Perspective-in-Dentistry
Perspective Dentistry
Perspective in Dentistry
is a course intended to acquaint the student with the scope and responsibilities of dentistry as a health profession and its relation with other professions.
Consideration is given to the application of his academic preparation to clinical practice.
Goal/Objective of the course
- To prepare dental students for clinical work
- To point out why and how one can enjoy a career in dentistry
Reasons for students’ choice of dentistry
- Personal
- External
Characteristics that a dental student should possess
- Energy
- Enthusiasm
- Patience
- Perseverance
People involved in training a dentist
- Dentistry teachers / clinical instructors
- Members of the allied professions (health professionals, x-ray/laboratory technicians)
- Government agencies (CHED, PRC)
Dental Licensure Examination
2 parts: theoretical and practical
- Private educational institutions
- The patients
- The community/the public
Definition of Dentistry
As a SCIENCE – is knowledge obtained through systematized investigation / study / inquiry concerning the various theories, principles and concepts of dentistry
As an ART – involves skilled craftsmanship / psychomotor skills / or technical skills in the practice of the profession
As a PROFESSION – is a calling or vocation requiring specialized knowledge and technical skills following lengthy and intensive preparation
Oral Needs of Humanity
- Conditions of the oral cavity / mouth (normal/abnormal)
- Relations of the oral cavity to the general system
- Preventive Services
- done to avoid the onset of disease.
Preventive services include: (medical field)
- taking in vitamins and minerals to make body strong and increase your resistance to infection
- Another preventive service is vaccination
- Twice-a-year dental check-up
- Oral prophylaxis /cleaning
- Fluoridization- dentist apply to children/patients
- Fluoridation- put fluoride on water (U.S)
- Oral health education
- Oral hygiene regimen
- Remedial /corrective /curative Services
Remedial services include (medical field)
- heart bypass surgery
- using medicines when one is sick
- kidney transplant, etc.
*Corrective- correct something
*Curative- what is destroyed
- Restorations
- RCT
- Oral Surgery
- Prostheses
Three-fold value of the Dental Profession
- Service to mankind
- Preventive services
- Remedial / corrective / curative services
Three factors responsible for immediate complaints of patients
- PAIN
- DISCOMFORT
- DEFORMITY
- Social security
- Ideal means of livelihood
- Career opportunities
- Prestige
- Title or degree DOCTOR (Dr.)
Ideal Traits of Dentists
- Dedication to service
- Honesty and sincerity
- Diligence and thoroughness
- Resourcefulness
- Charity
Employment and Career Opportunities of a Dentist
- Private Practice
- Individual/ Solo Practice
- Means the dentist practices as a one-man practitioner
- Partnership and Group Practice
- Defined as, either one is a practice of two/three or more dentists joined in a cost-sharing arrangement to provide improved service at a minimized cost.
- Multi-located Practice
- In need of more clientele, a dentist may apportion his time to serve other locations
- A difficult method of establishing a practice
- Can be very expensive
- Part-time Practice
- The practice is limited to a few hours only
2. Public Health Dentist
- Affords a novice dental practitioner a grand opportunity whether in the employ of the national or local government
3. Hospital Dentists
- Dentists practicing in a private hospital
4. Military Dentists (Dental Service Militare)
- Dentists who wishes to make use of their specialized skills serving in the AFP dental corps unit
5. Industry / Company Dentists
- Dentists employ by private company or industry in a full-time basis or retainership
6. School Dentists
- Dentists who seeks employment in a private school /college or university
7. Dental Educator
- Dentists who opt to pursue a career in teaching
- Requires education units in teaching
- Administrative skills and capabilities
8. Other Avenues / Opportunities
- Dental Assistant
- A novice dentist who seek employment to a private dentist
- Can serve as a buffer or period of re-adjustment during which one can acquire experiences and evaluate private practice opportunities
- Dentists who wish to seek employment abroad but are not licensed to practice as dentists in other countries
- Dental Researchers
- A dental practitioner who choose to do research or investigation in any dental field or specialization
- Usually inside a University (local or abroad)
- Graduate Study
- dentists opt for a limited practice of one or two specific fields
- Requires to pursue a 3 to 4 years additional graduate study such as Master of Science or Doctoral degree in Dentistry (Endodontics, Oral Surgery, Prosthodontics, Orthodontics, Pediatric Dentistry, Periodontics, etc)
- Heritage Practice
- Practice is retained in a family or class of practitioner with the patient load inherited by the beginner member.
