Space Exploration Section 1 + 2
Section 1.0
Section 1.1:
Solstice → The Shortest & Longest Day Of Year (Winter & Summer)
Equinox → Where Day & Night are equal (Fall & Spring)
Geocentric Model → Earth Centered Theory (Aristotle)
Heliocentric Model → Sun Centered Theory (Copernicus)
Elliptical → Oval patterns for planets to revolve around the sun (Kepler)
Different Monuments Used To Tell Time → Stonehenge, Pyramids, Chichen Itza, Aboriginal Circles
Section 1.2:
Sundial → Used to chart Sun’s progress around Earth’s sky (Early People)
Merkhet → Used to predict & chart star movement (Egyptians)
Quadrant → Used to measure star’s height above horizon (Egyptian)
Astrolabe → Used to make accurate charts of stars (Arabians)
Cross Staff → Used to measure the angle between the moon and any star. (14th Century)
Telescope → Used to clearly see stars & planets in the sky
Astronomical Units (AU) → Describe planets in relation to the sun (Equal to the average distance between the centre of the earth to the centre of the sun)
Light Years → Distance that light travels in one year (Distances outside of solar system)
When looking into the night sky, you are → Looking into the past
Section 1.3:
Star → Hot, glowing ball of gas (Mostly made of hydrogen)
Hertzsprung and Russell → compared surface temperature of stars to how bright they are (luminosity)
Star Temperatures → Blue color is hottest, red coolest
Sun → Biggest star in the galaxy which gives us heat and energy on Earth
Life Cycle Of A Star:
Interstellar matter → dust and gas between stars (can make nebulae)
Nebulae → Area of space with huge amounts of gas and dust, where stars form (5% hydrogen and 23% helium)
Protostar → Gravity between gas and dust cause small areas of the nebulae to start collapsing, collapse causes a rotating cloud of gas and dust. Hydrogen changes to helium, called fusion (Releases a lot of energy and radiation)
Red giants & Red supergiants → Hydrogen is eventually used up, Gravity causes contraction, Fusion reactions occur, Reactions lead to the star expanding (Causes sun like stars become red giants and Massive stars become red supergiants)
Sunlike Star Death → Fusion reactions stop, Core temp. no longer hot enough to keep reactions going, Gravity causes the star to collapse on its self (Continues to shrink and becomes a white dwarf, Eventually it will fade completely becoming a cold dark black dwarf)
Massive Star Death → Fusion stops when the star runs out of fuel, Star rapidly collapses on it’s self due to gravity, Collapse ends with an outgoing shock wave (Outer part of the star explodes, a supernova, Core is left as either a neutron star or black hole)
Neutron Star → The collapsed core of a massive supergiant star
Black hole → Highly dense remnant of a star with super strong gravity (No light can escape)
Constellations → Groupings of stars, patterns in the night sky
Asterisms → Unofficial groupings of stars (Big Dipper)
Galaxies → Grouping of millions or billions of stars, gas, and dust
Types of Galaxies → Spiral, Elliptical & Irregular
Section 1.4:
Inner Planets → The terrestrial planets, Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars (Earth like, Smaller, Rocky, No rings)
Outer Planets → The Jovian planets, Jupiter, Saturn Uranus, Neptune (Jupiter-like, Gas giants, Have rings)
Red planet → A planet is given a red appearance due to iron oxide in the surface
Asteroids → Small metallic or rocky bodies travelling in space
Comets → “dirty snowballs” Made of dust and ice, travel through space (Long tails and bright glow only appear when they are close to the sun
Meteoroids → Small pieces of rock flying through space with no particular path \n Meteor → Pulled into Earth’s gravity, heat of the atmosphere causes it to give off light \n Meteorite → What’s left once it hits earth’s surface
Eclipses:
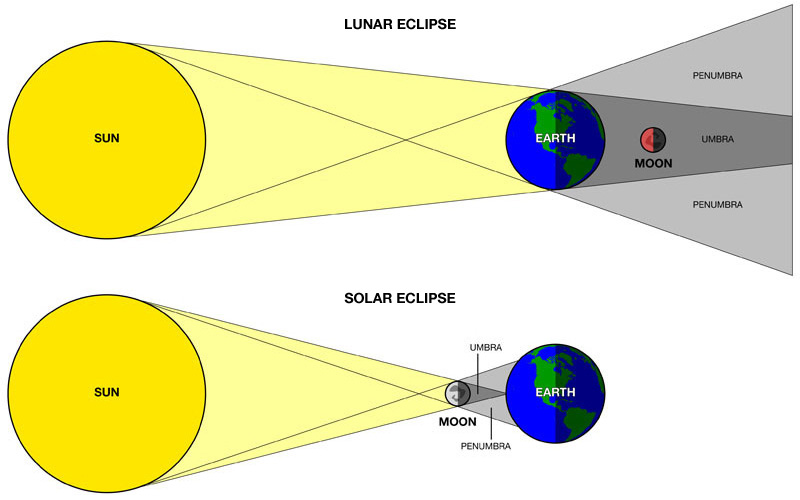
Section 1.5:
To Find a Star in the Sky → Must answer two questions, How high is it in the sky? and In which direction?
