Aggregate Demand
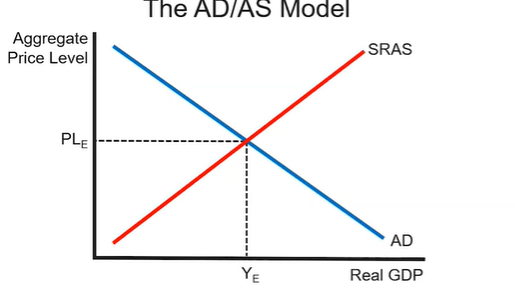
intersection = equilibrium real GDP
A change in RGDP is accompanied by a change in employment
real GDP equals aggregate spending, which equals consumption, investment, government spending and exports minus imports. Or
through aggregate income: wages, rent, interest and profit.
Aggregate price level is a measure of inflation, not inflation rate, it is the GDP deflator.
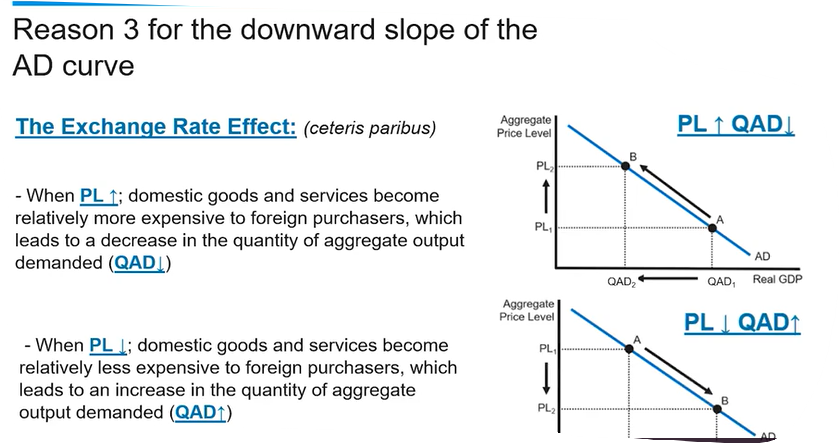
The downward-sloping AD curve represents the inverse relationship between the aggregate price level and the quantity of goods and services demanded, indicating that as prices decrease, consumer purchasing power increases, leading to higher overall demand.
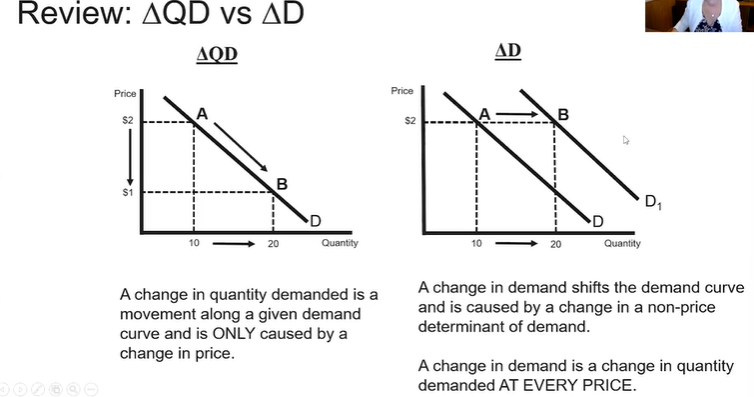
This relationship is the same for AD and QAD


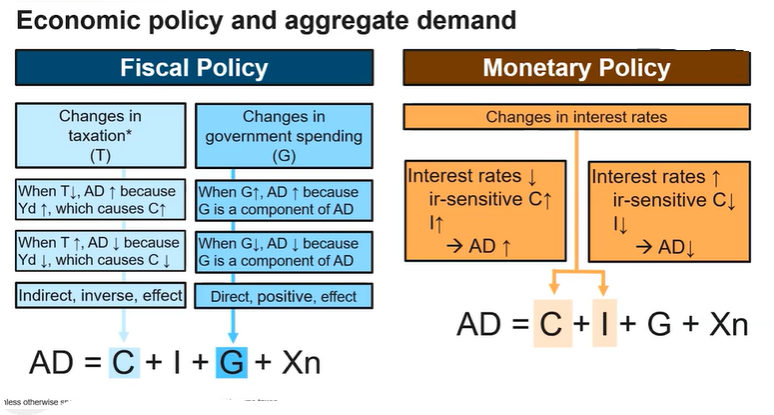
When interest rate changes, it shifts the AD curve, but a change in price level moves across the QAD

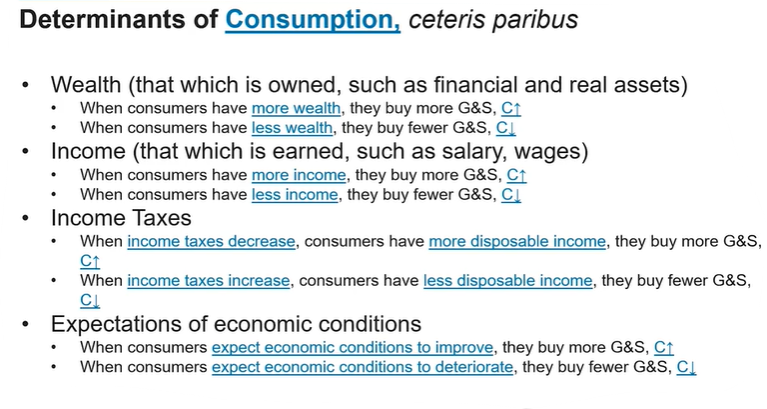
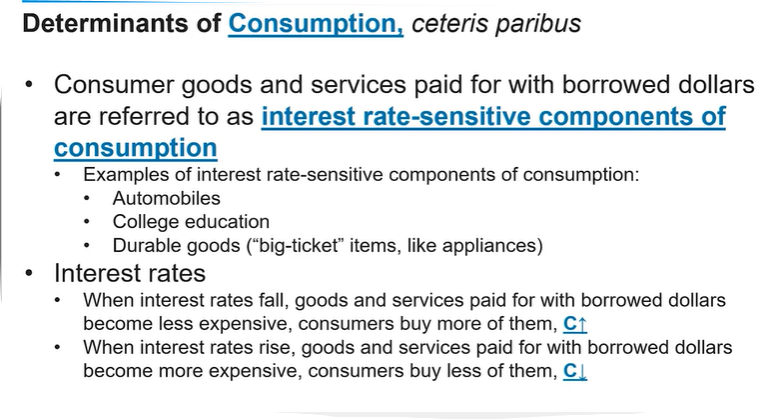
Investment spending is influenced by interest rates, as lower rates typically encourage more borrowing and spending on capital goods, thereby increasing aggregate demand. Includes: firm spending, residential investment, and business inventories.

An increase in AD is represented by a rightward shift of the AD curve.
A decrease in C, I, G, or X, or an increase in M (import spending), will lead to a leftward shift of the AD curve, indicating a decrease in aggregate demand.
Autonomous means regardless of income
Taxes and AD have an inverse relationship