surrounding it
- the cell membrane of the neuron is semi-permeable and prevents the ions from mixing
- (look at the picture above for the following bullet points) the reaction begins when the terminal buttons of one neuron are stimulated and release neurotransmitters into the synapse.
- these neurotransmitters fit into receptor sites on the dendrites of the other neuron
- once enough neurotransmitters are received, which is called the threshold, the cell membrane of the other neuron becomes permeable, which causes positive ions to rush into the cell, making the charge positive (+40mv)
- the change in charge spreads down the length of this neuron, which is called an action potential.
- once the charge reaches the terminal buttons, the process repeats if enough neurotransmitters are received to pass the threshold
- all-or-none principle - this states that the neuron either ires completely or it does not fire. if the dendrites of a neuron have enough neurotransmitters to push the neuron past the threshold, the neuron fires completely every time.
neurotransmitters
- there are different types of neurotransmitters.
- some neurotransmitters are excitatory, which means that they excite the next cell into firing
- other neurotransmitters are inhibitory, which means that they inhibit the next cell from firing
- each synaptic gap contains different amounts and different kinds of inhibitory and excitatory neurotransmitters
- the amount of inhibitory and excitatory neurotransmitters received at the receptor sites determine whether a neuron passes the threshold and fires
afferent neurons (or sensory neurons)
- afferent neurons - takes information from the senses to the brain
interneurons
- interneurons - once information has reached the brain or spinal cord, these take the messages and send them elsewhere in the brain or onto efferent neurons
efferent neurons (or motor neurons)
efferent neurons - takes information from the brain to the rest of the body
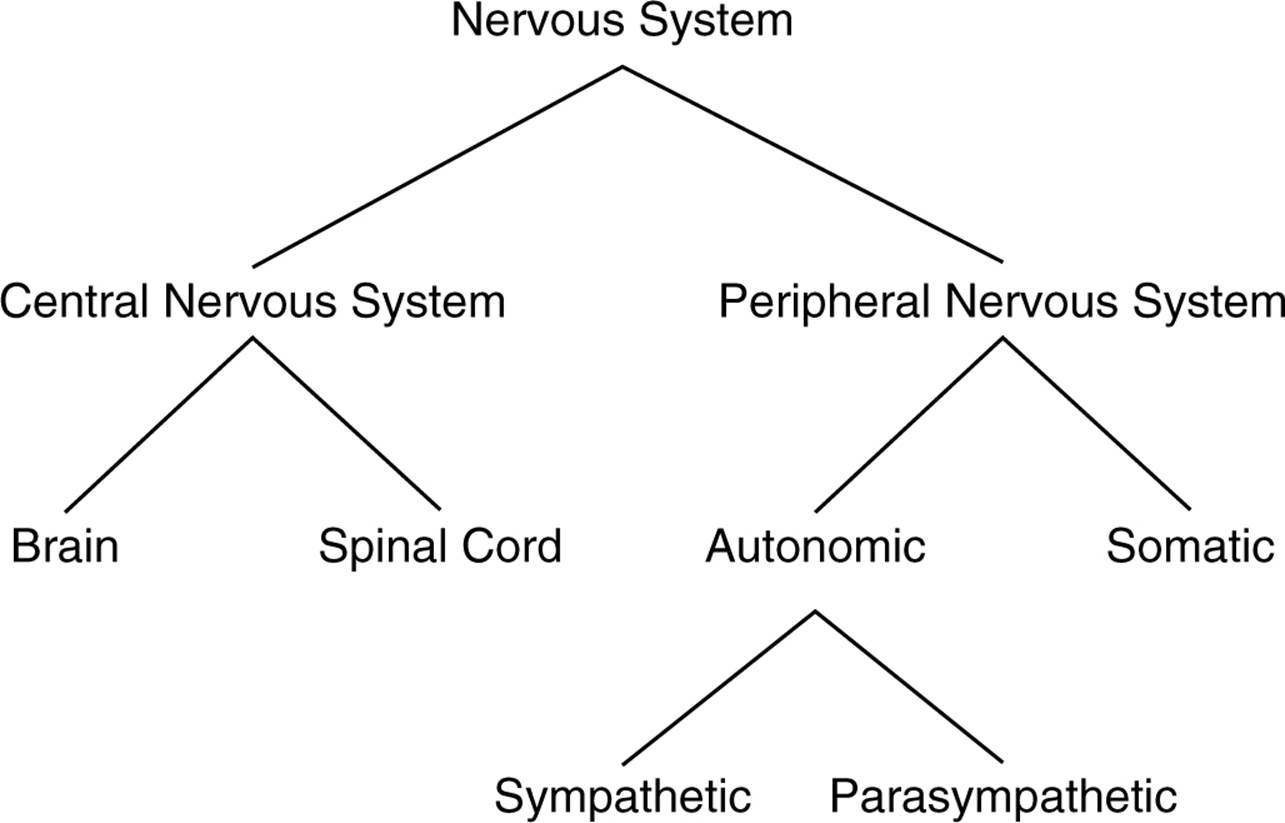
the central nervous system
- central nervous system - consists of our brain and spinal cord and all of the nerves housed which are within bones
- the spinal cord is a bundle of nerves that run through the center of the spine and transmits information from the rest of the body to the brain
the peripheral nervous system
- peripheral nervous system - consists of all the other nerves in your body or all nerves, not in bone
- this is divided into two categories: the somatic and the autonomic nervous systems
somatic nervous system
- somatic nervous system - controls our voluntary muscle movements
- the motor context of the brain sends impulses to the somatic nervous system and controls our muscles
autonomic nervous system
- autonomic nervous system - controls the automatic functions of our body, such as our heart, lungs, internal organs, and glands