- Ultimately, the latter takes over the entire practice
- Dental or Medical Representative
- One who seeks employment in major drug companies and dental traders
- Dental Consultants
- One who is employed by a dental company, laboratory and/or trader for his/her expertise
- Foreign Employment
- Dentists
- Dental assistants
- Dental hygienists
- Dental nurse
- Dental technician
CEU Dentistry Curriculum 2018-2019
- General Education
- Institutional Requirements (CEU)
- Basic Medical courses
- Basic Dental courses
- Dental courses
- Pre-clinical
- Dental Courses (clinical)
- Dental Public Health and other courses
- Clinical Dentistry
- Hospital Dentistry
General Education Courses
- Understanding the Self
- Mathematics in the Modern world
- Purposive Communication
- Health Economics
- General Zoology
- Art Appreciation
- Readings in Philippines History
- Organic Chemistry
- Politics and Governance
- Genetics
- The Life and Works of Rizal
- Science, Technology and Society
- Ethics
- The Contemporary World
Electives
- Filipino 1 & 2
- Internet of Things
Mandated Rqts
- PE 1,2,3,4
- NSTP 1 & 2
Institutional Rqts (CEU)
- Foreign Language 1 & 2
- Religion: History and Texts
- Man, Church and Society
- Empowering the Self
- Living and Loving Relationships
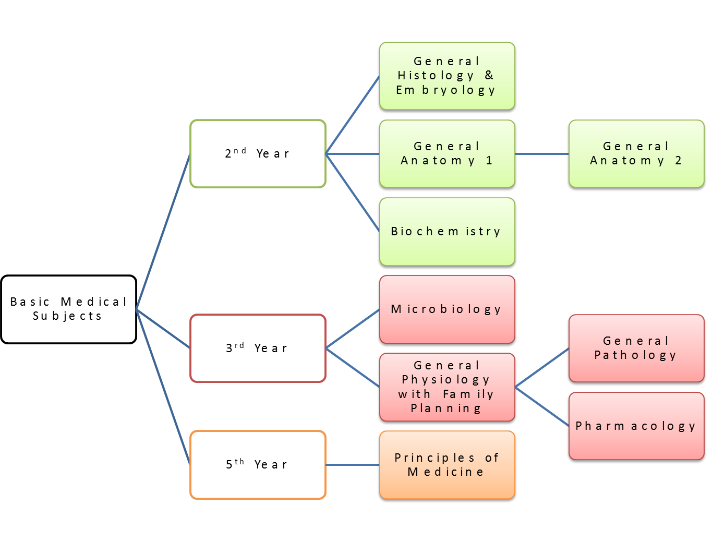
Basic Medical Courses
- General Anatomy 1 and 2
- General Histology & Embryology
- Biochemistry
- General Physiology with Family Planning
- General Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Microbiology
- Principles of Medicine
General Anatomy 1- Regional
- 5 units
- 3 units lecture;
- 2 units lab
- Study of the different parts of the human body by regions involving different tissues such as bones, muscles, nerves, blood vessels and different internal organs using human models.
- Regions of the human body from the shoulders to the feet.
- study of body system in macroscopic level (visible to the naked eye)
General Anatomy 2- Head and Neck
- 5 units
- 3 units lecture;
- 2 units lab
- Deals with the thorough study of the head and neck with anatomical details on the skull, face, oral cavity and other maxillofacial structures
General Histology and Embryology
- 4 units
- 2 units lecture
- 2 units lab
- Study of the cells and tissues that compose the human organ system (using the microscope) (microscopic)
- Includes the basic concept of embryonic development of the basic types of tissues
- microscopic
Biochemistry
- 5 units
- 3 units lecture
- 2 units lab
- the study of (bio)chemistry of the cells and organelles & their relation to the general metabolism of body ; metabolism of foodstuff and chemical processes by which human body derives and utilizes energy.
