Chapter 17
Physical Development in Late Adulthood

The meaning of longevity
Longevity = duration, or length, of life
Life expectancy = average number of years a perosn, or cohort, is expected to live
Life span = maximum number of years a species can live
Life Expectancy
The average number of years a person is expected to live can be affected by several factors (cultural, geographical, biological, etc.)
What are some examples of these factors?
Would your example increase or decrease life expectancy?
Life Expectancy (in years) changing
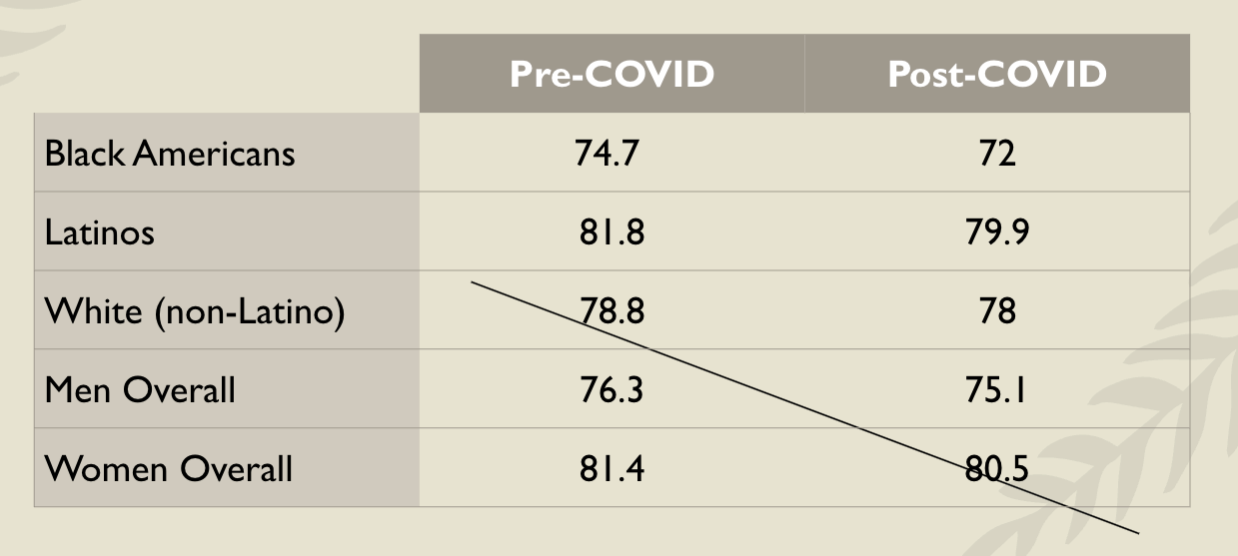
Life Span
What is the maximum time (in years) a person can live?
Centenarians = living the age of 100
There were approximately 97,000 centenarians in the US in 2020
Projected to reach 6000,000 by 2060
The US has the most centenarians, followed by Japan, China, and England/Whales
Supercentenarians = living to the age of 110
There are about 60 supercentarians alive in given year in the US and about 300 in the world
The world record for the oldest person with a documented birth record in Jeanne Calment of Arles, France. She was 122 years and 164 days old when she died.
Stages within Late adulthood
Young-old = 65-74
old-old = 75-84
Oldest-old = 85+
Older adults, retired, boomers = refer to young-old
Alderly, seniors, golden-agers = refer to old-old and oldest-old
Definitions of Age
Previously learned age definitions
Chronological age - time elapsed since birth (months/years)
Biological age - in terms of biological health
Psychological age - adaptive capacities compared to those of same chronological age
Social age - based on societal expectations of an individual’s involvement in social roles
Functional age - how a person compared to others of similar age in competence while carrying out tasks
Biological Theories of Aging

The Brain
On average, the brain loses 5-10% of its weight between the ages of 20 and 90
Brain volume also decreases.
It is 15% less in older adults than in young adults
Mainly due to shrinkage of neurons, lower number of synapses, reduces length and complexity of axons that connect schemas
More significant brain volume loss occurs in those with dementia
Brain atrophy occurs less in women than in men
Sleep
About 50% of older adults complain of having difficulty sleeping
Can result in earlier death
It is linked to a lower cognitive functioning
Strategies to sleep better at night:
Avoid caffeine
Avoid over-the-counter sleep remedies
Staying physically active during the day
Staying mentally active
Limiting naps
Physical Health and Appearance
Immune system:
Declines in functioning with age
Extended duration of stress and malnutrition (low levels of protein) can influence the decline
Exercise and vaccinations can improve its functioning
Physical appearance and movement:
Most noticeable changes are wrinkles and age spots
People get shorter with age due to loss in bone density
Older adults move slower than young adults
Sensory Development
VIsion:
Visual acquity, color, vision, and depth perception decrease even with corrective lenses (especially after age 75).
Diseases of the eye:
Cataracts: Thickening od the lenses of the eye that cause vision to become cloudy
Glaucoma: damage to the optic nerve because of pressure created by buildup of the fluid in the eye
Macular degenerations: deterioration of the macula of the retina, which corresponds with the focal center of the visual field.
Hearing
Severe impairments can become an impediment
Hearing aids and cochlear implants minimize the problems linked to hearing loss
Smell and taste
Decline of the chemical senses begin at about age 60-65 but it is very minimal
Touch and pain:
Older adults detect touch less in the lower extremeties
Decrease sensitivity to pain can help cope with disease and injury
But can also mask conditions that need treatment
Health
Probability of having some disease or illness increases with age, this is known as compression or morbidity
Chronic diseases with a slow onset and long duration are more common in late adulthood
Arthritis is the inflammation of the joints accompanied by pain, stiffness, and movement problems
Osteopenia and osteoperosis
Death in Late Adulthood
Causes of death in older adults:
Nearly 60% of the young-old (65-74) die of cancer or cardiovascular disease
For the old-old (75-84) and the oldest-old (85+), the leading cause of death is cardiovascular disease
Accidents are the 9th leading cause of death in late adulthood with falls being the leading cause of injury death
 Knowt
Knowt