- these nerves help with controlling our responses to stress
- stress - the fight or flight response that prepares our body to respond to a perceived threat
- this is divided into two categories: the sympathetic and the parasympathetic nervous systems
sympathetic nervous system
- sympathetic nervous system - prepares the body to respond to stress
- this carries messages to the control systems of the organs, glands, and muscles that direct our body’s response to stress
- in other words, this is the alert system of our body. while it does accelerate some functions, it also conserves resources that are needed for a quick response by slowing down other functions
parasympathetic nervous system
- parasympathetic nervous system - is responsible for slowing down our body after a stress response
- this carries messages to the stress response system and causes our body to slow down, almost like a brake pedal that slows down the autonomic nervous system
normal peripheral nervous system transmission
- an example of this can be where if you stub your toe, sensory neurons are activated, and a message is transmitted up a neuron that runs from your toe to the base of your spine, which is your afferent nerves.
- this message continues up your spinal cord until it enters the brain through the brain stem and is transmitted into the brain’s sensory cortex
- the motor cortex then sends impulses down the spinal cord to the muscles controlling your foot, causing a reaction of pain
reflexes: an important exception
- humans have a few reflexes that work differently
- if you stimulate the correct area below your kneecap, your leg will jerk without conscious control
- this is because that sensory information was processed by the spine, and the spine tells the leg to move
- another reflex occurs when we come into contact with heat or cold
- if we touch an object that is very hot or cold, our spine will send back a message jerking us away from the object, which could help keep us from getting harmed
ways of studying the brain: accidents
- accidents that occur and damage the brain bring research and give clues about brain function
lesions
- lesioning - the removal or destruction of part of the brain
- this is never done for experimental purposes but is done when doctors decide that this is the best treatment for certain situations
- any time brain tissue is removed, researchers can examine behavior changes and try to infer the function of that part of the brain
electroencephalogram
- electroencephalogram (or EEG) - detects brain waves
- researchers can examine what type of waves the brain produces during different stages of consciousness and use the information to generalize about brain function
computerized axial tomography
- computerized axial tomography scan (CAT or CT) - a sophisticated X-ray that uses several cameras that rotate around the brain and combine all the pictures into a detailed three-dimensional picture of the brain’s structure