- studies molecular and cellular processes that will govern treatment of mouth
General Physiology with Family Planning
- 4 units
- 2 units lecture
- 2 units lab
- Study of the functions of the human body -organs (tissues and cells) with emphasis given to the practical application to dentistry together with the integration of items on Family Planning.
General Pathology
- 4 units
- 2 units lecture
- 2 units lab
- Study of general and systemic pathology needed to provide an introductory and basic level proficiency in interpreting macroscopic (gross) and microscopic (histologic) changes in various organs.
- Study of diseases / abnormalities of man
Pharmacology
- 3 units
- 2 units lecture
- 1 unit lab
- Deals with the mechanism of drug action on living tissue that is used in prevention and treatment of (oral) diseases.
- Prescription writing
Microbiology
- 3 units
- 2 units lecture
- 1 unit lab
- Study on the biology of (pathogenic) micro-organisms (infectious agent) to serve as knowledge base in the control, prevention, diagnosis, management & treatment of infectious diseases with oral significance.
- Emphasis is given to the oral microflora.
Principle of Medicine
- 2 units lecture
 Course designed to provide a logical framework for learning and working knowledge of internal medicine needed for diagnosis of dental patients with medical illnesses in relation to and correlating these to dentistry.
Course designed to provide a logical framework for learning and working knowledge of internal medicine needed for diagnosis of dental patients with medical illnesses in relation to and correlating these to dentistry.
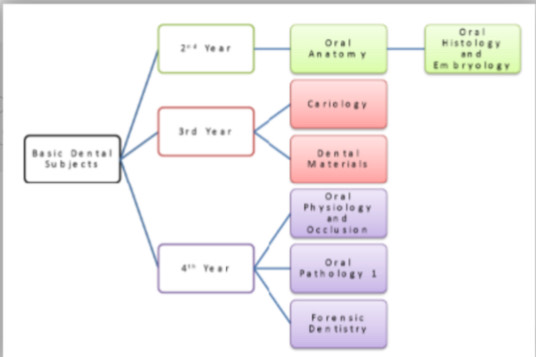
Basic Dental Courses
- Oral Anatomy
- Oral Histology & Embryology
- Dental Materials
- Cariology
- Infection Control
- Oral Physiology and Occlusion
- Oral Pathology 1
Oral Anatomy
- 4 units (2 units lecture; 2 units lab)
- Morphology of deciduous and permanent dentition (macroscopic or gross structure of the human teeth), alignment and relationships with supporting structures
Oral Histology & Embryology
- 4 units (2 units lecture; 2 units lab)
- Study of the microscopic structures of oral/dental tissues and their embryonic development
Dental Materials
- 5 units (3 units lecture; 2 unit lab)
- physical and chemical properties of metallic and non-metallic materials used in Dentistry,
- manipulation and uses of the different dental materials, different variables that affect the properties of the dental materials
Cariology
- 2 units lecture
- Diagnosis, etiology, microbiology, classification, prevention and management of dental caries in individuals and populations
Infection Control
- 2 units lecture
- Aseptic protocols that prevent spread of contaminants and infectious substances
- Proper sterilization of instruments
- Handling and disposal of infectious wastes
Dental Materials
- 5 units (3 units lecture; 2 unit lab)
- physical and chemical properties of metallic and non-metallic materials used in Dentistry, manipulation and uses of the different dental materials, different variables that affect the properties of the dental materials
Cariology
- 2 units lecture
- Diagnosis, etiology, microbiology, classification, prevention and management of dental caries in individuals and populations
- concerned with the study of tooth decay
Infection Control
- 2 units lecture
- Aseptic protocols that prevent spread of contaminants and infectious substances
- Proper sterilization of instruments
- Handling and disposal of infectious wastes
Oral Physiology and Occlusion
