Chapter 21: Sexual Reproduction in Animals
%%Gamete%% is a ^^reproductive cell containing the haploid number of chromosomes^^. In men sperm, and in women egg.
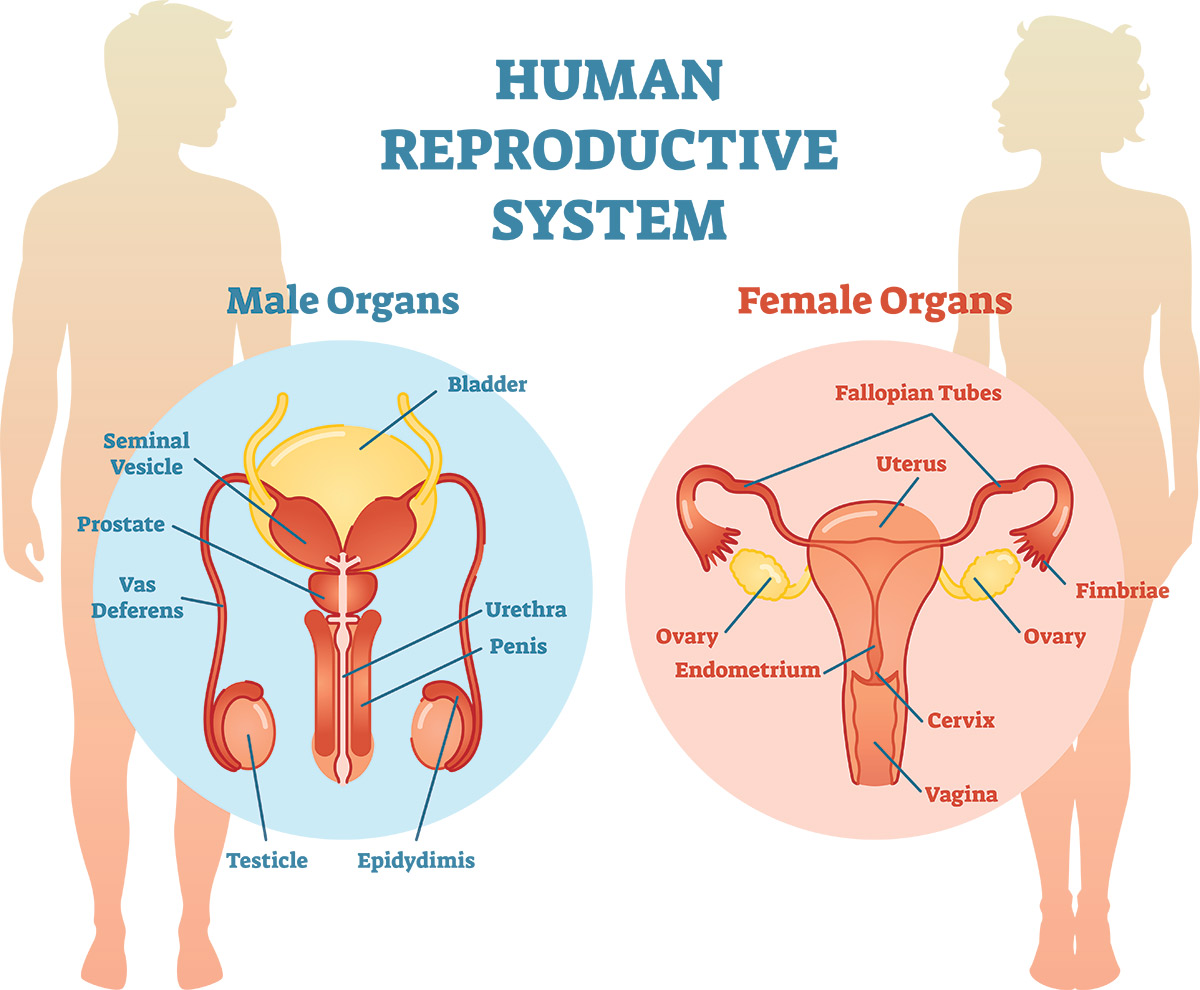
Male Reproductive System
- Testes
- There are two testicles.
- Sperm cells are produced, as well as testosterone.
- Scrotum
- Contains the testicles.
- Sperm ducts
- Tubes that carry sperm from the testes to the urethra.
- Prostate gland
- Secretes nutritive fluid which combines with sperm to form semen.
- Urethra
- Tube which allows excretion of urine and semen from body.
- Penis
- An erectile organ.
- Contains erectile tissues with numerous blood spaces- when blood spaces are filled with blood, the penis erects and hard.
Female Reproductive System
Ovaries
- There are two ovaries.
- Function is to develop egg cells.
- Woman have undeveloped egg cells from birth, ==whereas men produce new sperm throughout their lives.==
Oviducts/Fallopian tube
- Connect to each ovary.
- Contain cilia to transport the egg cells through the tube.