Azimuth → compass direction (Due north is 0o you measure degrees going clockwise) \n Altitude → Degree the object is above the horizon \n Zenith → Highest Point Directly Overhead
Section 2.0
Section 2.1:
Space → Anything outside Earth’s Atmosphere
Origin of rockets → comes from an Ancient Greek named Archytas
Rocket propelled arrows → Chinese used gunpowder to make them
First to launch a satellite into Earth’s orbit → Russians (1957) Called Sputnik
Another capsule → A month later they launched a dog named Laika (First time any living creature orbited the Earth, Started the path for human space travel)
Newtons 3rd Law → For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction
Basic Parts of a Rocket → Structural and Mechanical Elements, Fuel, Payload
What Does Each Part Mean? → (rocket, engines, storage), (Lit in exhaust chamber to cause propulsion), (materials needed for flight)
Thrust → (Push) causes the rocket to be pushed in the \n opposite direction
Ion Drives → Engines that use xenon gas
Solar Sail → Similar idea to sails on a boat, Harness the sun’s light, Uses electromagnetic energy of photons to move
Types of Space Craft → Shuttles, Probes, Space station \n
Section 2.2:
Atmosphere → Thin atmosphere around earth holds all we need to live
Environmental Hazards → Space is a vacuum = no air, no water, Cosmic rays and solar radiation, Possibility of being hit by meteoroids, Temperatures can range from really hot to \n really cold, No pressure to help regulate heartbeat
Psychological Hazards → Cramped quarters, Stuck with the same people for months at a time, You can’t just go take a walk…
Microgravity → When little or no gravity is acting on a body.
Effect on Bones → Have less pressure so they expand, Begin to deteriorate and release minerals (calcium) into the blood stream
Effect on Heart → Doesn’t have to pump as hard to circulate blood
Effect on Muscles → Lifting and walking muscles aren’t used much, they weaken and shrink
Effect on Kidneys → Form stones from increased calcium
Effect on Eyes → Depth perception is affected
Home in Space → Clean water, Breathable air, Comfortable air pressure and \n temperature, Power source to keep life support systems and instruments going
Recycling Water → International Space Station recycles most of their water, Urine is filtered, Moisture is captured from the air, Leads to longer missions
Electrolysis → Splitting water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity
Environmental Control and Life Support Systems → Recycle wastewater, Produce oxygen through electrolysis, Remove carbon dioxide from the air, Filter micro organisms from the air, Keep air pressure, temperature and humidity stable
Section 2.3:
Satellites → Small body that orbits a larger body \n Natural Satellites → Objects that orbit planets
Artificial Satellites → Built and sent into orbit by humans
Rotation → an object spinning on it’s own axis \n Revolution → An object travelling around another object
Satellites in Our Lives → GPS navigation, Communication, Forecast weather, Make long distance phone calls
Communication Satellites → Telegraph and telephone relied on wires at one point in time, This was expensive and couldn’t service a lot of people, Today satellites and digital systems allow for more users and better transmission
Geosynchronous orbit → Satellite moves at the same rate as the earth spins
Global Positioning System (GPS) → let’s you know exactly where you are (74 satellites have been launched, only need 24 for GPS to work correctly, Must have sightlines to 4 satellites to find your position)
\n
\n
\n
\n