- 3 units lecture
- Study of oro-facial mechanisms & dynamic interrelationships among dental, neuromuscular and TMJ as they influence establishment of functional occlusion, mastication, deglutition and speech
- Deals with the physiology of the Human Masticatory Apparatus (stomatognathic system) and occlusion
Stomatognathic System
- structures involved in speech, tasting; and in the receiving, chewing, and swallowing of food
Oral Pathology 1
- 4 units (2 units lecture; 2 unit lab)
- diseases and abnormalities afflicting oral and dental tissues
- several systematic diseases that present oral lesions as part of their pathology
 diseases after oral and dental tissues except oral caries
diseases after oral and dental tissues except oral caries
Basic Dental Courses
*PRE-CLINICAL
- Operative Dentistry 1 and 2
- Prosthodontics 1, 2 and 3
- Roentgenology
- Anesthesiology
- Orthodontics 1
- Endodontics
- Periodontics 1
- Oral Diagnosis and Treatment Planning
- Oral Pathology 2
- Forensic Dentistry
Operative Dentistry 1
- 4 units
- 2 units lec
- 2 units
- skills lab
- Diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of the teeth affected by dental caries and other non-carious tooth defects in order to restore the tooth to its proper form, function, and aesthetics
- Cavity preparation and the manipulation of filling materials necessary for the restoration of carious teeth.
![]() Operative Dentistry 1- cariology
Operative Dentistry 1- cariology
![]()
Operative Dentistry 2
- 3 units
- 2 units lec
- 1 unit
- Skills lab
- Focus on complex restorations
- Includes direct and indirect composite and other-tooth colored restorations, cast metal inlay/onlays, complex amalgam restorations and direct filling gold.
- Primary dentition- children
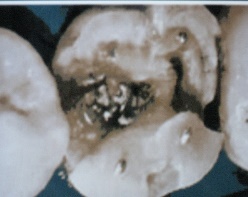
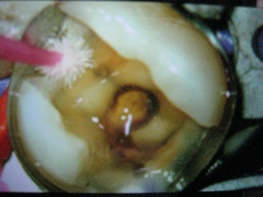 Permanent dentition- adult
Permanent dentition- adult
Prosthodontics 1- Fixed Partial Denture-FPD
- 4 units
- 2 units lec
- 2 units lab
- skills lab
- Restoration of damage tooth/teeth and the replacement of one or more missing teeth with an artificial substitute that is permanently attached to the prepared teeth.
- focuses on restoration of damaged and function of missing teeth
![]()
![]()
Prosthodontics 2 -
Removable Partial Denture – RPD
- 4 units
- 2 units lec
- 2 units lab- skills lab
- Basic principles of restoring missing teeth and associated structures of partially edentulous arches with removable prosthesis.
- Includes designing, prescription writing and the selection of the appropriate biocompatible materials
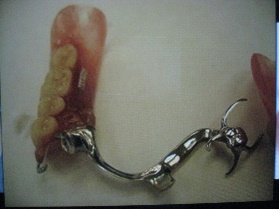
 form, function, and aesthetics
form, function, and aesthetics
Prosthodontics 3-
Removable Complete Denture
- 4 units
- 2 units lec
- 2 units lab- skills lab
- Replacement of all natural teeth and associated structures of a completely edentulous maxilla and/or mandible.
- rehabilitation of completely edentulous patient
![]()
![]()
Roentgenology
- 3 units
- 2 units lec
- 1 unit lab- skills lab
- Production of X-radiation, properties and techniques used in Dentistry.
- Principles of radiation safety and protection, health physics and clinical patient management
- Radiographic apparatus, their operations, application and maintenance.
- Included are processing, mounting, reading and interpretation of the radiographs
![]()
![]()
Anesthesiology
- 3 units
- 2 units lec
- 1 unit lab- skills lab
- Principles and techniques of local and regional anesthesia in dental practice.
- Pharmacology of different local anesthesia used in dentistry.
