Chapter 12: Homeostasis
- %%Homeostasis%% is the maintenance of constant internal environment.
- ^^for any homeostatic control there must be:^^
- A stimulus (change).
- A receptor (to detect a change).
- An automatic or self-regulatory corrective mechanism which brings;
- A negative feedback.
Examples of Homeostasis:
^^Regulation of blood glucose concentration^^
After a meal rich in sugar or starch:
- An increase in blood glucose concentration (stimulus).
- Pancreas is stimulated (receptor).
- Pancreas will start secreting more insulin; to convert glucose to glycogen in liver (corrective mechanism).
- Normal condition achieved.
- ^^The same thing happens when blood glucose level is low; but instead of insulin glucagon is released which converts glycogen to glucose.^^
^^Regulation of blood water potential (osmotic pressure)^^
Due to through profuse sweating:
- Water potential decreases (stimulus).
- More ADH secreted - more water reabsorbed by kidney tubules - less urine produced (corrective mechanism).
- Normal condition achieved.
- ^^The same happens when water potential increases; but instead of more ADH less ADH is released and less water is reabsorbed by kidney tubules and more urine is formed.^^
==Note====:== ADH is antidiuretic hormone.
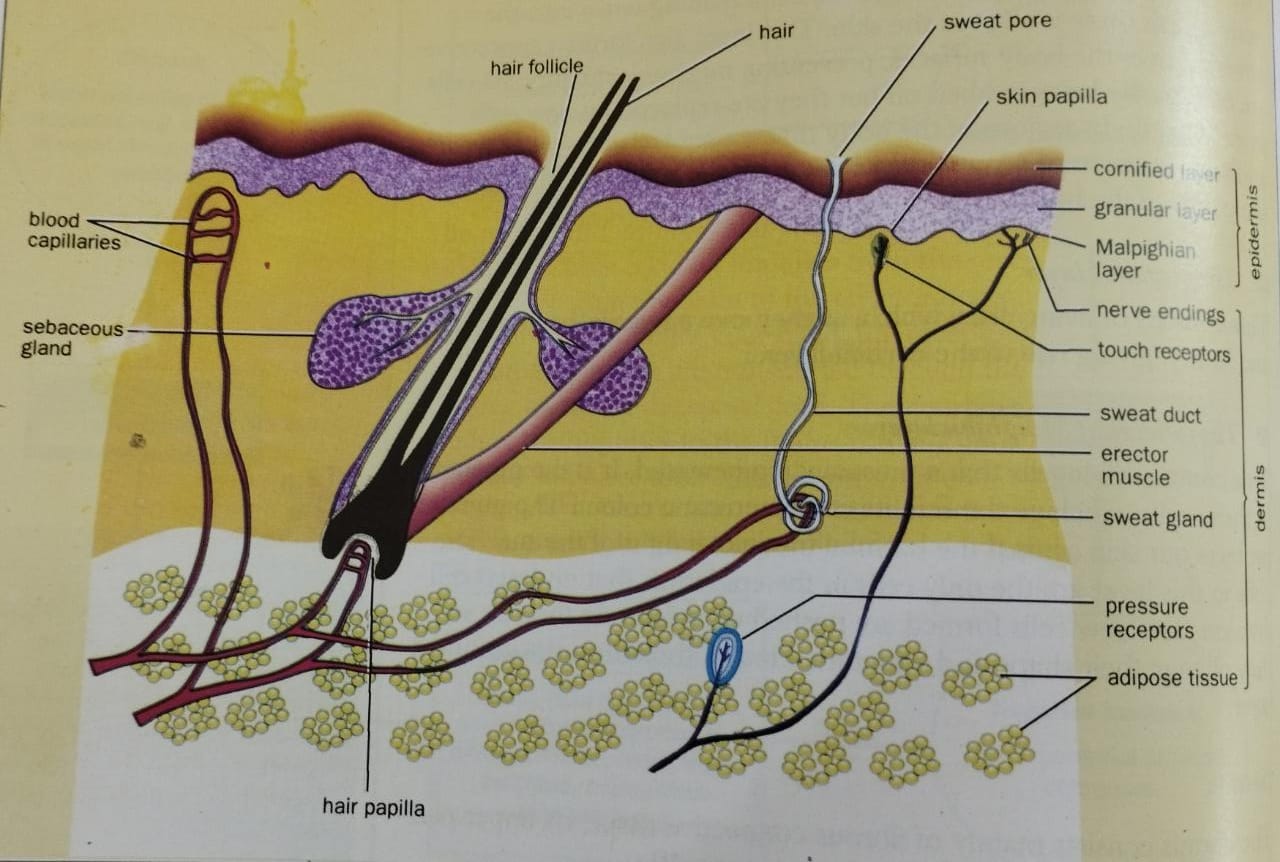
Mammalian Skin
Structure
@@Epidermis@@
- %%Cornified layer%%
- Cells are dead, dry, flat and horny - deposition of keratin.
- Water resistant and prevents uncontrolled water loss.
- Prevents germs from entering.
- %%Granular layer%%
- living cells - dry.
- %%Malpighian layer%%
- Living cells - give skin its colour.
- Pigment protects skin against UV.
- Undergo cell division.
@@Dermis@@
- %%Blood vessels%%
- Carry blood.
- Bring reflex contraction (vasoconstriction) and dilation (vasodilation).
- Vasoconstriction - reduced amount of blood flow.
- Vasodilation - increased amount of blood low.
- %%Hair%%
- %%Sebaceous glands%%
- Secretes oily substance; sebum
- %%Sweat glands%%
- Surrounded by blood capillaries
- Sweat is secreted which through sweat duct
- Sweat helps in regulation of body temperature as the sweat evaporates
- Sense receptors
- Nerve endings
- Enable us to sense pain, pressure or temperature change in the external environment
@@Subcutaneous fat@@
- Serve as insulating layer
Responses to change in temperature
| Stimulus | Corrective Mechanism | Negative Feedback | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rise in body temperature: | temperature receptor detect change - brain is stimulated and serve nerve impulses to relevant body part | arterioles dilate (Vasodilation) - sweat glands are active - sweat evaporates - hair erector muscle relaxes - metabolic rate decreases | blood temperature decreases & normal body temperature achieved |
| Drop in body temperature: | temperature receptor detect change - brain is stimulated and serve nerve impulses to relevant body part | arterioles constrict (Vasoconstriction) - sweat glands are less active - hair erector muscle contract - metabolic rate increases and shivering begins | blood temperature increases & normal body temperature achieved |