TAVI Update
Introduction
Speaker opens with a humorous statement about weather and personal reflections.
Notes that TAVI (Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation) use for pure aortic valve regurgitation is currently off-label.
Farming Analogy
Discusses personal life as a "farmer" in Minnesota with a hay field.
Introduces a metaphor regarding the necessity of using the right tools for different tasks:
Pitchfork for Hay: Represents TAVI valves designed for tricuspid aortic valves.
Potato Fork for Potatoes: Represents the distinct requirements for bicuspid aortic valves.
TAVI Valves Development
Discusses a slide from Mount Sinai with 32 TAVI valves that were all designed for three-cusp aortic valves, emphasizing:
Lack of valves designed specifically for bicuspid valves (potato forks).
Most operations performed on patients with aortic stenosis relate to three-cusp valves.
Highlights the financial investment and limited market for bicuspid aortic valve studies.
Calcification Characteristics
Illustrates and contrasts:
Tricuspid Valve: Uniform calcification providing structural stability.
Bicuspid Valve: Asymmetrical calcification, potentially complicating valve placement.
Size variations observed in bicuspid valves:
Maximum diameters differ: Tricuspid (26mm) vs. Bicuspid (30mm).
Bicuspid valves tend to be larger than tricuspid valves, complicating sizing for TAVI.
Sizing Challenges for TAVI
Challenges arise from:
Risk of valve migration or paravalvular leak due to incorrect sizing.
Bicuspid valves often non-tubular shapes lead to sizing difficulties.
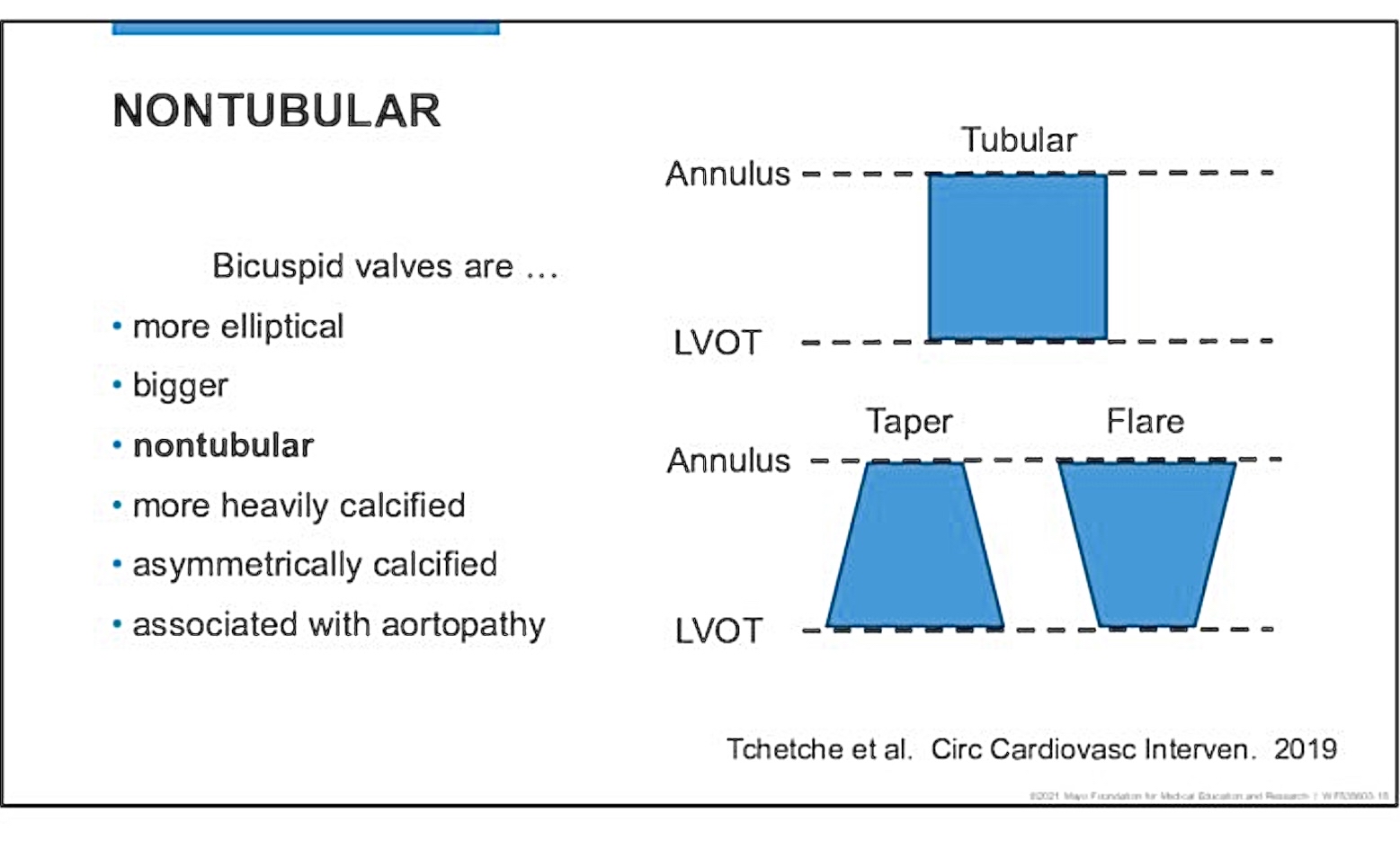
Consequences of improper sizing:
Possibility of rupture during valve inflation.
