Social Psychology
Social Psychology- the scientific study of how we think about, influence, and relate to one another
THEORY
Attribution theory- tendency to give a causal explanation for someone’s behavior, often by crediting oneself to a situation
Fundamental Attribution Theory
the tendency for observers, when analyzing another’s behavior, to underestimate the impact of the situation & to overestimate the impact of personal disposition
When you do something, you blame your surroundings. However, we someone else does something wrong, you blame their character
Attitude & Actions
attitude- belief and feeling that predisposes one to respond in a particular way to objects, people, & events
not positive or negative
attitude affects actions, and actions affect the attitude
Zimbardo Prison Experiment
An experiment where Zimbardo had two groups: prisoners and guards. Participants are assigned either role, and Zimbardo wanted to see how they would adapt to their role.
Suggest strongly that actions affect attitudes
roleplaying (role)
set of expectations about social position
defines how those in the position ought to behave
Lucifer Effect- we are all susceptible to the “dark side” because of negative social influence
Cognitive-Dissonance Theory
We act to reduce the discomfort (dissonance) we feel when two or more of our thoughts (cognitions) are inconsistent
Social Thinking & Influence
CENTRAL argument
convinces someone through a quality argument
car sales- HP, MPG, new technology, less $
PERIPHERAL argument
convinces you superficially, not detailed
a store may offer you drinks, snacks, and compliments
Foot-in-the-door phenomenon
the tendency of people who have first agreed to a small request to comply later with a larger request
door-to-door salesman, car salesman
Door-in-the-face phenomenon
presenting an unacceptable & large option first, so the subject will settle for a smaller option later
Conformity
adjusting one’s behavior or thinking to coincide with a group or standard
Solomon Asch Line Test (conformity study)
Criterion for Conformity
impressed by the status of others (normative)
high stakes (informational)
unsure of the answer (informational)
unanimous answers amount confederates (normative/informational)
Normative Social Influence
influence resulting from a person’s desire to gain approval or avoid disapproval
Informational Social Influence
influence resulting from one’s willingness to accept other’s opinions about reality
Stanley Milgram Obedience Study
teacher “shocks” the learner all the way up to the highest voltage
demonstrated how people are likely to obey an order that comes from an authority figure
role playing & power of mindless obedience are both catalysts for behaviors, but NOT EXCUSES
Social Facilitation
Yerkes-Dodson Law
improved performance or tasks in the presence of others
occurs with simple or well-learned tasks
Social Loafing
the tendency for people in a group to exert less effort when pooling their efforts toward attaining a common goal that when individually accountable
people loaf around when others are working on a common project with them
Social Inhibition
conscious or subconscious avoidance of a situation or social interaction
High-level = situational avoidance (possible disproval)
Deindividualization
loss of self-awareness & self-restraint in group situations that foster arousal and anonymity
Group Polarization
enhancement of a group’s prevailing attitudes through discussion within the group
discussions strengthen with like-minded beliefs
Groupthink
mode of thinking that occurs when the desire for harmony in the decision-making group overrides a realistic appraisal of alternatives
example: Challenger engineers agreed to launch the Challenger despite it having technical difficulties. this was due to the peer pressure of the press.
Social Relations
Stereotype
a generalized (sometimes accurate, but overgeneralized) belief about a group of people
Prejudice
unjustifiable (usually negative) attitude toward a group & its members
LEARNED, not innate
Ethnocentrism
the tendency for people of a particular race to gravitate toward those of the same race
not necessarily racist
Ingroup
“Us”- people with whom one shares a common identity with
Outgroup
“Them”- the others; perceived as different or apart from one’s group
you tend to see individuals in an outgroup as the same
Ingroup bias- tendency to favor one’s group
Scapegoat Theory
the theory that prejudice provides an outlet for anger by providing someone to blame
Hitler scapegoated the Jews
Just world phenomenon
the tendency for people to believe the world is just
people get what they deserve and deserve what they get (karma)
Aggression
any physical or verbal behavior intended to hurt/harm someone
Frustration-Aggression Principle
the principle that frustration (the blocking of an attempt to achieve some goal) creates anger, which can generate aggression
Catharsis Theory
the idea that watching violent stuff allows an outlet for aggression
you do not act of aggression
disproven by the Bandura Bobo Doll experiment
Conflict
perceived incompatibility of actions, goals, or ideas
Social Trap
the situation in which conflicting parties, by each rationally pursuing their self-interests, become taught mutually destructive behavior
Ex: individuals not educated on financial responsibility receive first credit card (then abuses it)
Ex. while driving, me and other people want to get to our destination quickly. This can cause conflict
Bystander Effect
the tendency for any bystander to be less likely to help when others are present
think “someone else will help”
Diffusion of Responsibility- a person is less likely to take responsibility for action or inaction when other bystanders or witnesses are present
Self-fulfilling prophecy
when a person causes a prediction to come true
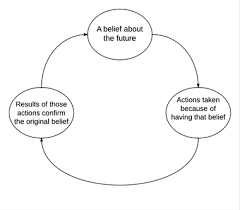
Chameleon Effect
unconscious mimicry of postures, mannerisms, facial expressions, & other behaviors of one’s partners, such that one’s behavior passively and unintentionally changes to match that of others in one’s current social environment
Mirror Neurons
Prisoner’s Dilemma
a paradox in decision-making analysis in which 2 individuals acting in their own self-interests do not produce the optimal outcome
people act in their own self-interests

Robber’s Cave Experiment
Muzafer Sherif argued that intergroup conflict (conflict between groups) occurs when 2 groups compete for limited resources
the experiment confirmed Sherif’s realistic conflict theory
the idea that group conflict can result from competition over resources
Ethical issues: the participants were deceived & denied basic resources (not protected from harm)
RELATIONSHIPS
Equity - a condition in which people receive from a relationship in proportion to what they give to it.
Self-disclosure - revealing intimate aspects of oneself to others
Altruism - unselfish regard for the welfare of others (selflessness)
Norms of Reciprocity
requires that we repay in kind what another has done for us
Understood as the expectation that people will respond favorably to each other by returning benefits for benefits, & responding with either indifference or hostility to harm
Social Exchange Theory (cost-benefit analysis)
the theory that our behavior is an exchange process, the aim of which is to maximize benefits and minimize cost
Like dating, if you take someone out to an expensive restaurant, you get greater benefits. However, if you go to McDonald’s, you may not even get a second date
Superordinate Goals -shared goals
Graduated & Reciprocated Initiatives in Tension-Reduction (GRIT)
a strategy designed to decrease international tensions
one side announces recognition of mutual interests & initiates the small conciliatory act
opens for reconciliation
Ex: Cold War
Attractiveness
Mere Exposure Effect
repeated exposure to novel stimuli increases liking of them
conceptions of attractiveness vary by culture
Passionate Love
aroused state of intense positive absorption in another
usually present at the beginning of a relationship
“honeymoon” phase
Companionate Love
the deep affectionate attachment we feel for those with whom our lives are intertwined