
how plants respond to the environment (2) + gibberellins
tropisms
tropisms are tropic movements (directional responses) seen in plants, in response to variety of possible stimuli
chemotropism: directional response to chemicals
phototropism: directional response to light stimuli
thermotropism: directional response to temperature
hydrotropism: directional response to water
thigmotropism: directional response to touch
shoots of climbing plants winding around other plants/solid structures ex. ivy
positive or negative
movement toward environmental stimulus is called positive tropism, movement away from stimulus is called negative tropism
shoot tips of plant that grow toward light source are positively phototropic
nastic movements
nasties are nastic movements (non-directional responses) which plants have in response to stimuli
chemonasty
photonasty
thermonasty
hydronasty
thigmonasty
gibberellins
named after fungus Gibberella fujikuroi - causes rice plants, on which it is parasitic, to grow abnormally tall.
disease of rice called ‘foolish seedling’ investigated in 1920’s by Japanese plant pathologist Eiichi Kurosawa.
substance causing abnormal growth was isolated from fungus + structural formulae identified
chemical found to belong to class of 100+ naturally occurring plant hormones called gibberellins
all acidic + usually referred to as GA (Giberellic acid)
overview: gibberellins
gibberellins are synthesised in apical portions of roots + stems
they play leading role in controlling stem elongation in growing stems of mature trees + shrubs, where it’s application characteristically promotes internode elongation
elongations effect also enhanced if auxin present
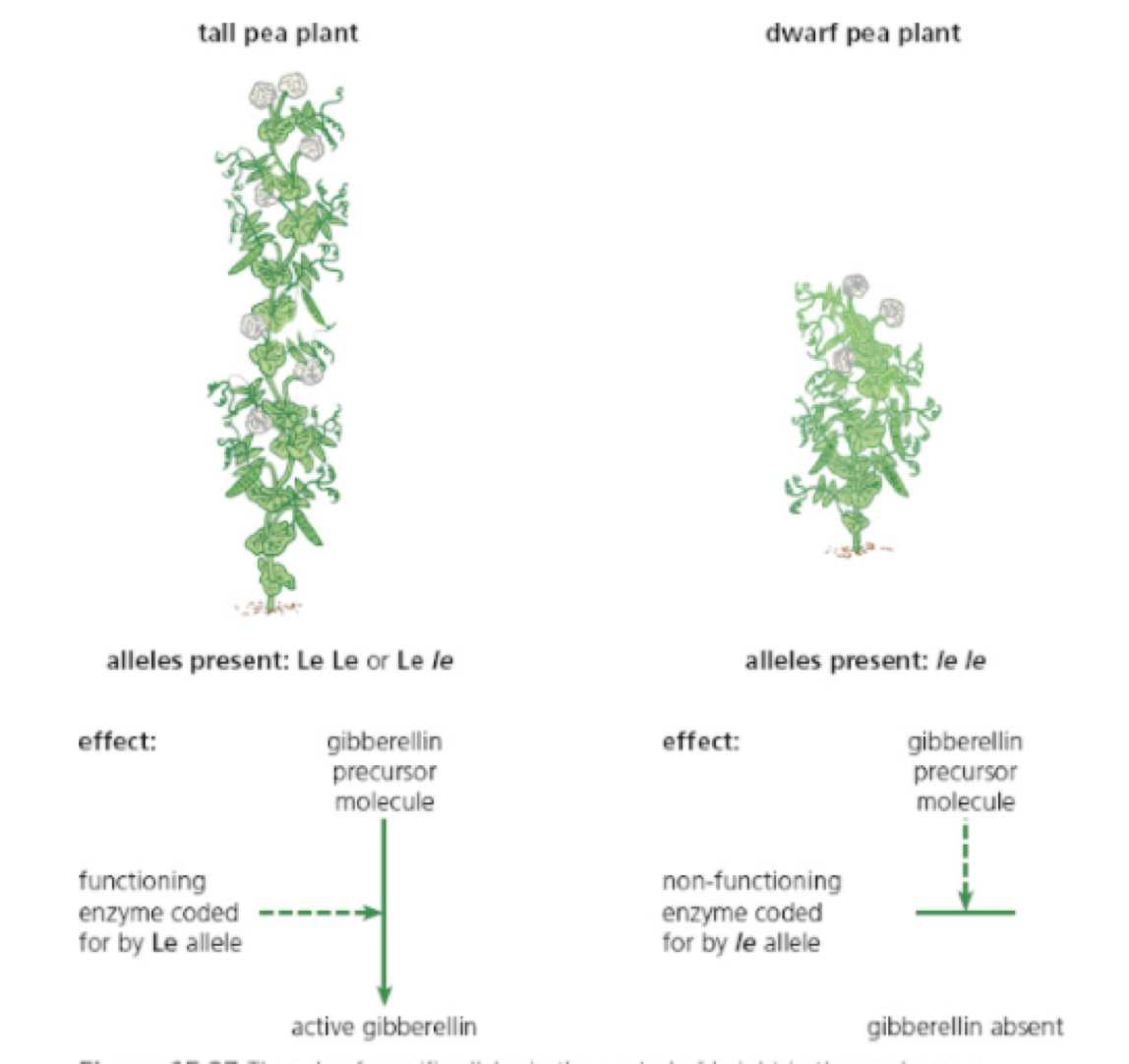
application of gibberellins to dwarf mutants is known to restore normal growth + development in many plants.