- Topics on general anesthesia, conscious sedation and anesthetic complications in dental procedures and basic life support.
Trigeminal nerve- maxillary and mandibular nerves
Periodontics 1
- 3 units
- 2 units lecture
- 1 unit lab- skills lab
- Introduction to Periodontics: normal periodontium as well as classification, diagnosis, etiology, and pathogenesis of periodontal diseases.
- Laboratory component includes oral prophylaxis and instruments.
- Perio- structures that surround the t
Orthodontics 1
- 3 units
- 2 units lec
- 1 unit lab-
- Deals with the fundamentals of growth and development of both normal and abnormal craniofacial structures and their relation to the stomatognathic system.
STOMATOGNATHIC SYSTEM
- structures involved in speech, tasting ; and in the receiving, chewing, and swallowing of food.
Endodontics
- 4 units lec
- 3 units lec
- 1 unit lab- skills lab
- Basic morphology, physiology and pathology of the human dental pulp, its root canal system and associated periradicular tissues.
- The study will focus on the diagnosis, etiology of pulp and periapical diseases, prevention and treatment of the progress of disease, as well as its management using the different treatment modalities.
Oral Diagnosis and Treatment Planning
- 3 units lec
- Principles and procedures in making a diagnosis and treatment planning, management of medically compromised patients and emergencies in the dental infirmary.
Oral Pathology 2- Oncology
- 3 units lec
- Deals with the pathology of neoplasm and other diseases of the oral cavity and adjacent structures with emphasis on laboratory and diagnostic procedures. ( cancers of the mouth)
Forensic Dentistry
- 1 unit lec
- Deals with the study of dental/oral parts of the body in the confirmation of identity of victims.
DENTAL COURSES - CLINICAL - 5th/6th YEAR
- Orthodontics 2
- Oral Surgery 1 and 2
- Periodontics 2
- Pediatric Dentistry
- Basic Dental Implantology
- Current Trends
- Interprofessional Approach in Patient Management
- Interdisciplinary Approach in Patient Management
- Management of Patients with Special Needs
ORTHODONTICS 2
- 3 units
- 2 units lec
- 1 unit lab
- Study of the prevention, interception and treatment of malocclusion.
- Prevention and interception of malocclusion through timely diagnosis of orthodontic problems
MALOCCLUSION - or bad bites. Your upper and lower teeth don’t align when you close your mouth
ORAL SURGERY 1
- 2 units lec
- Concepts and general principles of surgery and its application in dentistry
- Basic medical emergencies in dental practice
ORAL SURGERY 2
- 2 units lec
- Management of certain conditions through dental surgery, minor surgical procedures and major surgeries in relation to the other fields of dentistry, such as endodontics, orthodontics and prosthodontics
- Deals with surgical management of complicated extractions and fixation if traumatic injuries of the face and jaws and surrounding tissues, and other conditions related to lesions of the oral cavity
LESIONS - mouth ulcers or sores, they can include abnormal cell growth and rare tongue and hard-palate. Triggered by localized trauma, such as biting the side of your mouth, consuming highly acidic food and beverages, or even experiencing a great deal of stress
PERIODONTICS 2
- 2 units lec
- Principles and concepts in the prevention, differential diagnosis, and management of periodontal diseases
- Focuses on the different classification of periodontal diseases, various parameters that will lead to a good diagnosis and treatment procedures of periodontal diseases, including surgical and non-surgical treatment, and maintenance procedures
PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY WITH CHILD PSYCHOLOGY
- 3 units lec
- Study of the principles and techniques in the management of the child with oral and dental problems including treatment of injuries and interceptive orthodontics
BASIC DENTAL IMPLANTOLOGY
- 3 units lec
- Study of fundamental knowledge on biological and scientific basis for implant treatment
- Includes patients evaluation, diagnosis and treatment planning, implant selection, surgery and prosthodontic procedures, post-surgical care and maintenance procedures
INTERDISCIPLINARY APPROACH IN PATIENT MANAGEMENT
- 2 units
- This course deals with a collective interaction of all concerned dental specialties to generate a reliable, congruent and successful outcome in the management of oral health conditions of patients.