Asymmetric inflow may complicate deployment of the TAVI device.
Aortic Valve Calcium Scores
Highlights comparative data on valve calcification from tricuspid vs. bicuspid:
Tricuspid Generally average 3000 vs. Bicuspid average is 5000.
Implications for stroke risk related to calcification patterns (increased calcification typically = increased risk for disruption and therefore increased stroke risk).
Risks Associated with Bicuspid Valves
Emphasizes:
Increased risk of aortic root rupture due to calcification.
Potential for postoperative complications such as aortic dissection post-TAVI.
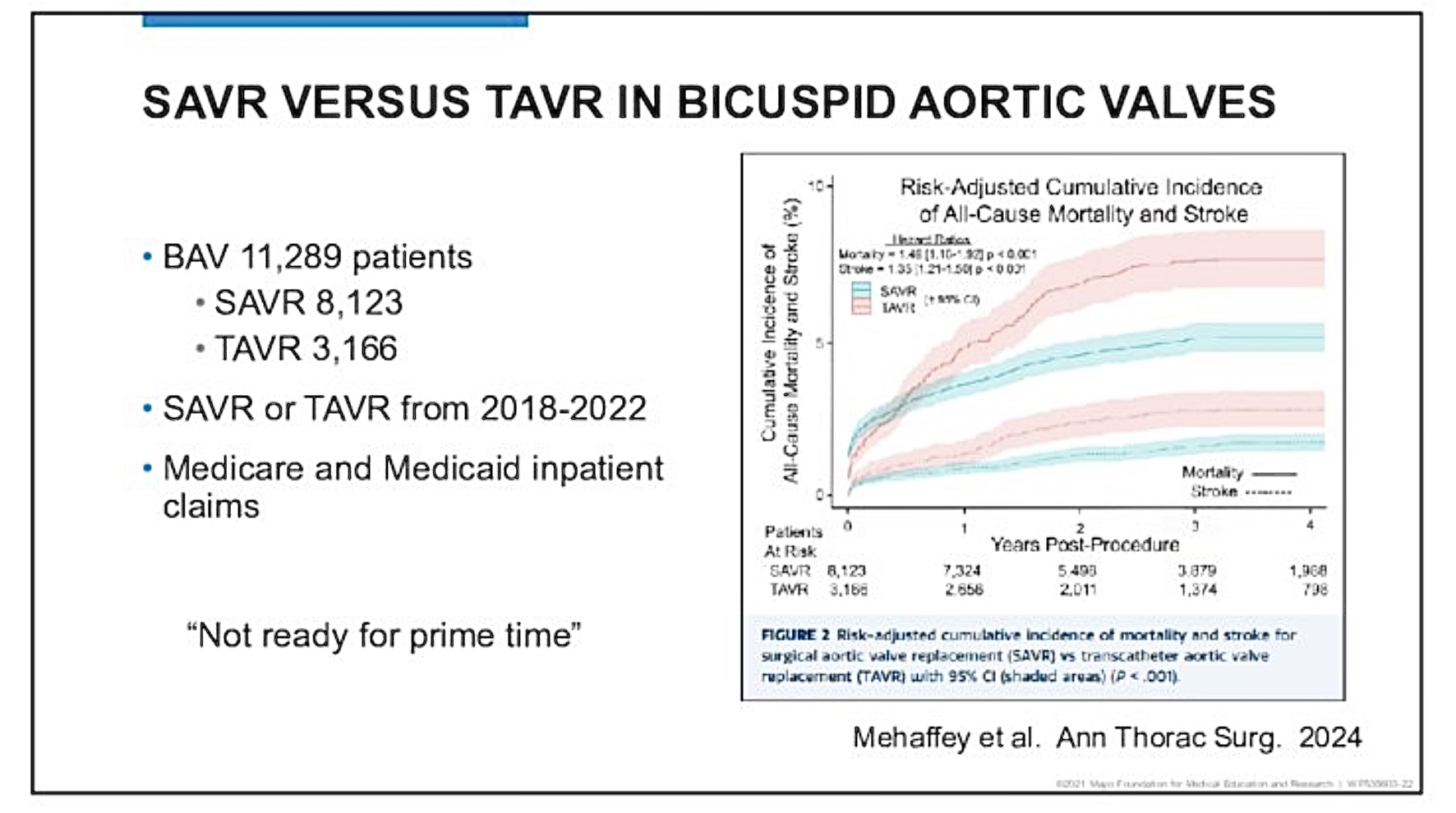
Comparative Outcomes: Surgical vs. TAVI
Presents data from over 11,000 patients regarding:
Increased risk of stroke and mortality linked to TAVI in bicuspid cases.
Shows long-term outcomes where surgery outperforms TAVI (in bicuspid valve cases) despite initial advantages.