- a CT scan can only show the structure of the brain, not the functions or activity of different brain structures
magnetic resonance imaging
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) - gives you pictures of the brain like a CT scan but uses magnetic fields to measure the density and location of brain material
- because an MRI doesn’t use X-rays as a CT scan does, the patient is not exposed to carcinogenic radiation
- similar to the CT scan, the MRI gives doctors information about only the structure of the brain, not the function
positron emission tomography
- positron emission tomography scan (PET) - lets researchers see what areas of the brain are most active during tasks by measuring how much of certain chemical parts of the brain are using
- the more chemicals used, the higher the activity
- different types of scans are used for different chemicals, such as neurotransmitters, drugs, and oxygen flow
functional MRI
functional MRI (fMRI) - a new technology that combines elements of the MRI and PET scans and can show details of brain structure with information about blood flow in the brain
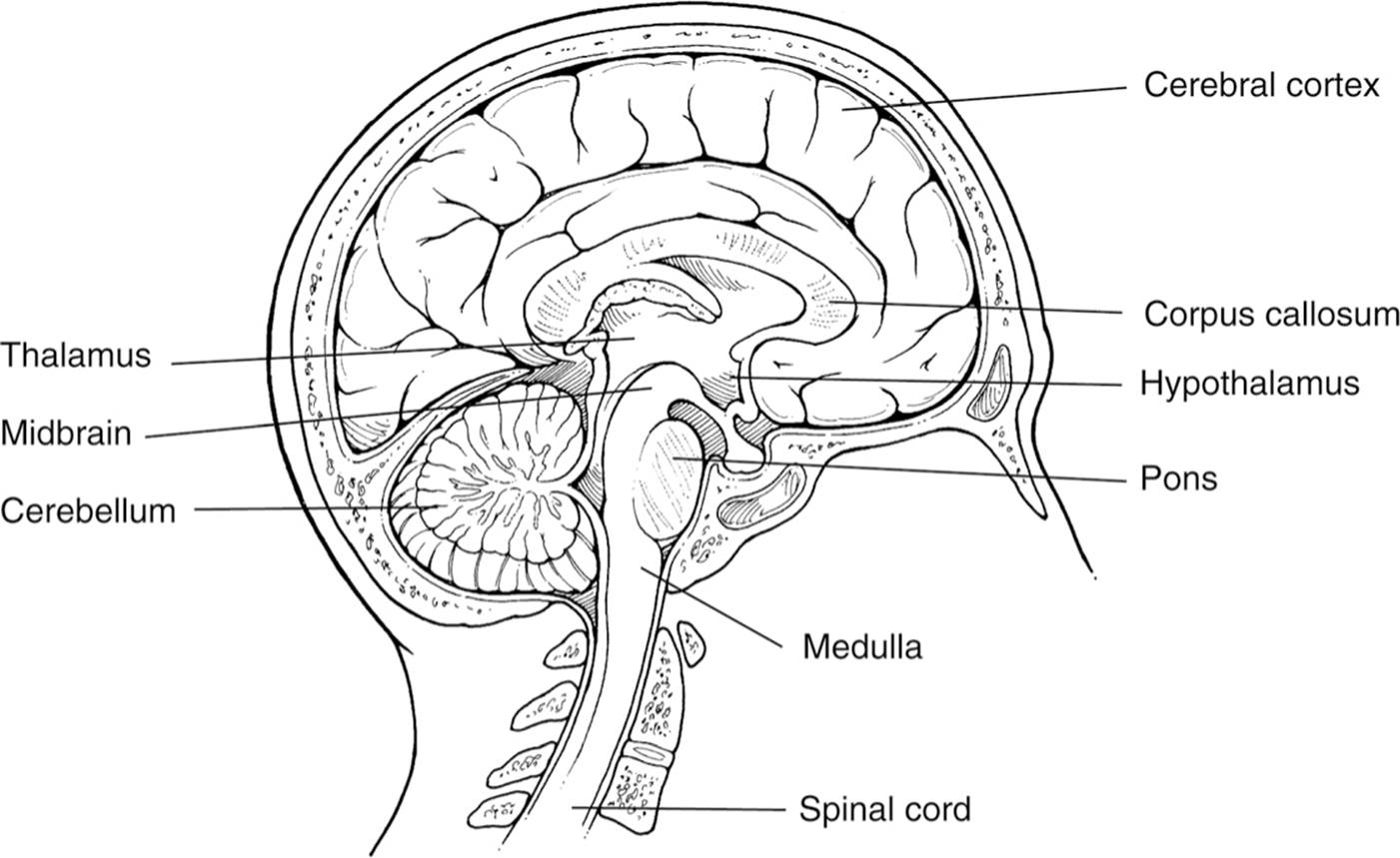
hindbrain
- hindbrain - contains structures in the top part of the spinal cord
- it is our life support system and controls basic biological functions that keep us alive
- important specific structures within the hindbrain are the medulla, pons, and cerebellum
medulla
- medulla - involved in the control of our blood pressure, heart rate, and breathing
- is also known as the medulla oblongata and located above the spinal cord
pons
- pons - connects the hindbrain with the midbrain and forebrain, also controls facial expressions
cerebellum
- cerebellum - coordinates some habitual muscle movements, such as tracking a target with our eyes
- means little brain since it looks like a smaller version of the brain
midbrain
- midbrain - coordinates simple movements with sensory information, is between the hindbrain and the forebrain, integrates some types of sensory information and muscle movements
- reticular formation - a netlike collection of cells throughout the midbrain that controls general body arousal and the ability to focus our attention
- if the reticular formation does not function, we fall into a coma
forebrain
- the forebrain is very important to psychologists and controls what we think as thought and reason
- the size of the forebrain makes humans human, which is why psychologists mostly focus on this area of the brain
- specific areas in the forebrain are the thalamus, hypothalamus, amygdala, and the hippocampus
thalamus
- thalamus - located on top of the brain, is responsible for receiving sensory signals coming up the spinal cord and sending them to the appropriate areas in the rest of the forebrain
hypothalamus