- This is the effective and skills in the various disciplines of dentistry.
- Its key is the combination if diagnostic, treatment planning and therapeutic procedures with extensive communication among the team members
- An interdisciplinary approach to the management of complex dentofacial problems produces consistent optimal results
INTERPROFESSIONAL APPROACH IN PATIENT MANAGEMENT
- 2 units
- Study on collaborative practice among health care professionals for the provision of comprehensive and quality services to patients
- Focuses on principles of mutual respect, effective communication, collaboration to integrate knowledge, skills and experiences across professions
MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH SPECIAL NEEDS
- 1 unit
- Study of basic protocol in management of patients with special oral health care needs (with physical, developmental, mental, sensory, behavioral, cognitive or emotional impairment)
CURRENT TRENDS IN DENTISTRY
- 1 unit lec
- The study concerned with the latest development in Dentistry like Dental Materials, Dental Technology, new techniques and other areas related to Clinical Dentistry like infection control practices, genetics and medically compromised patients.
DENTAL PUBLIC HEALTH AND OTHER RELATED COURSES
- Biostatistics and Epidemiology
- Dental Public Health 1, 2 & 3
- Nutrition in Dentistry
- Dental Informatics
- Undergraduate Research 1 & 2
- Practice Management with Entrepreneurship
- Jurisprudence and Ethics
- Andragogy- Teaching and Learning
BIOSTATISTICS AND EPIDEMIOLOGY
- 3 units
- Applications of techniques in statistics and epidemiology in research particularly in data collection, summarization and analysis of health- related and epidemiologic data
BIOSTATISTICS - application of statistical techniques to scientific research in health-related fields (dentistry). Identify health trends that lead to life-saving measures through application of statistical procedures
EPIDEMIOLOGY - scientific study of (oral) diseases/illness among the population
-SPECIFIC TO HOW, WHEN AND WHERE THESE DISEASES OCCUR
DENTAL PUBLIC HEALTH 1
- 2 units lecture
- Discussion and simulation activities perform in a School-based and Community-based dental program
- Includes concept on community organizing process, oral health education, epidemiology, atraumatic restorative treatment and program evaluation
- PURE LECTURE
DENTAL PUBLIC HEALTH 2
- 3 units
- 2 units lec
- 1 unit lab (school-based)
- Concepts, principles and methods of community dentistry, health service administration, oral health education, preventive dentistry and primary health care
- (school-based)
DENTAL PUBLIC HEALTH 3
- 3 units
- 1 unit lec
- 2 units lab (fieldwork: community based)
- The principles and methods designed in the practice of community dentistry in an adopted community
- Field experience
NUTRITION IN DENTISTRY
- 2 units lec
- Physical, chemical and biological processes that develop and renew tissues of the body by absorption and assimilation of food materials
- It related the importance of nutrition to dental health especially during the formation and maturation of tooth development
DENTAL INFORMATICS
- 3 units lec (with hands-on on computer lab)
- Introduces the field of Health Information Technology (HIT) and its role in healthcare delivery systems introduces the field of Health Information Technology (HIT) and its role in healthcare delivery systems
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
- The principles and programs of computer as applied to dental practice
UG RESEARCH 1 - METHODS OF RESEARCH
- 3 units lec (THESIS)
- Principles and methods in research and its application to dentistry focused on developing a research protocol (CHAPTER 1 - 3)
- UNDERGRADUATE GROUP RESEARCH (5)
UG RESEARCH 2 - RESEARCH PRESENTATION
- 3 units lec (THESIS)
- The basic principles in preparing a technical paper (CHAPTER 4 - 5) for presentation and discussion in scientific forum and/or for publication
UNDERGRADUATE RESEARCH
- Dental Research Forum