- This is where fertilisation occurs.
Uterus
- This is where the foetus develops.
Cervix
- Separates the vagina from the uterus.
- Also holds the baby in place during pregnancy.
- Made of muscular tissue.
Vagina
- Tube that leads from the cervix to outside of the body.
- Receives the penis during intercourse.
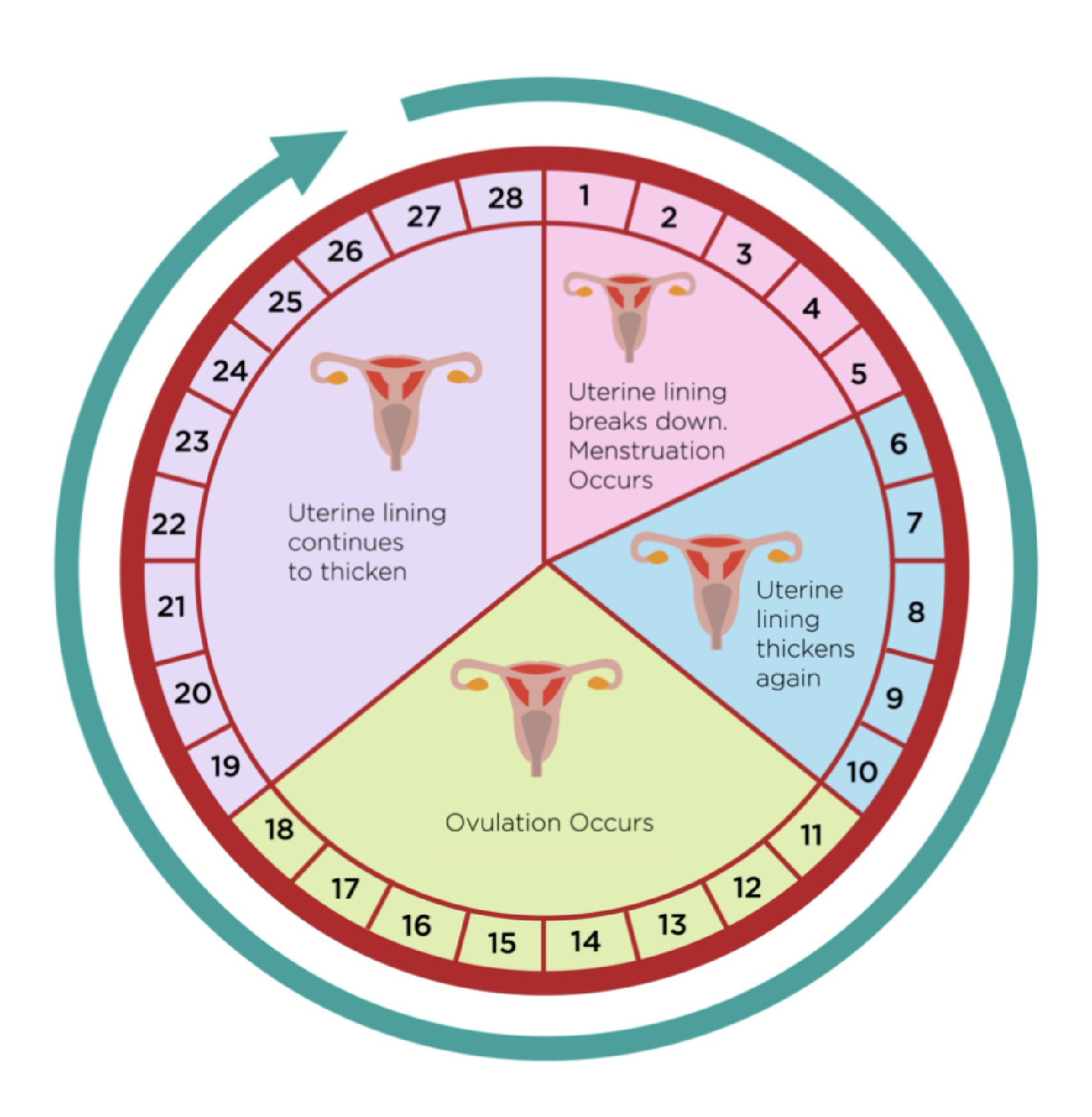
Menstrual Cycle
Is discharge of blood from the uterus via vagina.
Lasts for about five days.
Average menstrual cycle is of 28 days.
Regulated by 4 hormones:
- %%Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)%%
- Triggers the development of an egg cell in the ovary.
- Stimulates oestrogen production in the ovaries.
- Produced in the pituitary gland.
- %%Luteinising hormone (LH)%%
- Triggers an egg to be released.
- Stimulates progesterone production in the ovaries.
- %%Progesterone%%
- Responsible for maintaining the thick uterus lining in the cycle and during pregnancy.
- Decreases FSH production.
- %%Oestrogen%%
- Stimulates LH production, whilst decreasing FSH production.