- hypothalamus - a small structure right next to the thalamus, controls several metabolic functions, such as body temperature, sexual arousal, hunger, thirst, and the endocrine system
amygdala and hippocampus
- hippocampus - the two arms surrounding the hypothalamus
- amygdala - the structures near the end of each hippocampal arm
- the amygdala is vital to our experiences of emotion, while the hippocampus is vital to our memory system
- memories aren’t permanently placed in this area of the brain but are instead processed through this area and sent to other locations in the cerebral cortex for permanent storage
hemispheres
the cerebral cortex is divided into two hemispheres: the left hemisphere and the right hemisphere
they look like mirror images of each other but have some differences in terms of function
the left hemisphere receives sensory messages and controls the motor function of the right half of the body
the right hemisphere receives sensory messages and controls the motor function of the left half of the body
this is called contralateral control
brain lateralization or hemispheric specialization: the specialization of function in each hemisphere
most research about the differences between the hemispheres is done by examining split-brain patients
split-brain patients - patients whose corpus callosum has been cut to treat severe epilepsy
corpus callosum - the nerve bundle that connects the two hemispheres
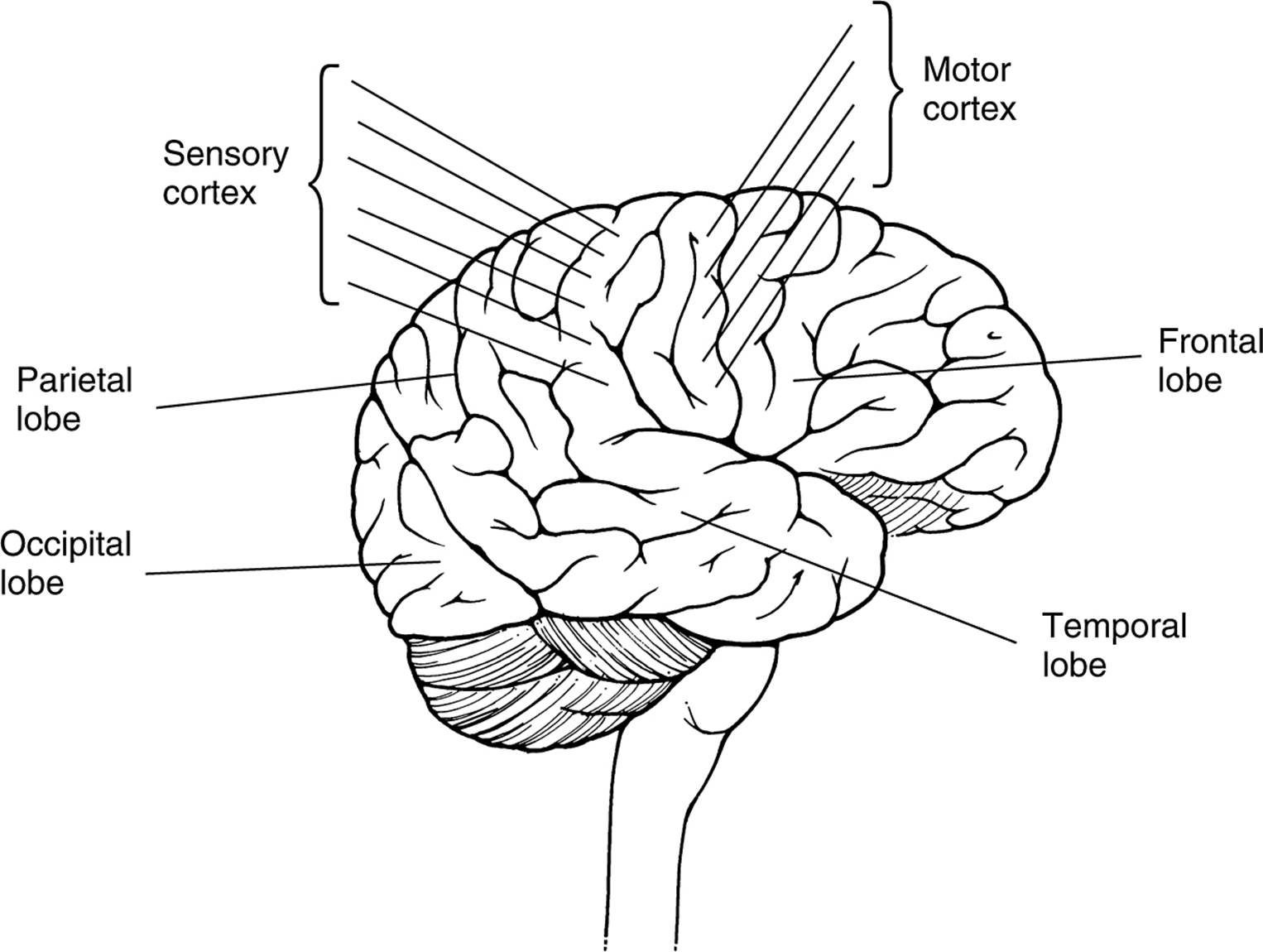
frontal lobes
- frontal lobes - large areas of the cerebral cortex located at the top front part of the brain behind the eyes
- prefrontal cortex - the front of the frontal lobe, plays a critical role in directing thought process and is important in foreseeing consequences, pursuing goals, and maintaining emotional control
- motor cortex - a thin vertical strip at the back of the frontal lobe and sends signals to our muscles, controlling voluntary movements
- the top of the body is controlled by the neurons at the bottom of this cortex and progresses down the body as you go up the cortex
- through this information, we can see that the top of the motor cortex controls the feet and toes of the body
parietal lobes
- parietal lobes - located behind the frontal lobe but still on top of the brain
- sensory cortex (or somatosensory cortex) - located right behind the motor cortex in the frontal lobe and is a thin vertical strip that receives touch sensations from the rest of our body
- this is similar to the motor cortex; the top of the sensory cortex receives reactions from the bottom of the body, while the bottom of the sensory cortex receives reactions from the top of the body
occipital lobes
- occipital lobes - are located at the very back of the brain, farthest from the eyes, one of the major functions is to interpret messages from our eyes in our visual cortex
- impulses from our retinas are sent to the visual cortex to be interpreted