- University Research Forum
- Local/National/Regional Research Competition
- Philippine Dental Association
- Dentsply Philippines
- DOST Regional Research Competition
- SouthEast Asia Research Competition
- International Research Competition
PRACTICE MANAGEMENT WITH ENTREPRENEURSHIP
- 2 units lec
- The practice of dentistry in relation to the social, economic and cultural conditions of the community
PRACTICE MANAGEMENT WITH ENTREPRENEURSHIP
- Covers economic business administration of a dental clinic, principles of business management, organization and investments, waste management, hazard and infection control, and regulatory code of dental profession
- A close study into the most common medical and dental emergencies in dental practice is well taken in order to prepare dental students to efficiently develop their professional skills and proficiencies in meeting them in actual practice
JURISPRUDENCE AND ETHICS
- Study of the relation of law and ethics to dental practice
- RA 9484
ANDRAGOGY
- 1 unit lec
- Art/science of teaching adults
- Concepts and principles of learning and characteristics of adult learners
- Theories of adult learning that details some of the ways in which adults learn differently than children
ANDRAGOGY (TEACHING AND LEARNING)
- 1 unit lec
- Concepts and principles of learning and characteristics of adult learners
- Theories of adult learning that details some of the ways in which adults learn differently than children
HOSPITAL DENTISTRY
- 3 units; 2 units lec; 1 unit lab
- Dental internship for senior students at a local or university training hospital or affiliated hospital designed to orient the students with hospital decorum, scope and overall functions of the different Department and Divisions
- East Avenue Medical Center
- V. Luna medical Center
CLINICAL DENTISTRY
PINNING AND WHITE COAT CEREMONY
Clinical Dentistry 1
- Clinical Dentistry 2
- Clinical Dentistry 3
- Clinical Dentistry 4
CLINICAL DENTISTRY 1 & 2
- 6 units
- Clinical application of the basic competencies acquired in Operative Dentistry, Prosthodontics, Roentgenology, Oral Surgery, Endodontics, Oral Diagnosis and Pediatric Dentistry
- Clinicians will work on actual patients and on typodonts under the close supervision of the clinical supervisor
- WRITTEN VALIDATION EXAMINATION
CLINICAL DENTISTRY 3
- 10 units each equivalent to 30 hours per week
- Application of principles and methods of providing dental care in the various clinical areas, given a set of clinical requirements with minimum supervision of the clinical supervisor
- WRITTEN VALIDATION EXAMINATION
CLINICAL DENTISTRY 4
- 10 units each equivalent to 30 hours per week
- Clinical applications of the competencies acquired in Clinical Dentistry 3. This is the continuation of the requirements in Clinical Dentistry 3
- A Clinical Proficiency Examination will be given in Operative Dentistry and Prosthodontics as a pre-requisite for graduation
- REVALIDA (WRITTEN PRE-BOARD EXAM)
CLINICAL CONFERENCES (SPECIAL STUDIES)
- 1 unit
- CC Operative Dentistry Seminar 1 & 2
- CC Prosthodontics Seminar 1 & 2
- CC Orthodontics- Pediatric Dentistry
Seminar 1 & 2
- CC Oral Surgery Seminar 1 & 2
- Endodontics -Periodontics Seminar 1 & 2
CLINICAL CONFERENCES
- Clinical conference on problems encountered in the clinics designed to develop critical thinking based on the principles and techniques learned and synthesized from previous foundation courses
Clinical conference on advances/trends in the speciality area along with problems commonly encountered in the clinics
Overview of Dental Practice
- Dental Records
- Patient’s information
- patient’s name, address, contact information
- Medical history
- allergy,diseases, previous medications,
- Dental history
- check past dental treatments, dental insurance, or if they seek other dentists before
- Chief complaint
- reason for the patient’s visit
- Dental examination findings
- include assessment of the gingiva, presence of caries, absence of teeth, bite of patient, oral cancer screening