Suggests misapplication of tricuspid valves to cases requiring bicuspid solutions.
Cerebral Protection and Surgical Considerations
Mentions challenges in using cerebral protection devices for patients.
Discusses the necessity of collaborative discussions between surgeons and interventional cardiologists.
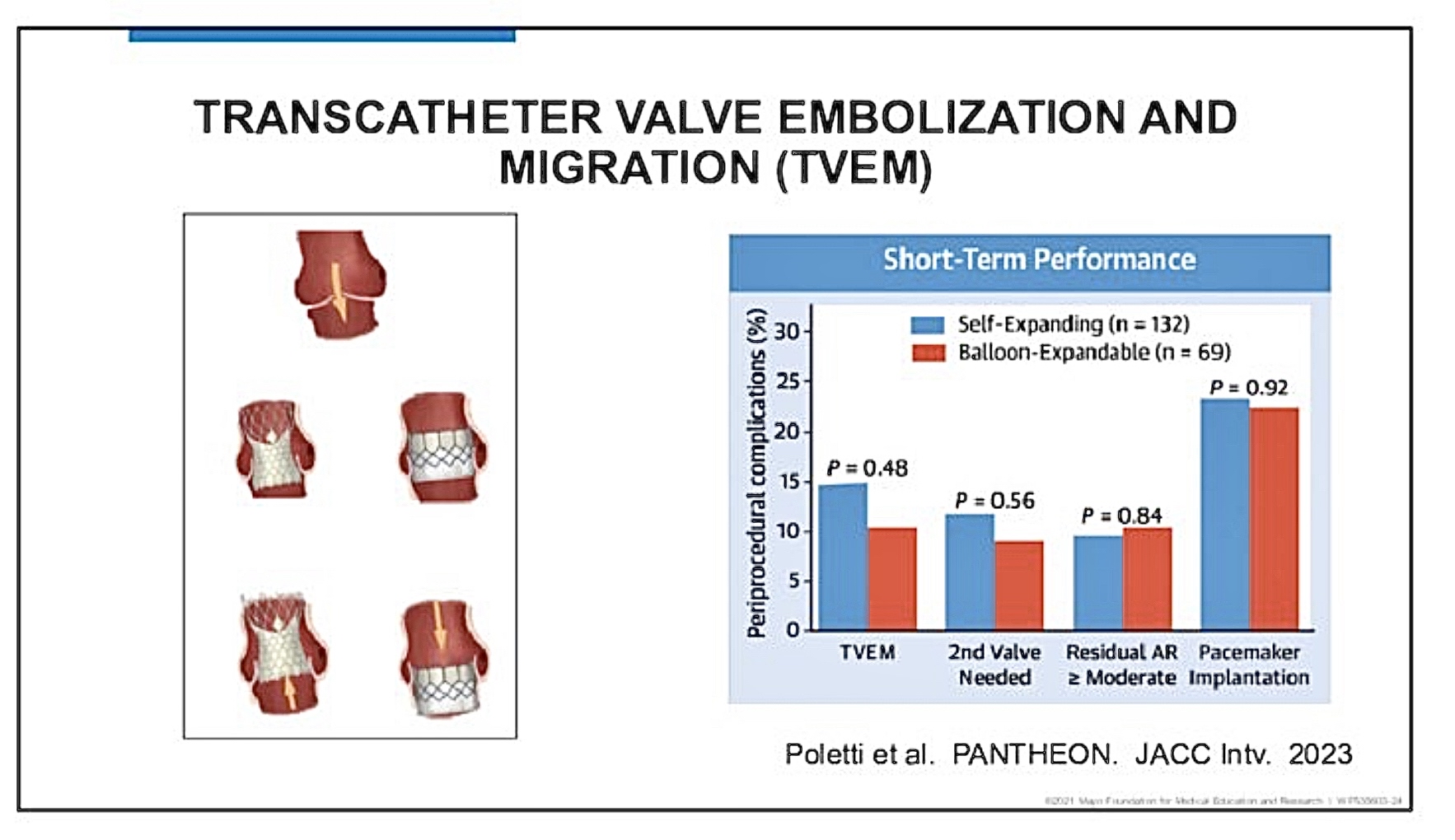
Aortic Valve Regurgitation Considerations
Shares features of regurgitant aortic valves:
Lack of calcification challenges secure valve placement during TAVI.
Higher risk of valve embolization and migration observed across study settings.
Emerging Valve Technologies
Introduces two new valves - Jena and J valves designed for aortic valve regurgitation:
Similar lock mechanisms to minimize migration risks.
Presents ongoing need for data on effectiveness and safety.
Summary of Findings
Current TAVI valves are not prepared for bicuspid anatomy or pure aortic valve regurgitation:
Suggests standard surgical aortic valve replacement remains preferred for bicuspid cases.
Notes potential but unproven niche value for newer Jena and J valves in regurgitation cases.
Highlights limitations in valve size options in relation to patient anatomy.
Conclusion
Concludes with a poetic metaphor about tranquility and spirituality amidst agricultural life.
Invites questions and reflections.
 Knowt
Knowt