- impulses from the right half of each retina are sent to the right occipital lobe while impulses from the left half of each retina are sent to the left occipital lobe
temporal lobes
- temporal lobes - process sound sensed by the ears. soundwaves are processed by the ears, turned into neural impulses, and interpreted in our auditory cortices
- sound that is received from the left ear is processed from both sides of the auditory cortex, unlike the visual cortex
endocrine system
- endocrine system - a system of glands that secrete hormones that affect many different biological processes in our bodies
- the endocrine system is controlled in the brain by the hypothalamus
adrenal glands
- adrenal glands - produce adrenaline and signal the rest of the body to prepare for fight or flight
ovaries and testes
- women’s ovaries and men’s testes produce sex hormones, which would be estrogen for women and testosterone for men
basic genetic concepts
- every human cell contains 46 chromosomes in 23 pairs, which are made up of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
- certain segments of DNA control the production of proteins that control human traits, and they are called genes
- genes could be either dominant or recessive. if we inherit two recessive genes for a trait, then that’s the trait that will be expressed. in any other combination of genes, the dominant trait is expressed.
twins
- identical twins (or monozygotic twins) share the same genetic material, researchers study them to examine the influence of genes on human traits
- a famous study showed that identical twins raised apart had a correlation coefficient of 0.69 for an IQ test, while identical twins raised in the same household has a correlation coefficient of 0.88.
- this showed that environment had an effect on IQ scores since twins raised in the same family had more similar IQs and the IQs of twins raised in separate families were highly correlated, showing that IQ is influenced by genetics
- there is one important critique where twins still look the same in terms of appearance which could cause people to treat them the same way, and creates the same effective psychological environment for both twins
chromosomal abnormalities
- gender is determined by our twenty-third pair of chromosomes.
- men have an X and Y chromosome while women have two X chromosomes
- men either contribute an X chromosome to their child, resulting in a girl, or a Y chromosome to their child, resulting in a boy
- sometimes, chromosomes can fail to combine or combine in an unusual way, which results in chromosomal abnormality.
- example: babies with Turner’s syndrome are born with only one X chromosome in the spot that is occupied by the twenty-third pair and causes different physical characteristics
- other examples include Klinefelter’s syndrome and Down syndrome