- Diagnostic Records
- radiograph, photographs, impression of patient’s mouth
- Treatment plan
- proposed treatment plan, procedures to be made
- Prescriptions and medications
- drugs that were prescribed to patients including dosage, specific drug, specific instruction to patients
- Informed consent (signed)
- part where patient has been informed about the treatment and risks of procedure; it is signing the consent form
- Referral and consultation records
- document the referral of patients to other specialist, if want patient to consult to other healthcare provider
- Radiographs
- imaging records, copies of X-ray, CT Scan; interpretation and report of results of radiologist
- Insurance Information
- details if patient insurance covers particular procedure
- Billing/ Financial Records
- how much did you charge patient, if the patient already paid, treatment cost and payments
- Communication records
- Appointment reminders follow up instructions
- Legal and ethical documents
- any legal documents related to patient care
- Treatment notes
- detailed notes on treatment performed, date and type of treatment, what tooth are involved, materials that are used, anesthesia administered, complications and unusual findings during treatment
- Progress notes- subsequent visit notes, details of the patient’s progress, patient’s response about the treatment
Tooth Identification System
- to make sure we treat specific tooth with precision, help ensure accuracy, consistency
Importance
- Precision in diagnosis and treatment
- standard tooth will provide universal,
- Consistency in documentation
- specific number of the tooth to be restored or extract
- Effective communications
- communication between assistant and dentist
- For research and education
- International Standardization
- easier worldwide to communicate research
- Clinical efficiency
- dentist and entire staff can quickly locate specific teeth to be treated
- DENTAL CHARTING
- there are specific numbers in dental chart
Terminologies
Oral Cavity
- the mouth
Upper Jaw
- Maxilla ( maxillary)
Lower Jaw
- Mandible (mandibular)
Classes of Teeth
- INCISORS
- Central incisors
- Lateral incisors
- four front teeth in the maxilla
- CANINES
- PREMOLARS
- MOLARS
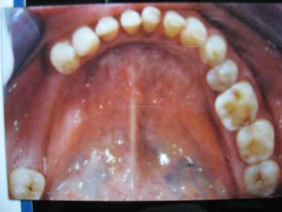
- Anterior Teeth
- teeth at the front
- 6 front teeth
- Incisors
- Canines
 Posterior teeth
Posterior teeth- teeth at the back
- Premolars
- Molars
HUMAN DENTITION
- all teeth in the upper and lower jaw are collectively referred to as DENTITION
- all teeth in the maxilla and the mandible
2 Sets of Dentition of Man
1. DECIDUOUS DENTITION
- primary dentition; dentition of children
2. PERMANENT DENTITION
![]() - dentition of adult
- dentition of adult
![]()
![]() System of Tooth Identification
System of Tooth Identification
- Palmer’s Notation
- Oldest known tooth designation system
- described by Zsigmondy in 1861
- Grid / brackets
- To denotes (4) quadrant
- Permanent dentition
- Numbers 1 – 8
- Primary/Deciduous dentition
- Letters A - E
Permanent Teeth
1. Central Incisor
2. Lateral Incisor
3. Canine
4. First Premolar
5. Second Premolar
6. First Molar
7. Second Molar
8. Third Molar
Deciduous Dentition
- Central Incisor
- Lateral Incisor
- Canine
- First Molar
- Second Molar
- International System or 2 digit system or the FDI system
- First digit – denotes quadrant and dentition
- 1 to 4 ( Permanent dentition)
- 5 to 8 ( Deciduous dentition)
![]() Permanent Dentition ( 1- 4)
Permanent Dentition ( 1- 4)
- Second digit
- – denotes the tooth
- 1 – 8 (permanent teeth)
- 1 – 5 (primary teeth)
![]()
Permanent Teeth
1. Central Incisor
2. Lateral Incisor
3. Canine
4. First Premolar
5. Second Premolar
6. First Molar
7. Second Molar
8. Third Molar
Deciduous Dentition (5-8)
![]()
Deciduous Dentition
- Central Incisor
- Lateral Incisor
- Canine
- First Molar
- Second Molar
- Universal or Military System
- First suggested by Parreidt in 1882
- Permanent – numbers 1 to 32
 Deciduous – letters A to T
Deciduous – letters A to T
 Knowt
Knowt