gibberellin application also induce some plants to grow out of rosette stage of + flower early during first growth year
also hastens seed germination, maybe bc can substitute for low light effects + temp requirements in this process
how gibberellins work
GA: all ‘terpenes’, complex group of plant chemicals related to lipids + are also acids
GA formed in:
Chloroplasts
Embryo of seeds
Buds
Root tips
Young leaves
Found to be absent from genetically dwarf varieties of plants.
migrate in non-polar manner that’s up/down plant in phloem + xylem
GA is involved in the extension growth of the stem, causing elongation of internodes.
highest concentration of GA is in fruits/seeds as they form plants + in seeds as they germinate.
other aspects of growth + development in higher plants:
Dormancy
Germination
Onset of flowering
main effects however is in stem elongation, mainly by affecting cell elongation


Absorption of water stimulates germination
Embryo synthesizes gibberellin in response to water uptake
Aleurone layer synthesizes amylase in response to gibberellin
Amylase mobilizes energy reserves: hydrolyses starch to maltose. Maltose is converted to glucose and respired to release ATP
questions
name plant hormone that initiates seed germination
gibberellin
which does not bring about directional growth response in plants
B: oxygen levels
when seed germinates it does not obtain energy through photosynthesis. explain where the energy for the initial growth of a seed comes from…
.digestion/breakdown of starch by enzymes. this produces sugar that is used in respiration
what is a non-directional response in a plant called?
nastic movement
mean height dwarf pea plant 1.18, 3.32, 4.68, 6.56, 8.54, 13.28, 15.78
mean height treated dwarf pea plant 0.82, 5.8, 14, 23.38, 26.64, 33.46, 35.2
standard deviation for day 20 on table 2 - 4.7
days bottom 0-20
side mean height 0-40
2 lines
control plant
then draw line from gibberelin plants
after plotted mean, plot little bar above and below to represent standard deviation
how plants respond to the environment (2) + gibberellins
tropisms
tropisms are tropic movements (directional responses) seen in plants, in response to variety of possible stimuli
chemotropism: directional response to chemicals
phototropism: directional response to light stimuli
thermotropism: directional response to temperature
hydrotropism: directional response to water
thigmotropism: directional response to touch
shoots of climbing plants winding around other plants/solid structures ex. ivy
positive or negative
movement toward environmental stimulus is called positive tropism, movement away from stimulus is called negative tropism
shoot tips of plant that grow toward light source are positively phototropic
nastic movements
nasties are nastic movements (non-directional responses) which plants have in response to stimuli
chemonasty
photonasty
thermonasty
hydronasty
thigmonasty
gibberellins
named after fungus Gibberella fujikuroi - causes rice plants, on which it is parasitic, to grow abnormally tall.
disease of rice called ‘foolish seedling’ investigated in 1920’s by Japanese plant pathologist Eiichi Kurosawa.
substance causing abnormal growth was isolated from fungus + structural formulae identified
chemical found to belong to class of 100+ naturally occurring plant hormones called gibberellins
all acidic + usually referred to as GA (Giberellic acid)
overview: gibberellins
gibberellins are synthesised in apical portions of roots + stems
they play leading role in controlling stem elongation in growing stems of mature trees + shrubs, where it’s application characteristically promotes internode elongation
elongations effect also enhanced if auxin present
application of gibberellins to dwarf mutants is known to restore normal growth + development in many plants.
gibberellin application also induce some plants to grow out of rosette stage of + flower early during first growth year
also hastens seed germination, maybe bc can substitute for low light effects + temp requirements in this process
how gibberellins work
GA: all ‘terpenes’, complex group of plant chemicals related to lipids + are also acids
GA formed in:
Chloroplasts
Embryo of seeds
Buds
Root tips
Young leaves
Found to be absent from genetically dwarf varieties of plants.
migrate in non-polar manner that’s up/down plant in phloem + xylem
GA is involved in the extension growth of the stem, causing elongation of internodes.
highest concentration of GA is in fruits/seeds as they form plants + in seeds as they germinate.
other aspects of growth + development in higher plants:
Dormancy
Germination
Onset of flowering
main effects however is in stem elongation, mainly by affecting cell elongation



Absorption of water stimulates germination
Embryo synthesizes gibberellin in response to water uptake
Aleurone layer synthesizes amylase in response to gibberellin
Amylase mobilizes energy reserves: hydrolyses starch to maltose. Maltose is converted to glucose and respired to release ATP
questions
name plant hormone that initiates seed germination
gibberellin
which does not bring about directional growth response in plants
B: oxygen levels
when seed germinates it does not obtain energy through photosynthesis. explain where the energy for the initial growth of a seed comes from…
.digestion/breakdown of starch by enzymes. this produces sugar that is used in respiration
what is a non-directional response in a plant called?
nastic movement
mean height dwarf pea plant 1.18, 3.32, 4.68, 6.56, 8.54, 13.28, 15.78
mean height treated dwarf pea plant 0.82, 5.8, 14, 23.38, 26.64, 33.46, 35.2
standard deviation for day 20 on table 2 - 4.7
days bottom 0-20
side mean height 0-40
2 lines
control plant
then draw line from gibberelin plants
after plotted mean, plot little bar above and below to represent standard deviation
 Knowt
Knowt