At the beginning of the cycle, ^^levels of FSH and LH are high^^ to stimulate egg production and ^^cause the production of oestrogen^^ which thickens the uterus lining. When the ^^egg is released, the levels of LH, FSH and oestrogen decrease^^, whilst ^^progesterone is released^^ to maintain the uterus lining. If the ^^egg is not fertilised, progesterone levels decrease^^ and the uterus lining breaks down, causing menstruation.
Fertilization
- Occurs when a sperm cell and an egg cell fuse their nuclei together.
- When the sperm cell reaches the egg cell, it digests the wall of the cell so that it can fuse their nuclei. This is done using enzymes located in the acrosome. The egg contains a jelly coat which changes after fertilisation and ensures that only one sperm cell can enter.
- Once fertilisation has occurred, the zygote undergoes mitosis (cell-division) to produce many cells which make up an embryo. The egg cell contains energy stores to allow this to happen. The embryo is implanted into the wall of the uterus, where it grows.
Development of Embryo
- The fertilized egg passes along the oviduct to the uterus, and as it does so it begins to divide to form a hollow ball of cells called the %%embryo.%%
- After five days embryo reaches uterus.
- The embryo sinks and embeds in the uterine lining. This is called %%implantation.%%
- %%Key features%%
- Umbilical cord
- Allows the exchange of substances between the foetus and the mother.
- Placenta
- Connects to the foetus end of the umbilical cord.
- Allows exchange of substances. (e.g glucose, amino acids and mineral salts enter and substances ike urea and CO2 diffuse out).
- Produces hormone progesterone.
- Amniotic sac
- Surrounds the foetus and produces amniotic fluid.
- Amniotic fluid protects the foetus.
Birth of Baby
- The amniotic sac breaks, releasing the amniotic fluid.
- Muscles in the uterus wall contract to push the baby out while the cervix dilates.
- The baby exits the mother through the vagina.
- The umbilical cord, which is still attached to the baby, is cut and tied.
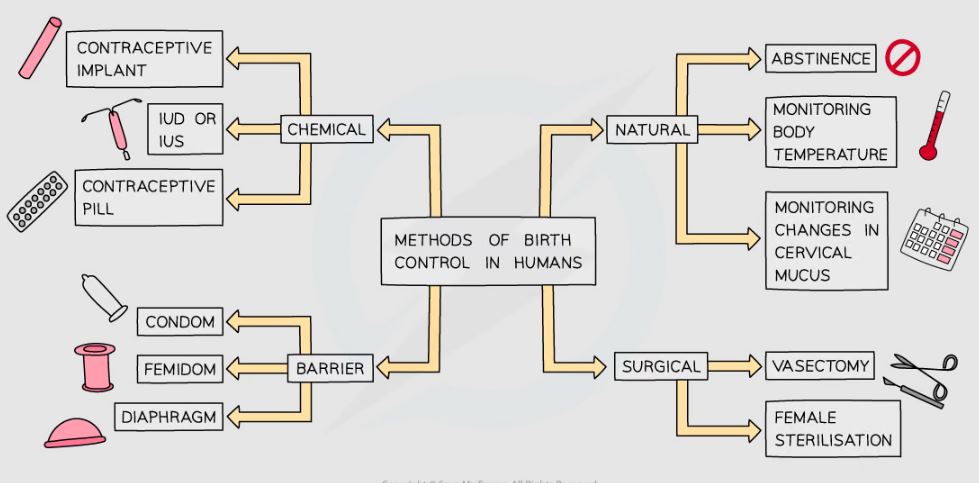
Family Planning
Use of contraception prevents pregnancy.
%%Birth control ways%%
- ^^Natural method^^
- By monitoring body temperature and cervical mucus.
- Unreliable method.
- ^^Mechanical method^^
- Use a condom or a femidom.
- Acts as a physical barrier.
- Prevents transmission of diseases.
- ^^Chemical method^^
- Use spermicides - they kill the sperms.
- Use contraceptive pills - prevent ovulation + a reliable method.
- ^^Surgical method^^
- Sperm ducts are cut and tied or;
- Oviduct is cut and tied to prevent release of egg from ovaries.
Sexually transmitted diseases
- %%Syphilis%%
- ^^stage 1^^
- A painless sore or chancre appears.
- Occurs on the penis or vagina.
- ^^stage 2^^
- Non - itchy rashes, sores in mouth, throat and genitals.
- Bald patches may appear on head.
- Lymph glands may become swollen.
- ^^stage 3^^
- Internal organs affected
- Brain and spinal cord may get damaged, resulting in paralysis, insanity or even death.
- Can be treated with antibiotics.
- %%Acquired Immune Deficiency (AIDS)%%
- Chronic fever.
- Severe diarrhea and pneumonia.
- Brain infection.
- Preventian: don’t share personal belongings with infected person.
- Is caused by HIV.